Singapore has emerged as a worldwide manufacturing powerhouse, renowned for its efficiency, innovation, and high-quality production standards. To sustain their competitive advantage, manufacturers must guarantee that their operations are well-structured and optimized.
Manufacturing process planning is crucial to attaining this goal by optimizing processes, allocating resources effectively, and lowering production costs while preserving product quality.
Manufacturing process planning is a systematic method for organizing and optimizing production, also involves devising a strategy for producing a product, from raw materials to finished products, ensuring efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, it aids in guaranteeing that the manufacturing process is both efficient and precise.
In a period of rapid technology breakthroughs and evolving market needs, Singapore’s industries require a well-planned manufacturing process to stay adaptable, scalable, and globally competitive. According to Reuters, investment pledges for Total Business Expenditure (TBE) in Singapore fell by S$0.5 billion to S$8.4 billion in 2024.
This reduction indicates the manufacturing sector’s difficulty in controlling operational expenses and long-term investments. As global rivalry heats up, manufacturing process planning becomes increasingly important for assuring optimal resource use, cost management, and long-term growth
- Manufacturing process planning is a systematic method for optimizing production from raw materials to finished goods, ensuring efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
- The activities of MPP ensure efficient production by defining operations, selecting methods, documenting steps, ensuring quality, and optimizing resources for cost-effectiveness.
- Key steps in manufacturing process planning include identifying inputs and outputs, product design, process selection, resource planning, layout design, and so on.
- ScaleOcean’s manufacturing software offers real-time tracking, automatic scheduling, and optimal resource management, allowing manufacturers to increase efficiency while remaining flexible.

What Is Manufacturing Process Planning?
Manufacturing process planning is a systematic way to create and organize the steps necessary to make a product efficiently and cost-effectively into finished goods. It encompasses the sequencing of operations, planning of machining processes, planning of assembly procedures, and the organization of assembly lines.
A well-planned process contributes to uniform product standards, waste reduction, and faster production deadlines. Key elements such as workflow design, scheduling, and a manufacturing bill of materials ensure that resources are allocated efficiently, minimizing unnecessary costs.
Manufacturing process planning focuses on optimizing production efficiency, ensuring products meet quality standards, are delivered on time, and are produced at the lowest cost possible.
In highly competitive industrial environments such as Singapore, strategic planning is critical for satisfying customer needs, adjusting to market changes, and maintaining long-term corporate success.
Here are the goals of manufacturing process planning for Singapore companies:
- Guarantee that processes are precise and effective
- Offer clarity to other departments, such as engineering
- Lower costs and avoid delays
- Reduce downtime and minimize waste
- Keep inventory levels as low as possible
Key Components of Manufacturing Process Planning
A successful manufacturing process plan includes numerous key components that ensure efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and high-quality results. Each stage is critical to improving production workflows and ensuring consistency. Here are the essential components of manufacturing process planning:
- Master Production Scheduling (MPS): MPS specifies the products to manufacture, their quantities, and the timelines, ensuring they meet production goals and customer demand, similar to the takt time definition.
- Production Planning: It develops a strategic approach to achieve production objectives effectively by outlining timelines, resources, and overall targets.
- Production Scheduling: Divides the overarching plan into detailed tasks, specific timelines, and sequences to streamline workflow and meet deadlines.
- Consider Production Options: Analyzing various methods and technologies enables manufacturers to select the most efficient and cost-effective production strategies.
- Capacity Planning: Verifies that the facility is equipped with the necessary resources to satisfy production requirements by evaluating labor, machinery, and material availability.
- Inventory Management: Process inventory control can monitor and regulate the materials and finished goods to maintain appropriate stock levels and prevent shortages or surpluses.
- Routing: Routing establishes the order of operations and the pathway products take to guarantee an efficient and well-organized production process.
- Adjust Plan: Adjusting the plan entails making real-time modifications to the schedule to respond to unforeseen disruptions or changes in demand.
- Dispatching: This component issues production orders and allocates tasks to particular resources, ensuring efficient execution of the schedule.
- Map Out Your Workflows: Workflow mapping provides a visual representation of the production process to pinpoint inefficiencies and enhance coordination.
- Production Mapping and Resource: Production mapping aligns processes with available resources to maximize efficiency and highlight potential improvements.
- Resource Allocation: Resource allocation designates labor, machinery, and materials to specific tasks, ensuring equitable workloads and effective production.
Why Manufacturing Process Planning is Important for Businesses?
