In today’s fast-paced manufacturing business, efficiency and precision are critical to competitiveness, especially in a hub like Singapore, where modern manufacturing processes are driving industrial growth.
Assembly production is critical in a variety of industries, especially electronics, automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. It involves the integration of produced components to form a complete product or sub-assembly.
This process frequently employs methods such as assembly lines and may incorporate techniques like 3D printing for the production of sub-assemblies. It ensures that individual components are flawlessly combined into a working final product.
With rising labor costs and increased demand for high-quality products, Singapore manufacturers must streamline assembly operations.
According to Business Times, unit labor costs in Singapore’s manufacturing sector would rise by 1.2% in 2024, with total labor costs per worker increasing by 4%, outpacing productivity increases.
To remain competitive, businesses must use cost-effective techniques such as assembly lines, partial assembly, or mechanical fastening to increase efficiency, decrease waste, and lower prices. This article looks at different assembly processes, their impact on cost savings, and how firms can improve production efficiency.
- An assembly manufacturing is numerous individual components are combined to form a larger, operational unit or product.
- The methods of assembly manufacturing include: assembly line, partial assembly, rivet assembly, weld assembly, and mechanical assembly
- The difference between assembly vs. manufacturing is that manufacturing transforms raw materials into finished goods, while assembly focuses on combining pre-made parts to create a final product.
- ScaleOcean software manufacturing can provide a centralized platform that incorporates important manufacturing processes, including assembly and all process manufacturing.

What is Assembly Manufacturing?
Assembly manufacturing involves combining various components or subassemblies and using methods like welding, screwing, or gluing to produce a complete, functional product. This step is essential and often occurs at the final stage of production.
It plays a key role in industries such as automotive and electronics, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and high-quality results. The process can be carried out manually, automatically, or through a combination of both.
The process of assembly manufacturing often employs methods such as welding, screwing, or gluing, and is prevalent in sectors such as automotive, electronics, and mechanical engineering.
These assemblies may consist of diverse materials and parts that are produced using various manufacturing techniques, such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
A prevalent technique in assembly manufacturing is the assembly line, in which the product progresses sequentially from one workstation to the next, with components being added in order until the final product is completed.
Other typical methods are weld assembly, which uses heat to fuse materials, and mechanical assembly, which connects pieces with screws, bolts, and nuts. Product complexity, production volume, and cost efficiency all play a role in technique selection.
In a mass production strategy, choosing the right assembly method is crucial to maintaining speed, consistency, and cost-effectiveness. Automation and specialized software have advanced assembly manufacturing, allowing organizations to improve precision, eliminate waste, and maximize overall production efficiency.
Assembly vs. Manufacturing: What’s the Difference?
While both assembly and manufacturing are integral parts of the production process, they differ in terms of scope and function.
1. Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials into finished goods, including resource procurement, processing, machining, and quality control. This procedure frequently entails shaping, cutting, molding, or chemically changing materials to produce components.
2. Assembly
Assembly, on the other hand, is a phase of manufacturing that concentrates primarily on merging pre-made components into a finished product. It does not require material transformation, but rather the arrangement and integration of pieces by techniques like riveting, welding, or mechanical fastening.
In essence, production develops the pieces, whereas assembly connects them to make the finished product, assuring functioning and quality.
3. Key Differences in Scope and Focus
After understanding each definition, it’s clear that assembly refers to the activity of assembling various components into a complete product, while manufacturing encompasses a broader process, from processing raw materials to producing finished goods.
Both play a crucial role in ensuring products are produced efficiently, consistently, and meet business quality standards. The following table outlines the scope and focus of assembly and manufacturing to help you understand the differences easily.
| Metrics | Assembly | Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Focuses on combining pre-made components into a finished or semi-finished product | Covers the entire production process, from raw material processing to finished goods |
| Key Steps | Part preparation, component fitting, fastening, testing, and final inspection | Material processing, forming, machining, assembly, quality control, and packaging |
| Overlap | Often represents one stage within a broader manufacturing process | Includes assembly as one of its operational stages |
Why Is Assembly Manufacturing Important?
Assembly manufacturing is a crucial stage in the production process that directly impacts product quality, production efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
By integrating pre-manufactured components into finished products, assembly manufacturing ensures that businesses can deliver reliable, consistent products to the market with faster lead times and lower costs. Here are the reasons why assembly manufacturing is important, including:
1. Quality and Consistency
Assembly manufacturing plays a vital role in ensuring high-quality products. By standardizing the assembly process and using pre-tested components, manufacturers can consistently produce products that meet required specifications.
