Material Requirement Planning (MRP) allows manufacturers to synchronize inventory management, supplier deliveries, and production schedules for maximum efficiency. By analyzing lead times, stock levels, and demand forecasts, MRP ensures materials arrive exactly when needed.
According to IMDA in Singapore, 72.4% of SMEs have adopted digital resource management solutions, including MRP systems, as part of their ongoing digitalization efforts. This flexible framework supports businesses to handle complex supply chains more effectively, adapt to changing production demands, and make data-driven decisions that boost profitability.
By integrating MRP into their operations, companies can better meet market expectations and thrive in competitive environments. MRP is useful for both large enterprises and smaller companies, as it streamlines the entire supply chain, from raw materials to finished products.
Its adaptable design continuously responds to shifting production requirements, ensuring processes remain efficient and outcomes consistently improve. So, this article gonna explores MRP’s critical function in modern manufacturing, defining its purpose, highlighting its key benefits, and illustrating how it supports better decision-making for optimized profitability.
- Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a software-based system that optimizes inventory management, supply management, and production processes.
- To incorporate MRP into manufacturing operations involves forecasting material demand, distributing inventory efficiently, planning production schedules, and tracking progress.
- Key benefits of MRP include improved inventory control, efficient production scheduling, cost reduction, enhanced collaboration, accurate demand forecasting, and higher customer satisfaction.
- ScaleOcean MRP Software is an effective system for Singaporean manufacturing businesses looking to improve resource management and production scheduling.

What is Material Requirement Planning (MRP)?
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a software-based system that optimizes inventory management, supply management, and production processes. By analyzing production schedules, demand forecasts, and inventory levels, MRP ensures materials are available when needed while avoiding overstock.
This software enables businesses to streamline operations, reduce waste, and meet customer demands more efficiently. Manufacturing process planning helps facilitate better decision-making through real-time data and accurate forecasting, thereby improving supply chain management.
It is critical for industries seeking to increase productivity and ensure optimal resource allocation in manufacturing processes.
History of MRP
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) first emerged in the 1960s, when manufacturers sought ways to manage production and inventory levels. Building upon the success of Toyota’s lean manufacturing principles, Joseph Orlicky developed the first MRP concepts, publishing his influential book, “Material Requirement Planning,” in 1975.
Early computer systems at that time supported companies in calculating precise material needs and scheduling production runs more efficiently. Over the decades, MRP evolved into MRP II, which integrated additional business processes.
Today, MRP remains an essential component in modern global manufacturing, enabling businesses to reduce waste, optimize resources, and respond swiftly to changing market demands and increased competition worldwide.
How to Incorporate MRP into Manufacturing Operations?
Incorporating Material Requirements Planning (MRP) into manufacturing operations is key to running things more smoothly. It helps businesses plan better by predicting material needs, managing inventory, and scheduling production more effectively, minimizing waste and delays.
Here’s how you can make MRP work in your operations:
- Forecasts material demand and requirements: MRP uses data to predict what materials will be needed and when. By doing so, it ensures you’re not left with too much stock or scrambling to find materials at the last minute. This contributes to operational production efficiency by keeping your supply chain steady and your operations running smoothly.
- Distributes material inventory accordingly: With accurate forecasts, MRP assigns materials to the right spots in your production process. This makes sure everything flows as it should, preventing bottlenecks and keeping each part of the production process on track without delays.
- Plans and schedules production timelines: MRP sets up a clear production schedule based on what’s needed and when. This helps you stay organized, ensuring products are made on time, and customers get what they need, all while keeping your factory running efficiently. It also helps manage the entire product lifecycle, from raw materials to final delivery.
- Tracks and oversees the production process: MRP helps monitor how things are going during production. It gives real-time updates on inventory and progress, making it easier to spot any issues and make adjustments quickly, so everything stays on schedule and runs smoothly.
Pros and Cons of Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a powerful tool used to optimize manufacturing processes by ensuring the right materials are available at the right time. While it offers significant benefits in terms of efficiency and inventory management, it also comes with challenges, especially during implementation.
Here is a table outlining the key pros and cons of using MRP in manufacturing:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Benefits of MRP
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) remains an essential resource for modern manufacturers. By synchronizing material requirements with production timelines, MRP helps optimize inventory, streamline processes, and lower costs, all of which improve operational performance.
Below are the core advantages of integrating an MRP system into your manufacturing operations:
1. Improved Inventory Control
MRP helps manufacturers maintain balanced stock levels by calculating precisely how much material is required at each stage of production. By preventing excess inventory and shortages, it increases efficiency and reduces storage expenses. Real-time tracking also ensures seamless inventory flow for consistent, uninterrupted production schedules.