Effective manufacturing process planning is essential to ensure smooth and efficient production operations. Complex businesses in Singapore can improve overall productivity by strategically organizing workflows, allocating resources efficiently, and using standard procedures.
Based on Group50, a manufacturing company that implemented value stream mapping successfully reduced production lead time by 50%, leading to significant cost savings. This demonstrates how structured planning can optimize efficiency and drive measurable improvements in operational performance.
The following are the primary benefits and goals of implementing a strong manufacturing process strategy:
Enhanced Efficiency
Optimizing manufacturing workflows reduces delays and waste, and increases overall operational speed. By reducing unnecessary stages and guaranteeing a logical sequence of tasks, manufacturers can increase output while preserving quality.
Efficient process planning also lowers production bottlenecks, allowing for smoother transitions between stages and ensuring that activities run continuously. This results in faster turnaround times, more manufacturing production capacity, and better overall performance.
Cost Reduction
Careful planning and product lifecycle strategies enable more efficient resource allocation, reducing material waste, energy usage, and labor expenses. Manufacturers can lower overhead costs while maintaining quality by identifying the most cost-effective methods at each production stage.
Furthermore, smart raw material acquisition and optimal machine usage might help to avoid high costs. The capacity to foresee and control expenses also helps organizations remain profitable, even in highly competitive sectors where pricing efficiency is critical.
Quality Improvement
Standardized manufacturing techniques help to ensure product quality consistency by guaranteeing that every unit fulfills the relevant criteria. A well-defined manufacturing process plan minimizes the possibility of faults and rework, resulting in fewer production losses.
Clear quality control checkpoints throughout the process enable early detection of problems and prevent defective items from reaching customers. Consistent product quality strengthens a brand’s reputation, increases customer satisfaction, and lowers warranty claims or returns.
On-Time Delivery
MPP helps ensure timely product delivery by optimizing production scheduling and workflows. It enables manufacturers to accurately forecast and plan their production cycles while considering potential delays.
With a structured plan in place, businesses can effectively coordinate their resources, avoid unexpected interruptions, and meet deadlines. This approach ensures that products reach customers promptly and as expected.
Flexibility
A well-planned production system enables firms to respond swiftly to changes in demand, market trends, and supply chain interruptions. This adaptability is critical in modern production when unanticipated changes in raw material availability, customer preferences, or regulatory requirements can disrupt operations.
Companies that use excellent production planning and control can apply alternative methods, scale production up or down as needed, and introduce new products without incurring major downtime or costs. This agility enables firms to maintain stability and responsiveness in a continually changing marketplace.
Improved Collaborations
Manufacturing process planning improves collaboration among departments like engineering, manufacturing, and sales by offering a clear and unified production plan. This effective communication helps ensure that all teams are aligned on objectives, timelines, and resource allocation.
By streamlining interactions and minimizing misunderstandings, MPP facilitates smooth coordination across departments, resulting in quicker decision-making and a more agile production process.
Data-Driven Decision
The manufacturing process planning depends on data collection and analysis to inform decision-making throughout the production process. By consistently monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production rates, material usage, and equipment performance, businesses can make informed choices that enhance process efficiency.
Data-driven insights enable manufacturers to make real-time adjustments, optimize workflows, and tackle potential issues before they measure production efficiency or product quality.
Key Activities in Manufacturing Process Planning
Manufacturing Process Planning (MPP) is essential for achieving efficient and cost-effective production. Without a well-structured plan, even the best resources can be wasted. MPP helps businesses streamline operations, improve product quality, and optimize resource use.
Here are the reasons why MPP is vital for manufacturers in Singapore companies:
Identifying the required operations
A successful production process begins by defining the exact sequence of operations needed to convert raw materials into finished products. Analyzing each stage ensures tasks are performed in the correct order, helping businesses avoid delays, reduce rework, and maintain a smooth workflow.
Selecting the most efficient methods
MPP highlights the selection of the most effective methods, tools, and materials for each stage of production. By considering factors like material properties, production time, and cost, manufacturers can optimize their processes, leading to efficient and cost-effective solutions that reduce waste and boost production efficiency.
Documenting the plan
A manufacturing process plan is vital for ensuring consistency and efficiency in production. This document outlines the necessary steps and procedures for a successful production cycle. Clear instructions help reduce errors, maintain quality control, and ensure all team members follow the same processes, leading to a smoother production flow.
This aligns with good manufacturing practices, which emphasize the importance of detailed documentation for tracking production and ensuring compliance with quality standards.
