In Singapore’s highly competitive manufacturing sector, efficiency and precision are critical for success. A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) plays a key role in streamlining production processes, improving real-time visibility, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
According to Forbes, as the manufacturing industry adopts Industry 4.0, MES systems facilitate the integration of automation, data analytics, and IoT to optimize operations.
MES improves efficiency and ensures high-quality production by allowing for greater resource utilization and reducing downtime, making it an essential tool for modern Singapore manufacturing.
This article focuses on recommending the best 12 Manufacturing Execution System (MES) options available in Singapore. It includes information on their features, benefits, and appropriateness for various sectors.
Whether companies want improved traceability, real-time monitoring, or increased production efficiency, these MES solutions provide sophisticated features to suit changing manufacturing requirements. Learn more here!
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is software that tracks and manages production, improving efficiency, quality, and decision-making.
- Benefits of implementing MES include better productivity, quality control, real-time data access, and regulatory compliance.
- Recommendation manufacturing execution system (MES) solutions in Singapore include ScaleOcean, Oracle, Infor, Epicor, and SAP for scalable, real-time solutions.
- Consider choosing MES software like industry needs, system compatibility, scalability, and vendor support to choose the right MES for optimal efficiency.
- ScaleOcean MES is the best choice it seamlessly integrates with ERP and IoT, enhancing tracking, quality control, and compliance. Request a demo now to get this solution.

What is Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)?
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is software that monitors, tracks, records, and manages the manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished products. It helps improve efficiency by tracking materials, machine performance, and productivity, making it easier to maintain product quality and costs.
MES serves as an interface between Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and shop floor operations, guaranteeing consistent data flow and improved decision-making. By integrating automation, IoT, and analytics, MES improves traceability, minimizes downtime, and raises product quality.
This technology helps manufacturers meet Industry 5.0 requirements and keep pace with manufacturing trends, which is critical for enterprises looking to streamline operations and maintain a competitive edge in Singapore’s modern manufacturing scene.
Benefits of Implementing Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are essential in modern factories because they optimize output, improve quality, and enable real-time monitoring. Implementing MES increases productivity, minimizes waste, and allows for seamless integration between planning and execution. Here are the benefits:
1. Enhanced Production Efficiency
MES automated workflows minimize downtime and optimize resource allocation to maximize production output. It simplifies operations, enables predictive maintenance, and prevents breakdowns.
For mass production industries, MES standardizes processes, minimizes waste, and boosts manufacturing speed, ensuring competitiveness in Singapore’s fast-paced industry.
2. Improved Quality Control
A reliable MES improves quality control by monitoring production parameters in real-time and assuring compliance with industry standards. By integrating product lifecycle management, it detects defects earlier, reduces rework, and maintains product consistency across all stages.
Manufacturers can avoid costly errors and maintain Singapore’s reputation for high-quality manufacturing standards by utilizing automated inspections and data-driven insights.
3. Real-Time Data Access and Decision-Making
MES provides instant visibility into production metrics, allowing managers to make data-driven decisions. With real-time analytics, businesses can respond quickly to operational issues, optimize production schedules, and minimize waste.
This ability to adapt is critical in Singapore’s dynamic manufacturing landscape, where precision and adaptability are required to maintain efficiency and competitiveness.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Traceability
Singaporean manufacturers must adhere to strict industry regulations. MES provides complete traceability by keeping detailed records of materials, processes, and quality checks.
By integrating material requirement planning, manufacturers can ensure that production efficiency is optimized. It simplifies audits, reduces compliance risks, and supports sustainability initiatives by tracking energy consumption and waste management, helping businesses meet regulatory requirements more efficiently.
5. Seamless Integration with ERP and IoT
MES integrates with manufacturing ERP solutions Singapore and Internet of Things (IoT) systems to create a fully integrated smart factory, enabling seamless data flow and enhanced operational efficiency across production processes.
It synchronizes data between business operations and the shop floor, allowing for real-time synchronization of inventory, production schedules, and supply chain activities. This integration improves agility and enables long-term scalability.
Key Features of Manufacturing Execution System (MES)
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is critical for managing and optimizing the production process on the shop floor. It serves as a bridge between enterprise-level systems and the production process, ensuring real-time visibility, coordination, and control of manufacturing operations.
Below are key features that MES software offers to streamline production and enhance efficiency.
1. Resource Allocation and Status
MES systems provide real-time data on the availability and status of resources, such as equipment, materials, and labor. This ensures that the production process can be managed efficiently, with optimal use of resources, minimizing downtime, and addressing resource constraints proactively.