2. Efficient Production Scheduling
With detailed data on material availability and production capacity, MRP creates optimized work schedules. By avoiding bottlenecks and minimizing idle time, this strategic planning improves output reliability.
3. Cost Reduction
MRP effectively manages costs by predicting the exact quantity of materials needed, decreasing the likelihood of emergency purchases or overstocking.
This demand-driven approach, such as make-to-order methods, cuts waste, lowers storage fees, and optimizes resource utilization. Ultimately, businesses can save on operating expenses and boost overall profitability.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
Centralizing production and inventory data improves communication across procurement, sales, and production teams. This unified platform eliminates data silos, enables real-time updates, and enhances production capacity. MRP streamlines workflows, aligns departments, and drives operational efficiency.
5. Accurate Demand Forecasting
To forecast customer demand, MRP’s analytics tools use current orders and historical trends. By implementing a takt time approach, businesses can better align production schedules and prevent stockouts. This helps reduce uncertainty, optimize resources, and improve customer satisfaction.
6. Higher Customer Satisfaction
By reliably delivering products on time and in the correct quantities, MRP helps businesses meet or exceed customer expectations. Higher customer satisfaction is one of the benefits of good manufacturing practices, as predictable lead times reduce delays and improve service quality.
By incorporating MRP into manufacturing processes, businesses can ensure timely deliveries and meet customer demands with precision. ScaleOcean’s manufacturing software enhances this by providing real-time insights and seamless integration, allowing for better control over production schedules and customer satisfaction.

Disadvantages of Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
While Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a popular method for increasing production efficiency, it also has significant downsides. These errors, however, can promote progress if tackled effectively, changing obstacles into opportunities for ongoing improvement. The following are a few downsides of MRP that can eventually lead to unanticipated benefits.
1. Implementation Complexity
MRP often requires careful setup and specialized training, which can be challenging for teams unaccustomed to advanced planning software.
However, the rigorous implementation process encourages businesses to refine existing processes and develop stronger cross-departmental collaboration, ultimately fostering a more disciplined and truly adaptive manufacturing environment.
2. High Initial Costs
Adopting MRP systems can demand significant financial investment in hardware, software, and staff training. Yet, this upfront commitment compels organizations to carefully assess operations, leading to strategic resource allocation and improved process efficiencies.
Over time, these refinements can deliver substantial cost savings and competitive advantages.
3. Dependency on Accurate Data
MRP calculations rely heavily on precise, up-to-date information, which can be difficult to maintain across multiple departments and systems.
However, this dependency encourages businesses to implement strong data management processes, standardize record-keeping, and increase cooperation, ultimately improving operational visibility, lowering errors, and driving improved decision-making.
4. Over-Reliance on Forecasting
Demand forecasts are prone to inaccuracies, and unexpected market shifts or supplier disruptions can render MRP schedules less effective.
Nevertheless, this shortcoming encourages continuous review and refinement of forecasting models, integrating real-time updates, and fostering flexible production strategies that adapt swiftly to change, increasing resilience.
5. Possible System Overhaul
Implementing MRP may include reevaluating existing software design and replacing outdated systems, which might cause disruptions in everyday operations.
However, this change frequently results in a modernized mass production system that better supports future growth, enhances process transparency, and integrates all departments with common goals, ultimately increasing overall organizational agility.
Why is MRP important?
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) plays an important role in modern businesses by optimizing production planning and resource allocation.
By accurately forecasting material requirements and aligning these needs with production schedules, businesses can effectively reduce inventory costs, minimize lead times, boost customer satisfaction, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
MRP accomplishes this by analyzing demand forecasts, monitoring real-time inventory levels, and adjusting production plans to match changing requirements.
As a result, businesses can make smarter decisions about what to produce, when to produce it, and in what quantities, ultimately achieving substantial cost savings and improving their competitiveness in the market.
How Does MRP Work?
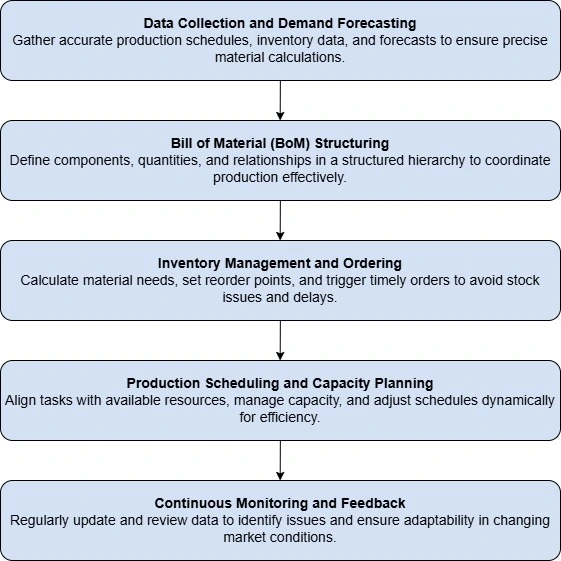
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) improves manufacturing efficiency by ensuring the right materials are available at the right time. Below are the essential steps illustrating how MRP functions for optimal production outcomes:
1. Data Collection and Demand Forecasting
MRP starts with gathering accurate information about production schedules, current inventory, and demand forecasts. Companies analyze sales data, seasonal trends, and customer orders to determine the exact amount of raw materials needed.