Ensuring quality
A key aspect of MPP is implementing strict quality control measures to monitor and maintain production standards. By setting quality checkpoints throughout the process, MPP ensures that only products meeting or exceeding these standards reach the market, resulting in increased customer satisfaction and reduced return and rework costs.
Optimizing resources
Maximizing resource efficiency is a key goal of Manufacturing Process Planning (MPP). By effectively managing labor, equipment, and materials, manufacturers can reduce waste, minimize idle time, and prevent overproduction. This leads to cost savings, increased productivity, and helps businesses meet their production targets.
Types of Manufacturing Process Planning
Manufacturing process planning differs according to the kind of production, product complexity, and market demand. Different sectors necessitate unique ways to maximize efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Below are the primary types of industrial process planning and their characteristics:
Flow production planning
This entails the smooth transition of each item from one stage of the assembly line to the subsequent stage. This approach is extensively used in industries such as electronics, textiles, and household appliances. Products go through a linear and standardized procedure, with little variance in design.
Batch production planning
This entails producing a specific quantity of products (or batches). This type is suitable for creating things in set quantities and strikes a compromise between efficiency and personalization. It is commonly utilized in industries such as food processing, medicine, and consumer goods production.
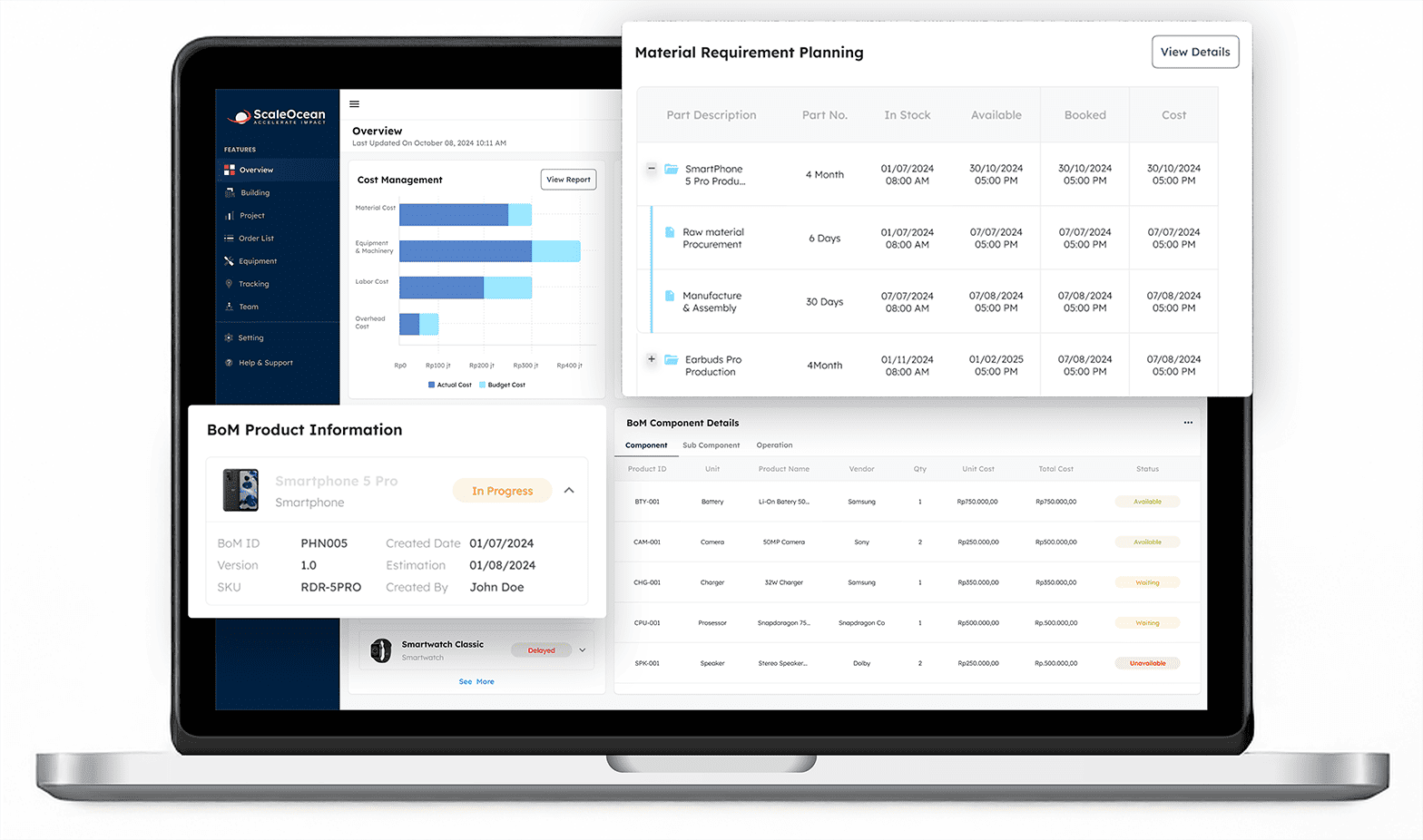
Material requirements planning (MRP)
Involves overseeing manufacturing processes, controlling inventory levels, and organizing manufacturing tasks. MRP (Material Requirement Planning) guarantees that the appropriate materials are available at the right moments and in the correct amounts to fulfill production requirements.