Automated systems and specialized labor further reduce errors, ensuring that every product is built to the same high standards, enhancing reliability and customer trust.
2. Final Product Realization
Assembly manufacturing is essential for transforming individual components into a fully functional product. This step brings all the parts together, ensuring they fit, work, and perform as intended.
It’s the critical stage where the final product takes shape, enabling businesses to deliver ready-to-use items that are ready for distribution, providing value to customers while meeting market demands.
3. Customization
Assembly manufacturing allows for greater product customization. By using modular components, manufacturers can easily adjust their assembly lines to accommodate different variations or features based on customer preferences.
This flexibility is particularly valuable in industries where customer specifications vary, enabling businesses to provide tailored products without disrupting the entire production process.
How Assembly Manufacturing Works
Assembly manufacturing is a structured process where individual components are brought together to form a final product. Depending on the complexity of the product and the scale of production, assembly can be done manually, automatically, or through an assembly line.
Each method has its own set of advantages, ensuring efficiency, quality, and customization in the production process.
1. Manual Assembly
Manual assembly involves skilled workers physically assembling components by hand. This method is ideal for low-volume, high-precision, or customized products.
Workers are responsible for fitting, connecting, or installing individual parts, often using hand tools or simple machines. While more labor-intensive, manual assembly provides flexibility for intricate or bespoke tasks, allowing for detailed craftsmanship and quality control.
2. Automated Assembly
Automated assembly uses machines, robots, and computerized systems to assemble components with minimal human intervention. It increases speed, consistency, and efficiency, particularly in high-volume production.
Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks, like part insertion or soldering, with precision, reducing errors and increasing throughput. This method is commonly used in industries like electronics, automotive, and consumer goods.
3. Assembly Line Production
Assembly line production is a manufacturing method where products move through a series of workstations, each performing a specific task. This setup allows for high-speed, mass production by optimizing workflow and reducing delays.
Workers or machines perform repetitive tasks at each station, contributing to faster assembly times. It’s ideal for products requiring standardized production processes and large quantities.
Assembly Manufacturing Process
The assembly manufacturing process normally consists of several major steps, each with a critical role in ensuring efficiency and product quality. Throughout production, components go through various work-in-progress stages before becoming a finished product.
A well-structured process lowers errors, shortens manufacturing time, and increases cost-effectiveness. Manufacturers can increase uniformity, streamline workflows, and maximize resource use by adopting a systematic approach.
Proper planning and execution at each level, along with understanding the types of manufacturing processes, are critical for maintaining high standards and achieving consumer expectations. The assembly manufacturing process typically consists of many essential stages:
1. Design and Planning
This first phase entails envisioning the product, designing components, and creating an optimum assembly sequence. Engineers and designers cooperate to generate accurate blueprints, 3D models, and prototypes that guarantee all elements fit and function properly.
Careful planning at this stage allows producers to eliminate manufacturing errors, reduce material waste, and improve assembly efficiency before full-scale production begins.
2. Sourcing Components
Purchasing high-quality materials and parts from reputable sources is critical for maintaining product consistency and avoiding problems.
Manufacturers must assess supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and material specifications to verify that all components fulfill industry standards. Effective sourcing techniques can also help to avoid delays, reduce costs, and increase overall supply chain efficiency.
3. Sub-Assembly
During this stage, smaller components are pre-assembled into functioning sub-units that are then integrated into the final product. This strategy simplifies the final assembly step, accelerates production, and ensures greater quality control.
Sub-assemblies are frequently inspected individually before proceeding to the next stage to detect and rectify flaws early in the process.
4. Final Assembly
During the final assembly step, all sub-assemblies and individual components are assembled to form the finished product. Precision and accuracy are essential for ensuring that all parts fit together effortlessly, perform correctly, and satisfy design standards.
This process may involve automated machinery, manual labor, or a combination of the two, depending on the product’s complexity and manufacturing volume.
5. Quality Control
Quality control is a critical phase that includes rigorous testing, inspections, and performance assessments to guarantee that the completed product fulfills all applicable standards.
