In a market that demands high levels of personalization, the Make-to-Order (MTO) strategy is a key efficiency strategy, enabling companies to produce goods according to customer specifications without the risk of inventory buildup.
Especially as consumer expectations in Singapore shift towards greater personalization, businesses must adjust to meet this growing demand. According to KPMG’s Customer Experience Excellence report, personalization has become the leading factor driving brand advocacy and loyalty in the country.
However, managing MTO without proper optimization poses a serious threat. Without a well-thought-out strategy, companies will face slow lead times, ballooning operational costs, and uncontrolled workload fluctuations.
The impact is significant: consumer confidence can collapse instantly, and inefficiencies will erode profitability. Therefore, a thorough understanding of MTO management is a strategic choice and imperative to maintain business continuity and competitiveness amidst increasingly rapid industry dynamics.
In this article, we provide a comprehensive guide to make-to-order (MTO), including its definition, benefits, pros and cons, and the key differences between make-to-order and make-to-stock, so that you can choose the most suitable strategy for your needs. Learn more here.
- Make-to-Order (MTO) is a manufacturing approach in which products are produced only after a customer submits a specific order.
- The advantage of MTO is allows companies to produce goods only after receiving confirmed customer demand, which significantly reduces excess inventory and storage costs.
- The disadvantage of MTO often results in longer lead times since production begins only after an order is placed, which may reduce customer satisfaction for time-sensitive purchases.
- ScaleOcean can be the one solution that offers advanced features to optimize MTO strategies by integrating the entire production process from customer orders to finished products in one centralized platform.
What is Make to Order (MTO)
Make-to-Order (MTO) is a manufacturing approach in which products are produced only after a customer submits a specific order, operating as a demand-driven “pull” system rather than producing items in advance for inventory.
This model enables extensive customization, lowers the risk of excess or unsold stock, and reduces warehousing expenses, making it well-suited for tailored products such as custom furniture, automobiles, computers, or specialized medical equipment.
However, despite its flexibility and efficiency, MTO often results in longer delivery times because production efficiency begins only once the order is confirmed.
Also Read: Product Life Cycle: Definition, Stages, and Strategies
Advantages and Disadvantages of Make to Order (MTO)
Make-to-Order (MTO) offers a unique balance between flexibility and control by aligning production directly with customer demand. This approach brings clear advantages, such as higher customization and lower inventory risk, while also introducing challenges like longer lead times and more complex manufacturing process planning.
Understanding both the benefits and limitations of MTO is essential for businesses to determine whether this production strategy aligns with their operational goals and customer expectations. Here is the complete explanation:
Advantages of Make to Order (MTO)
Make-to-Order allows companies to produce goods only after receiving confirmed customer demand, which significantly reduces excess inventory and storage costs. This approach supports high product customization, enabling businesses to meet specific customer requirements and increase satisfaction.
MTO also lowers the risk of obsolescence and waste, improves cash flow by avoiding upfront production, and helps align resources more efficiently with real demand rather than forecasts.
Disadvantages of Make-to-Order (MTO)
Despite its benefits, MTO often results in longer lead times since production begins only after an order is placed, which may reduce customer satisfaction for takt time-sensitive purchases.
The process also requires precise planning and coordination across procurement, production, and logistics. Fluctuating demand can strain capacity, and per-unit costs may be higher due to smaller batch sizes and limited economies of scale.
Pros and Cons of MTO
| Pros of MTO | Cons of MTO |
|---|---|
|
|
How the MTO Process Works
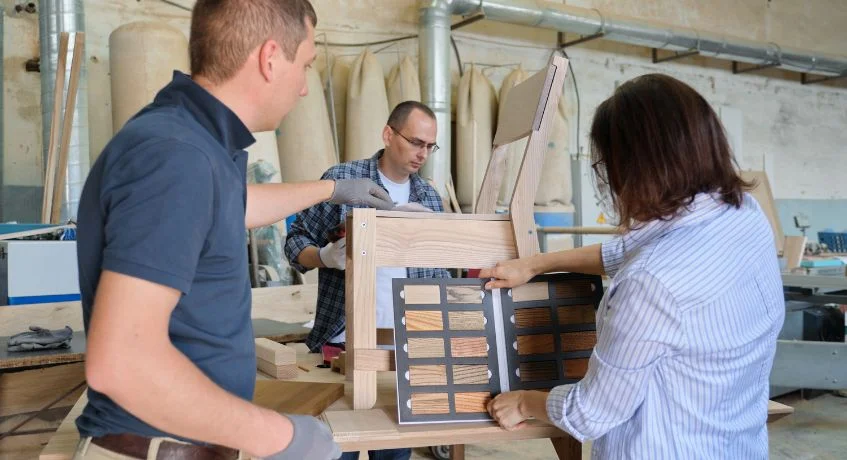

The following steps outline key actions needed for the Make-to-Order process to work, including:
Analyze Customer Demand
Understand order patterns, customization needs, and acceptable lead times. Clear demand analysis helps determine whether MTO is suitable, ensures realistic delivery commitments, and prevents production capacity strain caused by unpredictable or highly volatile orders.