This synchronization improves operational efficiency, decreases waste, and ensures timely product delivery. In the end, MRP plays an essential role in facilitating a smooth and economical manufacturing process, aiding in improved decision-making and resource distribution.
Mass Production Planning
This technique, which focuses on large-scale production of standardized items, is employed in industries including automotive, consumer electronics, and packaging. The goal is to maximize output while minimizing costs using economies of scale.
Automation and modern manufacturing process planning software are critical components in improving production speed and consistency. While mass-production saves money, it needs a considerable initial investment in machinery and infrastructure.
Process Production Planning
This technology is widely employed in industries such as chemicals, oil and gas, and food processing, and it entails continuous production of indistinguishable products. Process manufacturing creates things in bulk, such as liquids, powders, or gases, as opposed to discrete manufacturing, which involves individual pieces.
Precision in process control is essential for maintaining consistency, quality, and compliance with industry rules.
Generative Manufacturing Process Planning
Generative process planning is widely used in industries like electronics and consumer goods, where quick design changes are common. It helps create optimized manufacturing plans using algorithms, making production more efficient with fewer human inputs.
Electronics companies benefit from this method by adapting quickly to changes in product designs or production conditions. By minimizing manual planning, generative tools ensure that the process stays efficient and responsive to the fast pace of innovation in tech.
Repetitive Production Planning
Repetitive production planning works best in industries like food manufacturing or consumer electronics, where products are produced in large volumes. It streamlines processes by reducing setup times and keeping resources focused, ensuring consistent and efficient production.
In the food industry, snack manufacturers use repetitive production planning to maintain a steady output. By sticking to predefined schedules, they can consistently produce high-quality products without wasting resources or time, keeping their operations smooth.
Discrete Production Planning
Discrete production planning is used in industries like machinery manufacturing or custom furniture, where products are unique and made in batches. It ensures that each item is made to the specific customer’s needs while maintaining quality throughout the process.
Machinery manufacturers, for example, rely on discrete planning to build custom equipment based on client specifications. This method helps them plan each step with care, ensuring high-quality machines while also meeting the unique demands of their customers.
Key Steps in Manufacturing Process Planning
Production process planning is a process that requires effective strategies to maximize each stage. This will ensure that each step is carefully designed to optimize resources, time, and quality. Here are the key steps of the production process planning:
1. Identify Inputs and Outputs in Your Manufacturing Process
Identifying inputs and outputs is a key step in manufacturing process planning. Inputs like raw materials, labor, and equipment are essential to kickstart production. Managing these resources properly helps ensure the manufacturing process runs smoothly and efficiently.
Outputs are the finished products that come from the production process. By tracking these outputs, manufacturers can ensure that products meet quality standards. Monitoring both inputs and outputs helps businesses streamline operations and improve overall performance.
2. Product Design and Development
The second phase of planning the manufacturing process is to establish the product design, which is especially crucial in a make-to-order process. This entails developing comprehensive specifications, drawings, and prototypes that detail the product’s features, dimensions, and functionality.
Engineers and designers should work together to ensure that the product satisfies customer requirements while remaining practical to produce. This phase also involves selecting materials, taking into account factors such as durability, cost, and availability.
3. Process Selection
After the product design is completed, the next step is to choose suitable manufacturing techniques. This includes deciding between options such as casting, machining, molding, or additive manufacturing based on the complexity of the product and the materials used.
The objective is to strike a balance between efficiency, cost, and quality. For example, products produced in large quantities may take advantage of automated processes, whereas custom or low-volume products might need manual methods.
4. Resource Planning
Resource planning guarantees that all required materials, tools, and equipment are on hand at the right time. This process entails calculating the amounts of raw materials needed, planning machinery upkeep, and distributing human resources accordingly. Efficient resource planning reduces downtime and avoids production delays.