Visual inspections, functional testing, and stress analysis are some of the procedures used by manufacturers to find faults before they reach customers. A solid quality control procedure decreases recalls, lowers warranty claims, and increases customer satisfaction.
Methods in Assembly Manufacturing
Selecting optimal assembly methods is critical in manufacturing since it directly affects production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Manufacturers can save a lot of money by improving these processes.
The proper assembly method not only lowers labor expenses but also decreases material waste and improves product consistency. This process can involve various techniques, including:
1. Assembly Line
An assembly line, in which the product progresses from one workstation to another, with each station designated to carry out a particular task. This method is employed in the manufacturing of a wide range of products, such as vehicles, domestic appliances, and electronic devices.
This process includes products passing sequentially through a succession of workstations, with each station adding specific components or completing specified duties. This strategy improves efficiency by standardizing procedures, decreasing manual labor, and boosting production speed.
2. Weld Assembly
Weld assembly involves melting and fusing materials, resulting in a strong and lasting bond. This approach is critical for producing constructions with high strength and longevity, such as autos, heavy machinery, and metal frameworks.
Welded joints are seamless and can endure severe temperatures, making them the ideal choice for structural stability. However, welding necessitates competent personnel and sufficient safety precautions to achieve high-quality outcomes and prevent material distortion.
3. Screwing/Bolting
This method involves using fasteners to secure components in place, such as screws or bolts to securely join components. The fastener is inserted through pre-drilled holes in the parts and then tightened to hold them firmly together.
It allows for disassembly, making it ideal for repairs or adjustments. This method is commonly used in industries where components must be easily replaced or serviced.
4. Gluing/Adhesion
Adhesive bonding is a method of assembly manufacturing that uses adhesives to join materials together and is commonly applied to the surface to be bonded and then allowed to cure and create a strong bond.
This method is often used for materials that are difficult to fasten with mechanical methods, like glass or plastics. It offers smooth, aesthetic finishes and can also bond dissimilar materials, though it may not be as strong as mechanical fastening for heavy-duty applications.
5. Brazing/Soldering
This method, employing adhesives for the assembly of components, both brazing and soldering, involves joining metal parts by melting a filler metal, which has a lower melting point than the base metals.
In brazing, the filler metal melts above 450°C, while soldering occurs below that temperature. The filler metal flows into the joint by capillary action, creating a strong, durable bond.
This method is used for joining delicate or thin metal parts without weakening the base material, commonly seen in electronics and plumbing.
6. Partial
Partial assembly entails building a component of a product and then transporting it to another place for completion. This technique enables producers to split tasks across specialized facilities, increasing productivity and lowering operational expenses.
Businesses that use partial assembly can reduce manufacturing lead times and increase quality control, particularly when specific components require specialized skills or equipment for final assembly.
7. Rivet
Rivet assemblage links components with rivets, resulting in strong, vibration-resistant connectors for the aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors. It is a low-cost alternative to welding that does not require heat or substantial preparation.
According to ProtoLabs, a crucial advantage is its ability to attach various materials, such as aluminum to steel or stainless steel to galvanized metal, which provides more flexibility than welding. This makes riveted joints long-lasting and dependable, particularly for permanent applications.
8. Mechanical
Mechanical assembly connected components using hardware such as screws, bolts, and nuts. This approach allows for quick disassembly for maintenance, upgrades, or repairs, making it excellent for electronics, appliances, and modular systems.
Unlike permanent attaching methods, mechanical assembly enables design flexibility and low-cost adjustments. However, producers must use adequate torque and fastening techniques to prevent loosening over time, particularly in high-vibration situations.
Best Practice of Assembly Manufacturing
Transforming assembly manufacturing into reality necessitates a systematic approach to guarantee efficiency, precision, and quality. Each phase, from the initial data submission to the final delivery, is vital in optimizing the overall process. Below are four straightforward yet impactful steps to finalize your assembly.
1. Staging (Provide Product Specifications)
Staging in the assembly process involves preparing all necessary components and parts for the assembly line. This step ensures that materials are organized, sorted, and easily accessible to workers, minimizing downtime during production.
It allows for a smoother flow, ensuring that all items are available at the right time to prevent delays in the assembly process.
For build-to-order manufacturing, providing detailed and accurate specifications is crucial as it ensures that manufacturers can fully understand your unique needs and customize the product accordingly. The more detailed the input, the more seamless the assembly process will be.