2. Production/Operations Scheduling
With MES, companies can automate and optimize scheduling processes. It ensures that production runs smoothly by determining the most efficient way to allocate tasks, adjusting production plans in real-time, and minimizing delays caused by bottlenecks, while aligning with demand forecasts.
3. Dispatching Production Units
This feature involves the allocation of work orders to production units, ensuring the right tasks are sent to the right workstations or machines. MES facilitates the coordination of tasks, ensuring that production flows in a timely manner and that any changes to order statuses are updated immediately.
4. Work Order Management
MES enables efficient management of work orders by tracking their progress through each stage of production. It ensures that work orders are assigned correctly, all required resources are available, and timely completion is achieved, which directly impacts production performance and order fulfillment.
5. Machine and Equipment Integration
Integrating machines and equipment with MES ensures seamless data exchange. The system monitors machine performance, tracks production cycles, and identifies any issues that could lead to downtime, ensuring maintenance and repairs are performed proactively to avoid disruptions.
6. Material and Inventory Management
MES provides real-time visibility into material usage and inventory levels, helping businesses reduce stockouts and excess inventory. It ensures materials are available as needed, enabling efficient material handling, reducing waste, and improving overall supply chain visibility.
7. Labour Management
With MES, companies can track and optimize labor productivity. It provides detailed insights into employee performance, work allocation, and labor costs, helping managers improve workforce efficiency, ensure regulatory compliance, and reduce operational costs.
8. Product Tracking and Genealogy
Product tracking and genealogy enable the traceability of every product throughout the production cycle. MES records key data, including batch numbers, timestamps, and machine settings, providing a detailed history of each product’s journey, which is essential for quality control and regulatory compliance.
9. Integration with Higher-Level Systems
MES integrates with higher-level systems like ERP and SCM to ensure data consistency across the enterprise. This integration allows for better coordination between production, inventory management, procurement, and order fulfillment, improving overall business efficiency and decision-making.
Best 12 Manufacturing Execution System Solution in Singapore
Choosing the right Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is critical to optimizing production efficiency and compliance. You can consider your company’s specific needs and preferences. Here are the best 8 MES solutions in Singapore for 2025, designed to streamline operations and improve traceability.
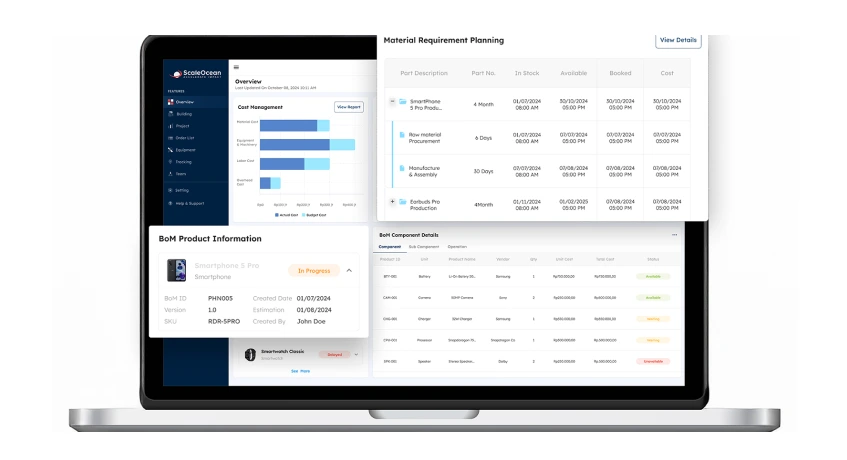
1. ScaleOcean
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing industry, efficiency and compliance are crucial. ScaleOcean MES streamlines production with real-time visibility, automation, and data-driven insights.
Seamlessly integrating with ERP and IoT enhances tracking, quality control, and compliance. AI-powered analytics and automation minimize errors, optimize resources, and improve planning that boosts output while reducing risks.
To help manufacturers make informed decisions, ScaleOcean MES offers free expert consulting, system simulations, and a free demo. Our specialists work closely with you to assess operations, identify inefficiencies, and deliver tailored solutions at no cost.
Through hands-on demonstrations and real-world simulations, you can experience firsthand how ScaleOcean MES enhances efficiency and compliance in your production processes. Beyond improving efficiency and compliance, ScaleOcean MES delivers scalability, flexibility, and seamless integration.
It provides secure access from anywhere, while the modular design adapts to evolving business needs. By reducing manual data entry, enhancing traceability, and enabling predictive maintenance, it empowers manufacturers to boost profitability, maintain product quality, and future-proof operations with ease.
Key Features:
- Real-Time Production Monitoring: Tracks production status, machine performance, and work orders in real-time, ensuring immediate insights and fast decision-making.