Redesign Production Workflow
Adjust manufacturing processes to support flexible, order-driven production. This includes modular designs, smaller batch sizes, and adaptable scheduling so production can start quickly after order confirmation without disrupting overall operations.
Strengthen Supplier Coordination
Build strong relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure timely material availability. Short lead times, clear communication, and backup suppliers are essential to avoid production delays once customer orders trigger the good manufacturing practices.
Set Clear Lead Times and Policies
Define realistic production and delivery timelines and communicate them clearly to customers. Well-defined policies help manage expectations, improve customer satisfaction, and prevent operational overload during peak demand periods.
Implement Supporting Technology
Use manufacturing ERP software or production planning systems to manage orders, inventory, and schedules in real time. Technology helps automate workflows, improve visibility, reduce errors, and ensure smooth coordination across departments.
You can use one of the best manufacturing ERP systems, Scaleocean, which provides advanced solutions to optimize Make to Order (MTO) strategies by integrating the entire production process from customer orders to finished products in one centralized platform.
Additionally, Scaleocean also offers customized solutions, allowing you to tailor the system to your needs and business processes across various specific industries. To find the most appropriate solution for your business, request a free demo and consultation now.
What Industries Commonly Use Make-to-Order Strategies?
Make-to-Order (MTO) is widely adopted in industries where customization, precision, and demand variability are critical. By producing goods only after receiving confirmed orders, companies can reduce inventory risks while delivering products tailored to specific customer needs.
Below are industries that commonly rely on MTO strategies and why the model fits their operations:
Furniture and Interior Design
This industry frequently uses MTO to produce custom furniture based on size, material, and design preferences. Once specifications are finalized, orders trigger production supported by material requirement planning to ensure the right materials are available at the right time.
This approach can also help manufacturers minimize unsold inventory while delivering highly personalized products that fit customer spaces and aesthetic requirements.
Automotive and Transportation
Automotive manufacturers apply MTO for custom vehicle configurations, including engine types, interiors, and technology features. Production begins after order confirmation, helping reduce excess stock of expensive components while meeting customer demand for personalized vehicles with specific options.
Manufacturing and Industrial Equipment
Heavy machinery and industrial equipment are often built using MTO due to their high cost and specialized functions. Each order is produced according to technical specifications, with careful control of work in progress to ensure precision, regulatory compliance, and a reduced risk of unused or obsolete inventory.
Electronics and Technology
Technology companies use MTO for configurable products such as computers and networking equipment. Customers select components and features, and assembly starts after the order is placed. This approach reduces component obsolescence and aligns production with rapidly changing technology trends.
Healthcare and Medical Devices
Medical device manufacturers rely on MTO to produce specialized equipment tailored to clinical needs or patient requirements. This strategy supports compliance with strict regulations, reduces waste, and ensures devices are manufactured precisely to the required medical standards.
Example of Make-to-Order (MTO) Process
To make it easier to understand, here is an example of implementing the MTO strategy in a specific industry.
In the custom furniture industry, the MTO process begins when a customer places an order for a made-to-measure item, such as a sofa or dining table. The customer selects the design, dimensions, materials, and finishes.
Once the order is confirmed, the manufacturer finalizes specifications and procures the required wood, fabric, and hardware. Production then starts, including cutting, assembly, finishing, and quality inspection based on the exact order details.
After completion, the furniture is packaged and delivered to the customer. This process allows high customization, minimizes unused inventory, and ensures each product is built to meet specific customer requirements.
What is Make to Stock (MTS)
Make to Stock (MTS) is a production strategy where companies create products based on predicted demand and keep them in stock until customers place orders. This approach ensures that products are ready for immediate sale whenever customers need them.