It also encompasses budgeting for expenses related to materials, labor, and overhead. By predicting requirements and possible shortages, manufacturers can ensure a continuous workflow and avert expensive interruptions.
5. Layout Design
The arrangement of the factory is an essential component of process planning, as it influences the movement of materials and personnel within the production facility. A well-organized layout decreases unnecessary movement, shortens handling time, and maximizes the use of available space.
Typical layouts include process-oriented, product-oriented, and cellular configurations, each tailored for specific production types. A thoughtfully crafted layout improves productivity, enhances safety, and fosters communication among employees, ultimately leading to a more efficient manufacturing process.
6. Workflow and Scheduling
The process of workflow and scheduling entails developing a comprehensive timeline for every phase of manufacturing. This involves designating tasks for employees, establishing timeframes, and facilitating coordination among various departments.
Utilizing advanced scheduling tools and software can enhance production orders, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively and deadlines are adhered to. Effective scheduling also takes into consideration possible setbacks, enabling adaptability and backup planning.
7. Quality Control Planning
Quality control plays a vital role in the planning of manufacturing processes, guaranteeing that the end product adheres to established standards. This phase includes establishing inspection stages, testing protocols, and quality criteria during the production cycle.
Methods such as Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) can be utilized to reduce defects and increase uniformity. By incorporating quality control into the planning stage, manufacturers can detect and resolve problems early on, decreasing waste and improving customer satisfaction.
8. Cost Estimation and Budgeting
Precise cost estimation is essential for sustaining profitability. This process requires assessing the costs related to materials, labor, equipment, and overhead. Proper budgeting guarantees that the manufacturing operation stays financially viable while achieving quality and production goals.
Cost estimation also assists in setting competitive prices for the product in the market. By predicting expenses and tracking costs during the process, manufacturers can make well-informed choices and prevent overspending.
9. Implementation and Monitoring
The last phase involves executing the designed procedure and observing its performance. This includes establishing production lines, training staff, and starting the manufacturing process. Ongoing observation enables immediate modifications, guaranteeing that the process operates effectively and efficiently.
By utilizing ScaleOcean’s manufacturing software, businesses can streamline every step of the production process. From resource planning to scheduling and quality control, ScaleOcean helps manufacturers optimize workflows, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency for smoother operations.

Manufacturing Process Planning Example
A production schedule example provides a standardized framework for planning and tracking industrial processes. It guarantees that production meets demand and maintains efficiency throughout the process.
The major components of an effective manufacturing process planning example are listed below, including:
Production Phases
This section outlines each step of the production process, from raw material preparation to final assembly and packaging. Measuring cycle time metric at each phase helps track progress, identify dependencies, and maintain efficiency, ultimately reducing bottlenecks and increasing productivity.
Resource Allocation
Assigning the appropriate materials, people, and equipment at each stage of production is critical for avoiding shortages and ensuring smooth operations.
This component guarantees that resources are available when needed, hence reducing downtime and increasing efficiency. Proper allocation also helps to optimize costs by preventing assets from being overused or underutilized.
Time Frames
Establishing start and finish dates for each manufacturing step allows manufacturers to stay on track and achieve deadlines. Setting realistic timeframes allows firms to ensure timely product delivery, avoid rush manufacturing costs, and improve supply chain coordination.
Accurate scheduling also helps manage work in progress, allowing flexibility in dealing with unanticipated delays while maintaining total production.
Quality Checks
Inspection and testing points are built into the production schedule to ensure product quality and conformity to industry requirements. Regular quality assessments at important phases aid in early defect detection, saving rework and waste.
A structured approach to quality control assures consistency and increases customer satisfaction by providing dependable, defect-free products.
Tools for Manufacturing Process Planning
Manufacturing Process Planning (MPP) serves as the cornerstone of efficient production, enabling smooth operations and maximizing output. In today’s fast-paced manufacturing in Singapore, advanced technologies are transforming how we plan and manage production processes.
These tools play a vital role in optimizing resources and ensuring quality. Here’s why incorporating various MPP tools is essential for success:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): ERP systems integrate production, finance, and supply chain functions. They provide real-time insights into resources and schedules, helping businesses cut costs, boost efficiency, and make informed decisions.
- Computer-Aided Process Planning (CAPP): CAPP uses computer systems to simulate workflows, identify bottlenecks, and optimize production. This leads to faster production, improved planning accuracy, and fewer errors during design and production stages.