- Automated Compliance Management: Digitally enforces quality and safety regulations, reducing audit risks and ensuring full compliance with industry standards.
- AI-Driven Predictive Analytics: Analyzes production data to forecast issues, optimize workflows, and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Seamless ERP & IoT Integration: Connects with existing enterprise systems and smart devices for a unified, automated production process.
- Cloud-Based & Mobile Accessibility: Provides secure, real-time access to production data from any location, ensuring flexibility and remote monitoring capabilities.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
2. Siemens Opcenter
Siemens Manufacturing Execution System (MES), part of the Siemens Opcenter suite, is an enterprise-level solution that uses automation, real-time data, and analytics to maximize production operations.
Manufacturers can use it to monitor production processes, uphold quality standards, and increase operational effectiveness. With deep IoT integration, AI-powered insights, and seamless connectivity with PLM, ERP, and automation systems, Siemens MES supports smart, data-driven manufacturing at scale.
Key Features
- Seamless integration with PLM, ERP, and IoT
- AI-powered predictive quality and maintenance
- Advanced automation and workflow optimization
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
3. Plex Smart Manufacturing Platform
The Plex Smart Manufacturing Platform is a cloud-based platform that integrates MES, ERP, QMS, and SCM functions for manufacturers. It allows businesses to monitor production in real-time, align shop-floor activities with corporate systems, and enhance operational visibility and control.
Key Features:
- Finite production scheduling to allocate tasks based on work-center availability.
- Closed-loop quality management with inline controls, traceability, and statistical process control (SPC).
- Real-time inventory management and end-to-end traceability from receiving to shipping.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
4. AVEVA
AVEVA MES is a modular and scalable system designed to help businesses monitor production, inventory, and quality in real-time across single or multiple locations. It synchronizes human and machine activities, tracks material transformation to finished goods, and enables continuous improvement.
Key Features:
- Modular deployment
- Real-time production control
- Quality and compliance management
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
5. Rockwell Automation MES
Rockwell Automation MES is a system that connects automation systems (PLCs, IIoT) with ERP and shop-floor operations. It enables businesses to monitor, control, and optimize production processes in real-time, driving efficiency, visibility, and compliance.
Key Features:
- Real-time production monitoring and control
- IoT/OT integration with ERP
- Analytics & reporting
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
6. Oracle Cloud Manufacturing
Oracle is a cloud-based manufacturing software designed to optimize and automate shop floor operations. It assures smooth coordination between quality control, production, and planning by giving real-time visibility into production processes.
Oracle MES gives manufacturers the tools they need to streamline operations, cut waste, and stay in compliance with industry standards through strong data analytics, IoT integrations, and AI-driven insights.
Key Features
- Real-time production monitoring and analytics
- IoT and AI-powered process automation
- Seamless integration with Oracle Cloud ERP
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
7. Infor MES
Infor MES is a cloud-based solution that offers analytics, automation, and real-time visibility to maximize manufacturing operations. It connects shop floor activities with enterprise-wide data, helping manufacturers streamline production, enhance quality control, and improve decision-making.
Key Features
- AI-powered production tracking and analytics
- Seamless IoT and smart factory integration
- Real-time quality and compliance monitoring
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
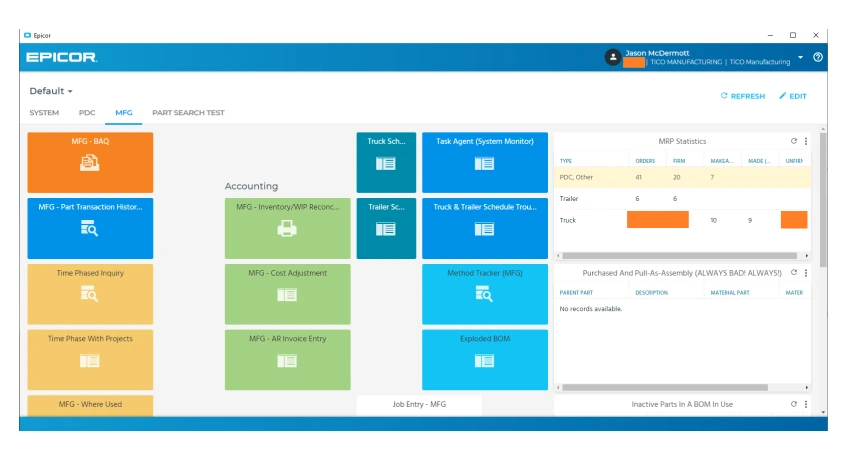
8. Kinetic
Kinetic MES by Epicor is a cloud-based Manufacturing Execution System designed to create automation, AI-driven insights, and real-time data to optimize shop floor operations.