By producing goods ahead of time according to forecasts, MTS helps reduce delivery times and meet customer needs quickly. Accurate forecasting is crucial, as overestimating demand can lead to excess inventory and unnecessary costs.
How the MTS Process Works
In the MTS process, companies first look at past sales data to predict future demand. They then use these forecasts to plan production and schedule the manufacturing of products, ensuring that items are ready before customers even place orders.
Once they’ve forecasted the demand, companies produce the goods in large quantities. After production, they store these items in inventory, making them available to ship as soon as customers place their orders, speeding up delivery times.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Make to Stock (MTS)
Make to Stock (MTS) is a production strategy where companies manufacture products in advance based on predicted demand. It helps businesses ensure product availability and meet customer demand quickly. However, it also comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s take a closer look at the key advantages and disadvantages of the MTS process:
Advantages of Make to Stock (MTS)
MTS allows businesses to produce goods ahead of time and store them in inventory, making products readily available when customers need them. This reduces lead times, boosts customer satisfaction, and improves cash flow by having products ready for immediate sale.
Additionally, MTS helps companies achieve economies of scale by producing in bulk, reducing per-unit costs. With efficient production planning, businesses can avoid the risks of stockouts and ensure they have enough inventory to meet demand, especially for popular products.
Disadvantages of Make to Stock (MTS)
One major downside of MTS is the risk of overproduction. If companies misforecast demand, they might end up with excess inventory, leading to high storage costs and potential waste. Managing inventory becomes crucial to prevent these issues.
MTS also limits flexibility since businesses produce based on forecasts rather than actual orders. This makes it harder to adjust to sudden changes in customer preferences or demand spikes, which could lead to slower response times and missed opportunities.
Pros and Cons of MTS
| Pros of MTS | Cons of MTS |
|---|---|
|
|
Examples of MTS Process in an Industry
In an MTS example, retailers like toy and clothing manufacturers analyze past sales data to predict demand and plan production. They make products in advance and store them in inventory, so they’re ready when customers place orders.
For example, a toy manufacturer knows that demand spikes in the last quarter of the year. They boost mass production during slower months to ensure they have plenty of stock available when customers start shopping for the holiday season.
Similarly, companies that produce electronics or everyday items manufacture goods in bulk based on expected demand. They keep the products in stock, making sure they can ship quickly when customers make their purchases.
What is Made to Order
Made-to-Order (MTO) is a production method where companies start making a product only after receiving a confirmed order from a customer. This way, businesses only produce what’s needed, reducing waste and preventing excess inventory.
With MTO, companies can tailor products to fit specific customer requests. While this helps control inventory costs and offers customization, it may result in longer wait times since production only starts after receiving the order.
How the Made-to-Order Process Works
In the Made-to-Order (MTO) process, companies wait for customers to place confirmed orders before they begin production. Once they receive an order, they plan the manufacturing steps, gather materials, and schedule production to meet specific demand.
When production starts, businesses focus on creating products that match each customer’s exact requirements. This method helps minimize excess inventory and waste, while offering more customization, although it may extend lead times.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Made-to-Order
Made-to-Order is a production method where companies start making products only after customers place an order. This strategy helps businesses save on inventory costs and offer products tailored to customer needs, but it also has its own challenges.
Let’s take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of the Made-to-Order process:
Advantages of Made-to-Order
Made-to-Order helps businesses avoid the costs of overproduction and excess stock by only producing goods after receiving confirmed orders. This reduces waste and storage expenses while ensuring products meet real customer demand.
Made-to-Order also allows businesses to offer customized products. Customers can specify their preferences, which lets businesses deliver exactly what they want, resulting in higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Disadvantages of Made-to-Order
One drawback of Made-to-Order is the longer wait time for customers. Since production begins after an order is placed, customers may need to wait before they receive their products, which can lead to frustration for those who expect faster deliveries.
Made-to-Order can also create challenges with production planning. When demand fluctuates, companies may struggle to manage resources and production schedules effectively, increasing cycle times and leading to delays and higher costs.
Pros and Cons of Made-to-Order
| Pros of Made-to-Order | Cons of Made-to-Order |
|---|---|
|
|
Examples of Made-to-Order Process in an Industry
Many businesses that follow the Made-to-Order approach wait for customers to place an order before starting production. For example, custom clothing brands or catering services create products only after clients specify what they want, ensuring everything matches the customer’s needs.