2. Mechanical and Electrical Assembly
Mechanical and electrical assembly combines both mechanical and electrical components into a functioning product. It’s crucial for ensuring the product operates as intended.
This step requires skilled technicians who are capable of assembling complex systems, including wiring, fitting mechanical parts, and ensuring all electrical connections are secure and functional.
3. Coordinate the Project
Successful assembly hinges on effective communication among all stakeholders. This phase entails synchronizing schedules, addressing any technical issues, and ensuring that all teams are aligned.
A well-coordinated project reduces the likelihood of delays, mitigates miscommunication, and maintains an efficient workflow.
4. Testing
Testing is a critical step to verify the functionality and quality of the assembled product. During this phase, products undergo various tests, including performance checks, safety assessments, and reliability tests, depending on the type of product.
It helps identify any defects or weaknesses early, ensuring the final product meets all necessary specifications and quality standards.
5. Request a Quotation
After clarifying the requirements, the manufacturer will issue a cost estimate that reflects the materials, labor, and complexity of production.
A clear and transparent quotation process is essential for budgeting and informed decision-making. Careful examination of the quote ensures it meets your expectations before moving forward with production.
6. Packaging
Packaging is the step in the assembly process where finished products are carefully packaged for shipping and distribution.
This step includes labeling, adding protective materials to prevent damage during transport, and ensuring that the product reaches customers in optimal condition. Proper packaging also includes branding and provides information for end-users.
7. Manufacturing, Quality Assurance, and Delivery
The concluding phase encompasses the fabrication of components, assembly of parts, and rigorous quality inspections. Thorough testing guarantees that the assembly adheres to industry standards before it is shipped.
Once it receives approval, the final product is meticulously packaged and delivered, ready for use or distribution.
Example of Assembly Manufacturing in Various Industries
The use of assembly manufacturing methods is a solution for various industries to form everything easily. Each process and its application in each industry has different components that are precise and efficient. Here are some industries in production that usually use the assembly system, including:
1. Automotive
In the automotive industry, this method is used to build cars, trucks, and other vehicles. The process involves assembling various parts such as engines, chassis, and interiors into a complete vehicle. This method in automotive ensures high-volume production and consistent quality across vehicle models.
2. Electronics
Assembly manufacturing in the electronics industry is used for creating computers, televisions, smartphones, and other devices. In this industry, automated machines and pick-and-place robots are commonly used for precise component placement on circuit boards.
The assembly process is crucial to achieving the high performance and reliability required in consumer electronics.
3. Mechanical Engineering
In mechanical engineering, assembly manufacturing is applied to the production of machinery, equipment, and complex systems. This includes items like industrial machines, HVAC systems, and turbines.
The process often involves the precise assembly of various parts, including gears, motors, and hydraulic systems. Assembly lines and skilled workers ensure that the final systems meet the required specifications for performance, safety, and reliability.
4. Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, assembly manufacturing is used to construct aircraft, spacecraft, and components like engines and landing gear. This process requires high precision due to the safety and performance demands.
Automated systems, along with skilled workers, are involved in assembling parts such as wings, fuselages, and avionics. Rigorous testing and quality control are essential throughout the assembly process to ensure that the aircraft meets all safety regulations and performance standards.
5. Furniture
In the furniture industry, assembly manufacturing is used to create everything from office furniture to home furnishings. Components such as legs, frames, upholstery, and hardware are assembled to create the final product.
Automated and manual labor work in tandem to assemble the parts efficiently, ensuring quality and durability. This method allows for mass production of furniture while offering customization options for various designs and materials.
6. Medical Devices
Assembly manufacturing in the medical device industry involves creating products like diagnostic machines, implants, and surgical tools. The process requires strict adherence to quality control and regulatory standards due to the critical nature of these devices.
Precision assembly is key, with workers and machines collaborating to assemble intricate components like microelectronics, sensors, and casings to ensure proper function and safety for patient use.
ScaleOcean manufacturing software optimizes assembly processes by providing a variety of features that improve production efficiency across various industries. With high flexibility and comprehensive module integration, ScaleOcean provides a system that can be tailored to the needs of each industry sector.
Take a free demo now to discover this solution!

Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DfMA)
DfMA is an engineering approach that emphasizes the enhancement of the manufacturing and assembly processes of a product, aiming to lower expenses and increase efficiency.