- Manufacturing Software: CAPP uses computer systems to simulate workflows, identify bottlenecks, and optimize production. This leads to faster production, improved planning accuracy, and fewer errors during design and production stages.
- Multi-Bill of Materials (BOM): A BOM lists materials and components needed for production. It ensures accurate procurement and cost estimation, avoiding delays and maintaining quality while ensuring smooth and efficient production.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Software: PLM software manages a product’s lifecycle from design to end-of-life. It tracks product details, promotes collaboration, and ensures industry standards and quality control are met throughout the manufacturing process.
- Simulation Tools Software: Simulation tools help manufacturers model production processes before implementation. They identify potential problems, optimize performance, and reduce costs, ensuring smoother and more efficient production outcomes.
- Quality Assurance Systems: Quality assurance systems monitor and control product quality during production. They detect defects early, ensure consistency, and improve customer satisfaction by maintaining high standards and reducing rework.
- Sales Forecasting Tools: Sales forecasting tools predict demand based on past data and trends. They help businesses make informed inventory decisions, minimize stockouts, and ensure production aligns with actual consumer demand.
Leveraging ScaleOcean Solutions for Effective Manufacturing Process Planning
ScaleOcean’s manufacturing process planning software offers real-time tracking, automatic scheduling, and optimal resource management, allowing manufacturers to increase efficiency while remaining flexible. This System also provides a free demo to manufacturers aiming to improve efficiency and control.
It demonstrates how its manufacturing process planning software can optimize production planning and resource allocation. ScaleOcean uses automation, real-time tracking, and data-driven insights to help firms enhance accuracy, decrease operational bottlenecks, and preserve flexibility in a competitive manufacturing industry.
Here are the unique features of the ScaleOcean manufacturing software:
- Integration: Seamless connection with existing systems, such as ERP and inventory management, ensures data consistency and smooth information flow across departments. This eliminates redundancies and enhances operational transparency.
- Simulation: The ability to model and test processes virtually before implementation helps manufacturers identify inefficiencies, test alternative workflows, and optimize production without costly real-world trial and error.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Live tracking of production progress, machine utilization, and workforce performance enables proactive decision-making. This ensures potential issues are identified early, reducing delays and improving overall productivity.
- Collaboration Tools: Manufacturing involves multiple teams and departments, making effective communication essential. Collaboration tools allow different units, such as production, quality control, and supply chain teams.
Conclusion
Effective manufacturing process planning is critical for Singaporean manufacturers to maintain efficiency, cut costs, and ensure excellent product quality. Optimizing workflows, resource allocation, and scheduling enables organizations to remain competitive and react to changing market needs.
Leveraging automation and digital technologies boosts productivity while reducing risks. To remain competitive, enterprises must use innovative production process planning software to improve efficiency and scalability.
ScaleOcean manufacturing ERP software provides an automated solution for streamlining operations using real-time tracking and data-driven decision-making. Schedule a free demo today to learn how ScaleOcean may help you enhance your manufacturing operations.
FAQ:
1. What are the 7 steps of manufacturing?
1. Develop the Idea: Identify product needs and conceptualize the design.
2. Perform Market Research: Analyze demand, competitors, and feasibility.
3. Design the Product: Create technical specifications and blueprints.
4. Finalize & Prototype: Build and refine a working model.
5. Prototype Testing: Assess functionality and make improvements.
6. Manufacture the Product: Begin full-scale production.
7. Monitor the Process: Ensure quality and optimize efficiency.
2. What is process planning in manufacturing?
Process planning outlines the sequence of operations to produce parts efficiently while ensuring quality and cost control. Essential for both custom and mass-production content, it optimizes resources, selects materials, and streamlines workflows to enhance productivity and minimize waste.
3. What are the 7 steps in the planning process?
1. Set Objectives: Define clear goals and expected outcomes.
2. Outline Tasks: Identify necessary actions to achieve objectives.
3. Allocate Resources: Determine budget, manpower, and tools required.
4. Establish a Timeline: Create a schedule for execution.
5. Plan Monitoring & Evaluation: Define tracking and assessment methods.
6. Finalize the Plan: Review and refine for implementation.
7. Communicate & Execute: Share the plan with the team and implement it.
4. What are the 4 types of manufacturing processes?
1. Casting & Molding: Shaping materials by pouring them into molds to form solid structures.
2. Machining: Cutting, drilling, or shaping materials using tools for precision.
3. Joining: Assembling components through welding, soldering, or adhesives.
4. Shearing & Forming: Cutting and bending materials to create desired shapes.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