In industries like automotive or aerospace, manufacturers build vehicles or parts only after receiving specific orders. They use a bill of materials to outline the required components, allowing them to create products tailored to each customer’s requirements without building unnecessary stock.
Made-to-Order also works for businesses offering personalized products like custom furniture or printed items. These companies plan, source materials, and start production only after receiving the customer’s order, ensuring each item meets their exact specifications.
Make-to-Order vs. Make-to-Stock vs. Made-to-Order
Choosing the right production strategy has a significant impact on cost efficiency, inventory management, and customer satisfaction. Make to Order, Make to Stock, and Made to Order each represent different approaches to balancing demand, production timing, and customization.
Here is a comparison of Make to Order, Make to Stock, and Made to Order that we have summarized in a table:
| Categories | Make-to-Order | Make-to-Stock | Made-to-Order |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Trigger | Production begins after receiving the customer order, focusing on real demand. | Production starts based on forecasted demand, ahead of time. | Production starts after receiving the customer order, tailored to specific needs. |
| Inventory Requirements | No stock is kept, so production starts only after an order. | Holds inventory in anticipation of demand. | May hold some materials, but does not keep finished goods in stock. |
| Delivery Lead Time | Longer lead time, as production starts after an order is placed. | Faster delivery since products are already in stock. | Similar to MTO, with lead times depending on customization. |
| Customization Flexibility | Offers high customization based on customer needs. | Limited customization, as products are made in bulk. | Offers the highest level of customization, with detailed adjustments. |
| Risk of Overproduction or Stockouts | Reduces overproduction but may face stockouts if demand exceeds capacity. | Risks of overproduction and excess inventory if demand forecasts are wrong. | Avoids overproduction but may face delays during high-demand periods. |
| Cost Implications | Lower inventory costs but higher production costs due to smaller batch sizes. | Benefits from economies of scale but incurs inventory storage costs. | Keeps costs low by minimizing inventory, but may have higher production costs. |
| Demand Planning and Forecasting | No need for forecasting, responds to real-time demand. | Heavily depends on forecasting to maintain the right stock levels. | Combines forecasting with customer-specific production for better alignment. |
After understanding how these models compare from the comparison table above, it will definitely help businesses determine which strategy best fits their market needs, operational capabilities, and customer expectations. So if you want to understand the comparison further, here is a more detailed version of the comparison:
Production Trigger
In MTS, companies start production based on forecasted demand, making items ahead of time and storing them. MTO and Made-to-Order only begin production after receiving a customer order, ensuring products are made to meet real demand.
MTS works well for high-demand, standardized products. On the other hand, MTO and Made-to-Order focus on producing exactly what customers need, offering a flexible production planning and control approach that responds to actual sales.
Inventory Requirements
MTS keeps inventory on hand in anticipation of demand. MTO doesn’t hold stock and starts production only after an order comes in. Made-to-Order may hold some materials, but usually doesn’t keep finished goods in stock.
MTS can lead to excess inventory and storage costs if demand changes unexpectedly. MTO reduces inventory but may face longer lead times, while Made-to-Order keeps costs low but may struggle to deliver quickly during high demand.
Delivery Lead Time
MTS has a clear advantage in faster delivery since products are already in stock. With MTO, customers face longer wait times because production starts only after they place an order. Made-to-Order often follows similar timelines depending on customization.
MTS allows businesses to ship products quickly since everything is ready. MTO offers a customized solution but requires more time to manufacture. Made-to-Order is similar, but delivery times depend on the level of customization requested by the customer.
Customization Flexibility
MTS offers limited customization because products are made in bulk based on forecasts. MTO and Made-to-Order are ideal for customization, as production starts after customers place orders, allowing them to request specific features or designs.
MTO provides flexibility by creating products exactly as customers want. Made-to-Order takes customization a step further, allowing even more detailed adjustments, making it perfect for high-end, personalized products.
Risk of Overproduction or Stockouts
MTS risks overproduction if the forecast is inaccurate, leading to excess inventory. MTO reduces this risk but may face stockouts if demand exceeds production capacity. Made-to-Order avoids overproduction but may have trouble meeting demand during busy periods.
MTS often results in wasteful surplus inventory if demand doesn’t match forecasts. MTO keeps overproduction in check but might face stockouts. Made-to-Order avoids excess stock but could miss delivery deadlines during unexpected demand spikes.