It is also a set of principles and techniques aimed at improving the design process to reduce production manufacturing costs and improve efficiency during assembly manufacturing.
The core idea is to design products in a way that simplifies the manufacturing and assembly processes, making them easier, faster, and cheaper to produce. DfMA involves analyzing the product design to identify potential production challenges, such as complex parts, difficult assembly processes, or expensive materials.
1. Key Strategies DfMA
- Reducing Part Count: By simplifying product designs and reducing the number of components, assembly becomes quicker and more efficient. Fewer parts lead to less complexity during both manufacturing and assembly, reducing the chances of errors and defects.
- Standardization of Parts: Using standardized components across different products helps streamline production processes. It simplifies inventory management, as companies only need to stock a limited set of parts.
- Designing for Ease of Assembly: In this approach, parts are designed to be easy to handle, align, and assemble. Factors like part orientation, assembly sequence, and the elimination of special tools are considered early in the design phase.
- Material Selection: Choosing materials that are cost-effective, readily available, and suitable for easy manufacturing is a core principle of DfMA. By opting for materials that are easier to process and assemble, companies can reduce production time and minimize costs.
2. Key Benefits of DfMA
- Cost Reduction: Optimized designs and simplified manufacturing methods contribute to lower overall production expenses.
- Accelerated Time-to-Market: By decreasing the amount of work required on-site, projects can be finished more swiftly, facilitating quicker product launches.
- Improved Quality: A stronger emphasis on quality assurance during manufacturing leads to greater consistency and a reduction in defects.
- Enhanced Efficiency: DfMA enhances both manufacturing and assembly processes, resulting in improved operational efficiency.
- Sustainability: By minimizing waste and conserving resources during production, DfMA promotes more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Assembly Manufacturing Efficiency with ScaleOcean Integrated Software
Implementing specialist software, such as ScaleOcean, can greatly improve assembly manufacturing efficiency by automating essential tasks and enhancing workflow coordination. Managing complex assembly activities manually can result in inefficiencies, errors, and delays, particularly in large-scale production.
ScaleOcean software manufacturing can provide a centralized platform that incorporates important manufacturing processes, including component tracking and real-time production monitoring. Businesses can use data-driven insights and automation to decrease costs, limit downtime, and increase overall assembly line efficiency.
ScaleOcean allows manufacturers to have greater control and insight over their assembly operations, resulting in increased productivity and lower operational expenses. Interested in improving your production workflow? Get a ScaleOcean free demo today and discover how it can improve your assembly production operations.