Smooth communication between machinery, workers, and enterprise systems helps manufacturers in monitoring production, enhancing efficiency, and improving quality control.
Key Features
- Real-time production tracking and analytics
- Cloud-based architecture with mobile access
- Seamless integration with Epicor ERP
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
9. SAP
SAP Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a cloud-enabled solution designed to optimize manufacturing operations by providing real-time production insights, automation, and digital connectivity.
Its smooth integration with S/4HANA and SAP ERP enables manufacturers to monitor production performance, implement quality control, and improve process effectiveness. SAP MES facilitates data-driven and agile manufacturing through IoT integration, AI-driven analytics, and smart factory manufacturing features.
Key Features
- IoT and AI-powered process automation
- Advanced quality management and compliance tools
- Smart factory capabilities for Industry 4.0
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
10. MasterControl
MasterControl Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a cloud-based, paperless production solution that supports efficiency, compliance, and traceability in highly regulated sectors like pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and biotechnology.
It reduces errors and boosts operational efficiency by digitizing batch records, automating quality control, and guaranteeing real-time production visibility. MasterControl MES ensures compliance with FDA, ISO, and GMP standards while maintaining high product quality through integrated compliance management.
Key Features
- Automated compliance with FDA, GMP, and ISO
- Seamless integration with ERP and QMS
- AI-powered quality control and process automation
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
11. Tulip
Tulip MES software is a no-code/low-code cloud-based platform designed to streamline shop floor operations. Unlike traditional MES solutions, Tulip offers a highly flexible and user-friendly interface that allows manufacturers to create custom applications for real-time production tracking, quality control, and workflow automation.
Key Features
- No-code/low-code app-building for customization
- Cloud-native with real-time production tracking
- Seamless IoT and sensor integrations
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
12. BacthMaster
BatchMaster is a software platform built specifically for formula and batch‑based manufacturers. It enables businesses to manage production scheduling, formulation, inventory, quality, and compliance in real‑time, aligning manufacturing operations with business systems.
Key Features:
- Recipe/formulation management and batch production control
- Lot traceability, quality control, and regulatory compliance modules.
- Mobile warehousing and inventory management to support plant floor operations.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Mobile and warehousing functionality adds support for plant‑floor operations, improving real‑time visibility. Strong compliance, traceability, and quality‑control features aid regulated industries. | Total cost of ownership may be high for smaller manufacturers with limited IT budget and resources. User training and change management can be demanding |

Future Trends in Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
As manufacturing industries continue to evolve, MES systems are adapting to new technological advancements. These trends are shaping the future of production management, offering businesses more advanced, flexible, and efficient solutions to meet the demands of the modern manufacturing landscape.
Below are some of the key future trends in MES that are driving innovation, including:
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
The future of MES will integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to shift from reactive monitoring to proactive decision-making. AI algorithms will process vast real-time data to enable predictive maintenance, predicting equipment failures before they lead to downtime.
Additionally, they will dynamically adjust production schedules and quality parameters, working toward fully autonomous, self-optimizing operations.
2. Cloud & Edge Computing Architecture
MES is moving towards Cloud and MES as a Service (MESaaS) models, enhancing scalability and lowering the total cost of ownership (TCO).
Combined with Edge Computing, which handles high-frequency IIoT sensor data on the shop floor, this setup ensures ultra-low latency and uninterrupted production, even during temporary cloud outages.
3. Deep Vertical and Horizontal Integration
MES is breaking down traditional silos by enabling deep vertical integration with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and seamless horizontal integration across the supply chain.
Its data powers the Digital Twin, a virtual model of the production process used to test and validate changes, layouts, and improvements before they are physically applied. This closed-loop system is crucial for agility, traceability, and mass customization.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an MES
Choosing the right Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is essential for improving production efficiency and keeping operations running smoothly. You can consider factors like industry requirements, system compatibility, scalability, and vendor support to ensure the MES meets its long-term goals.
Here are the factors that businesses can consider to choose the best manufacturing execution system, including:
1. Industry and Specific Process
Different industries have unique manufacturing needs, from regulatory compliance in pharmaceuticals to real-time monitoring in electronics.
An MES that supports industry-specific workflows and integrates material requirement planning ensures smooth operations by optimizing inventory and production. Singapore manufacturers must choose a system that meets sector regulations and operational demands for maximum efficiency.
2. Company Size
The right MES solution depends on the scale of your business. Small enterprises may benefit from solutions that are simpler and cost-effective. Medium and larger enterprises with complex needs may opt for scalable systems like ScaleOcean, which can grow alongside their operations.