Cost Implications
MTS enjoys economies of scale, producing in bulk at a lower per-unit cost, but storing inventory can add to expenses. MTO, by producing only when needed, has lower inventory costs but faces higher production costs due to smaller batch sizes.
MTS lowers per-unit costs by making items in bulk, but it can lead to waste if demand is overestimated. MTO has more flexibility but can have higher production costs since it makes products based on individual orders, making each unit more expensive.
Demand Planning and Forecasting
MTS depends heavily on demand forecasting to produce the right amount of inventory ahead of time. MTO avoids forecasting by producing only when an order comes in, while Made-to-Order combines forecasting with customer-specific production for a balanced approach.
MTS struggles when demand changes unexpectedly, leading to excess inventory or stockouts. MTO avoids these issues by responding to real-time demand, while Made-to-Order balances forecasting and customization, better matching customer needs.
Optimize Make-to-Order, Make-to-Stock, and Made-to-Order Process with ScaleOcean’s Software
ScaleOcean is a manufacturing software that supports the entire make-to-order process by enhancing efficiency and resource management. By automating key operations and providing real-time insights into production, ScaleOcean helps businesses reduce lead times and minimize production costs.
By automating critical processes and providing real-time visibility into production, ScaleOcean’s manufacturing software can help you align manufacturing with actual customer demand, reducing delays and minimizing unnecessary expenses.
This ensures that your company can quickly respond to market needs while maintaining high-quality standards and efficient resource usage. One of the standout features of ScaleOcean is its advanced AI technology, which helps predict customer demand and optimize resource allocation.
This not only allows you to stay ahead of market trends but also reduces waste and prevents overproduction. The real-time insights provided by the software empower your team to make data-driven decisions.
ScaleOcean also offers a free demo, allowing you to experience firsthand how this powerful software can enhance your make-to-order process and drive long-term success for your business. In addition, there are several special features offered by Scaleocean to optimize the make-to-order process, namely:
- Order management automation: From receiving and processing customer orders, everything is done directly on a single platform, ensuring that the unique specifications of each MTO order are accurately recorded and can be immediately processed into production without manual delays.
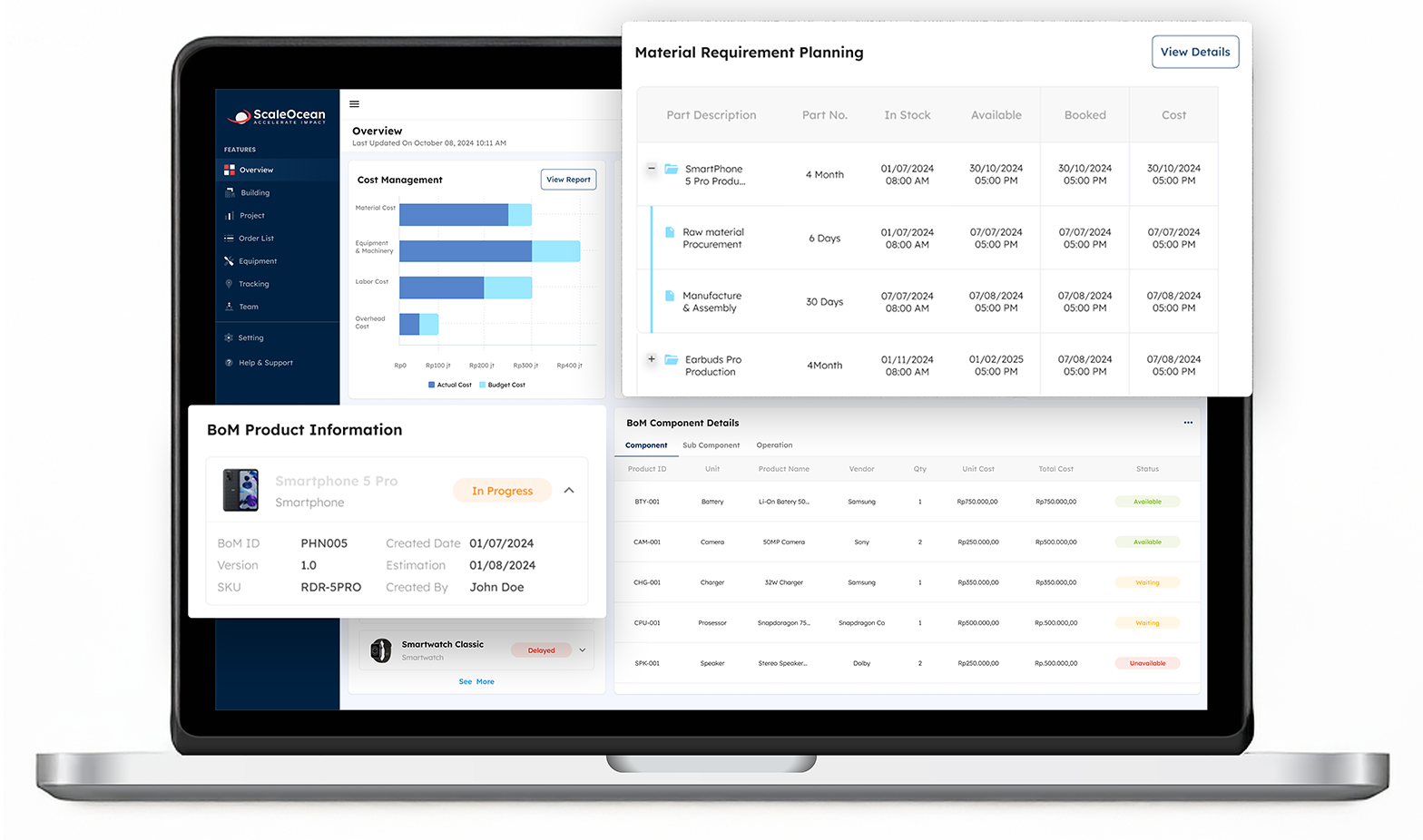
- Smart MRP: Automatic calculation of raw materials based on production schedules and lead times, as well as timely ordering in accurate quantities.