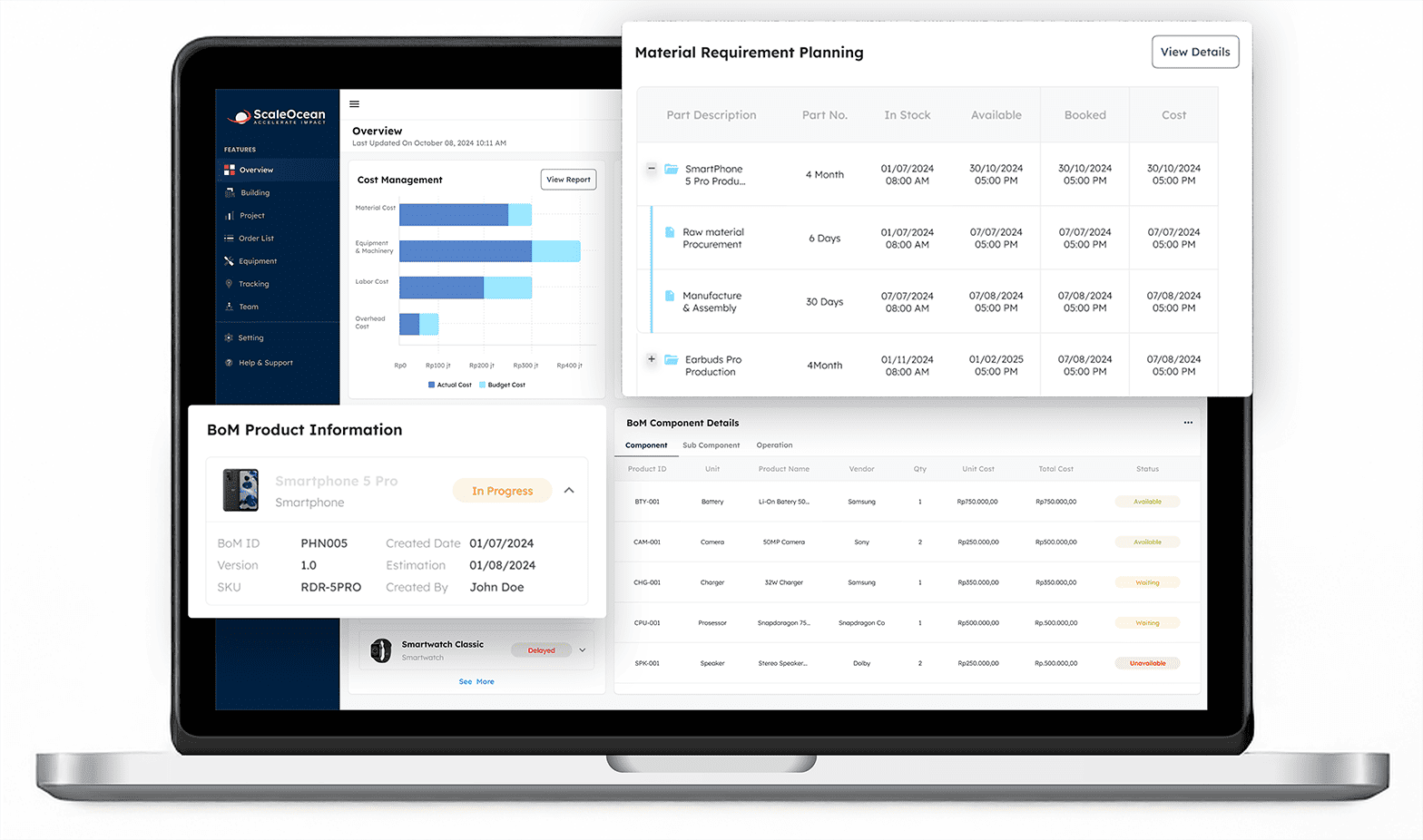
- Bill of Materials (BOM) Management: Efficiently handles multi-level BOMs, ensuring accurate tracking of components, materials, and sub-assemblies throughout the entire production process.
- Production Scheduling: Optimizes assembly line operations by managing timelines, workloads, and resource allocation to prevent bottlenecks and delays.
- Inventory Management: Provides real-time stock monitoring, helping manufacturers reduce material shortages, prevent excess inventory, and streamline supply chain operations.
- Quality Assurance Tools: Integrates automated quality checks at various assembly stages, reducing defects and ensuring that finished products meet industry standards.
- Supplier Management: Enhances communication with suppliers and vendors, ensuring on-time delivery of essential components while improving cost efficiency.
Conclusion
Assembly manufacturing is critical for successfully merging components into a final product, and the correct methods and processes influence cost savings, efficiency, and quality.
A well-structured methodology, combined with meticulous planning, sourcing, and quality control, provides seamless production while reducing errors. As production scales, technology-driven solutions become critical to preserving precision and efficiency.
To optimize assembly operations, companies want a centralized software solution that improves workflow coordination and quality management. ScaleOcean improves BOM monitoring, scheduling, and supplier management, increasing production efficiency.
Get a free demo today and learn how ScaleOcean can help you streamline your assembly production operations.
FAQ:
1. What is an example of assembly production?
Assembly production is used to efficiently manufacture mass goods, often with robotic workers alongside humans. A common example is automobile manufacturing, where parts like engines and electronics are systematically assembled. Other examples include household appliances and electronic devices.
2. Is assembly the same as production?
Assembly is a stage within manufacturing, not the entire process. While some use the terms interchangeably, manufacturing covers everything from raw materials to the final product, whereas assembly specifically refers to putting together pre-made components into a finished item.
3. What is the process manufacturing or assembly process?
Process manufacturing creates products through chemical or mechanical transformations, common in industries like food and pharmaceuticals. Assembly manufacturing, however, focuses on joining individual parts to form a final product, as seen in automobile and electronics production.
4. What is an example of an assembly industry?
An assembly industry creates finished products by combining various pre-made components. Examples include automobile manufacturing, where engines and frames are assembled into cars, and electronics production, where parts like screens and circuits form computers, televisions, and watches.












 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