3. Integration Capabilities with Existing Systems
A well-integrated MES should seamlessly connect with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), IoT devices, and other manufacturing systems. This supports real-time data exchange, reduces manual data entry, and improves decision-making.
Singaporean manufacturers should prioritize MES solutions that have robust API capabilities and are compatible with existing digital infrastructure to ensure smoother transitions and optimized workflows.
4. Cloud vs. On-Premises
Consider whether a cloud-based solution (SaaS) or an on-premises system suits your needs. Cloud solutions offer flexibility, lower upfront costs, and easier updates, while on-premises solutions offer more control over data security and customization, though they typically come with higher maintenance.
However, if you need both types, which is a hybrid MES, you can use Scaleocean as your choice. Understanding the types of manufacturing is crucial, and Scaleocean provides customization to tailor the system to your business needs, including cloud, on-premises, and hybrid.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Manufacturing demands evolve with business growth, requiring an MES that adapts to increasing production volumes and new technologies.
Scalable MES solutions support expanding operations, while flexible configurations enable businesses to tailor features to specific workflows. Singaporean manufacturers should invest in future-proof systems that can expand without requiring costly upgrades.
6. Vendor Support and Training
Reliable vendor support is essential for an effective MES deployment and ongoing maintenance. Businesses should choose providers who offer comprehensive training, technical support, and regular software updates.
Localized support in Singapore ensures quick resolution of issues, reducing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency while equipping teams with the necessary skills to optimize the system.
7. Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
MES deployment demands a large investment, making cost-effectiveness is important. Businesses must include licensing fees, customization charges, and long-term maintenance expenses when calculating possible ROI.
A well-chosen MES boosts productivity, lowers waste, and improves overall efficiency, guaranteeing that Singapore manufacturers reap significant financial and operational benefits in the long term.
Case Study of Successful MES Implementations in Singapore
Manufacturers in Singapore are increasingly implementing Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) to improve quality and real-time monitoring. Successful MES implementations show how companies can improve business operations by nearly 85% across the board. You can understand the following case.
For instance, a mid-sized manufacturing company in Singapore struggled with inefficient workflows, manual tracking, and inconsistent reporting. These issues led to production delays and difficulties in meeting customer demands.
To address these challenges, the company implemented a Manufacturing Execution System (MES). The system is integrated with ERP, shop floor equipment, and Singapore manufacturing cost estimating tools, enabling real-time data collection, automated work order tracking, and improved scheduling.
The deployment involved system selection, IoT integration, employee training, and a phased rollout. Change management ensured a smooth transition. Automated inspections boosted productivity by 20% and reduced quality issues by 30%.
Real-time dashboards improved decision-making and compliance. With MES, the company optimized operations, reduced inefficiencies, and strengthened its market position in Singapore.
Conclusion
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) have become essential for Singaporean manufacturers looking to boost efficiency, quality, and compliance. MES improves overall operational performance by integrating real-time monitoring, automation, and data-driven decision-making into production workflows.
When selecting the right MES solution, businesses must carefully consider industry requirements, integration capabilities, scalability, and vendor support. For manufacturers in Singapore seeking a scalable, flexible, and integrated MES solution, ScaleOcean offers a robust platform that aligns with Industry 4.0 standards.
With its comprehensive features and seamless ERP connectivity, ScaleOcean MES software empowers businesses to enhance productivity, maintain regulatory compliance, and drive long-term growth in an increasingly competitive manufacturing landscape.
FAQ:
1. What is the difference between ERP and MES?
An ERP system integrates various business functions across an organization, improving data flow between departments. MES, however, focuses on enhancing operational efficiency on the shop floor by integrating directly with equipment and production processes to optimize manufacturing operations and product quality.
2. What does MES do in Manufacturing?
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a software solution that enhances the manufacturing process by monitoring, tracking, documenting, and controlling production from start to finish. It ensures efficient resource management, quality control, and real-time visibility, optimizing the entire production lifecycle for improved operational performance.
3. What is the Main Goal of MES?
The primary goal of an MES is to track and document the transformation of raw materials into finished products in real-time. By capturing data from machines, sensors, and operators it provides accurate insights into production activities, ensuring efficient processes, high-quality output, and improved overall performance in manufacturing.
4. Which Industries use MES?
MES is widely adopted in regulated industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, medical devices, aeronautics, aerospace, defense, and biotechnology. These sectors benefit from MES by ensuring compliance, improving production efficiency, and maintaining high product quality standards through real-time monitoring and control.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