- BOM Management: Real-time tracking of customer order status, efficient work schedules, and machine utilization.
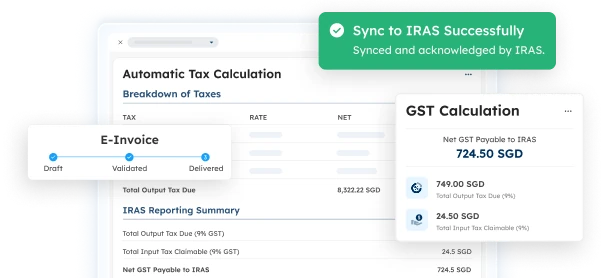
- Cost Management: Automatically calculates detailed COGS for each unique MTO order.
- Integrated quality control: Monitors every stage of production to ensure the quality of the final output meets order specifications.
With these capabilities and features, you can implement Scaleocean as the best solution for optimizing your MTO strategy, achieving unprecedented levels of operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Take a free demo now.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Make to Order is a strategic production approach that helps businesses align manufacturing with actual customer demand, reduce inventory risks, and deliver highly customized products.
While it requires careful planning, strong supplier coordination, and clear lead-time management, MTO offers long-term efficiency and flexibility for industries where personalization matters.
To successfully manage this process, the right technology plays a crucial role. Scaleocean can help streamline order management, production planning, and coordination, making it easier to run an efficient and reliable MTO operation without unnecessary complexity.
Experience firsthand how ScaleOcean can transform your MTO process by scheduling a free demo today. See how its advanced technology can reduce waste, increase efficiency, and drive your business toward long-term success.
FAQ:
1. What is the difference between MTO and ATO?
Make to Order (MTO) involves manufacturing the complete product only after a customer places an order, offering maximum customization but typically resulting in longer delivery times. In contrast, Assemble to Order (ATO) combines forecasting and flexibility by pre-producing standard components and keeping them in stock, then completing the final assembly once the customer order is received.
2. What is the opposite of make-to-order?
The opposite of Make to Order is Make to Stock, which determines whether customer orders are fulfilled from existing inventory or produced and purchased only after demand is confirmed.
3. How to prepare MTO?
The document describes a set of steps for setting up a system, such as determining the file path for storing exported data and defining component categories. It also highlights the need to establish a clear hierarchy and create related records to ensure proper configuration.
4. What kind of products use MTO?
Industries that frequently apply MTO include aerospace, automotive, particularly luxury vehicles, custom furniture, industrial machinery, specialized medical equipment, construction, and bespoke fashion. In general, MTO is best suited for sectors that produce highly customized, high-value, or complex products.



.webp)
.webp)

.webp)
.webp)



.webp)
.webp)



.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)

