Reliable forecasting ensures that MRP calculations are accurate, reducing the risk of inventory shortages and costly overstock situations.
2. Bill of Materials (BOM) Structuring
The Bill of Materials outlines each component and subassembly used in manufacturing a product. By detailing required quantities, specifications, and relationships among parts, MRP systems establish a clear hierarchy for production.
This structured approach enables accurate calculations, allowing businesses to coordinate procurement, production timelines, and resource allocation seamlessly. Additionally, a well-structured bill of materials invoice ensures that the correct materials are billed accurately, supporting smoother financial tracking and cost management.
3. Inventory Management and Ordering
Based on BOM details and forecasts, MRP calculates material requirements and reorder points. When stock levels approach predefined thresholds, automated alerts prompt timely orders.
This continuous monitoring prevents disruptions by ensuring that components arrive at the correct time, lowering holding costs, and avoiding both excess inventory and unexpected production delays or shortages.
4. Production Scheduling and Capacity Planning
MRP aligns production tasks with available resources, analyzing capacity limits and machine availability alongside personnel availability. It schedules work orders in logical sequences, considering lead times and overlapping tasks to maximize efficiency.
This data-driven method helps managers identify bottlenecks, balance workloads, and quickly adjust plans if demand fluctuations or sudden supply issues arise.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
Finally, MRP benefits from continuous review. As production data changes, the system updates schedules and order quantities to ensure accuracy. Regular audits uncover issues like forecast deviations or material defects, prompting corrections. This feedback loop, including stages of work in progress, encourages improvement and adaptability.
What are the 3 Primary Outputs of MRP?
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) systems generate valuable outputs through their calculations and analysis of input data. These results provide important insight into effective production planning and execution. The primary types of MRP outputs are:
1. Planned Order Releases
Planned order releases indicate when new manufacturing orders will be released, ensuring that materials and components are available on time. This helps to maintain optimal inventory levels and a smooth production flow, lowering the risk of delays.
They also facilitate better coordination between production planners and suppliers, enhancing just-in-time delivery and minimizing excess stock.
2. Order Release Notices
Order release notifications notify production and procurement teams of the need to release specific orders to the shop floor or suppliers. They ensure that production and procurement activities are completed on time, in accordance with the overall production schedule.
Additionally, they help establish clear priorities, allowing teams to allocate resources efficiently and respond promptly to changing demands.
3. Exception Reports
Exception reports highlight discrepancies or issues in the production plan, such as material shortages or production delays. They provide critical information for managers to identify and address problems promptly, ensuring that production remains on track and any disruptions are minimized.
Moreover, they serve as a valuable tool for continuous improvement by highlighting recurring problems and enabling data-driven decision-making.
What are the Inputs of MRP?
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) relies on various inputs to create effective production plans. These inputs ensure the availability of materials, optimal inventory levels, and efficient production schedules as outlined below.
1. Demand
Accurate demand forecasting is important for balancing production and customer requirements. By analyzing historical sales trends, market conditions, and seasonal fluctuations, companies can predict future product needs more precisely.
This enables them to allocate resources efficiently, reduce waste, and maintain adequate stock levels. Timely adjustments ensure a sustainable competitive advantage.
2. Bill of Materials (BOM)
An organized Bill of Materials clearly identifies each component, subassembly, and raw material required to produce an item. Listing part numbers, quantities, and specifications prevents errors and delays in production.
Detailed BOM data also facilitates ongoing cost estimation, supplier coordination, and consistent product updates, ensuring seamless manufacturing processes.
3. Inventory
Accurate inventory management ensures materials and finished goods are available to meet production and customer needs. By tracking stock levels and turnover rates, businesses can avoid shortages or excess buildup. Understanding the function of cycle time helps improve reorder planning and cash flow.
4. Master Production Schedule
A master production schedule integrates demand, resources, and inventory into a single timeline for producing finished goods. It effectively combines demand forecasts, BOM details, and current stock data to generate a workable plan.
This schedule guides production priorities, optimizes capacity, and ensures on-time delivery while minimizing operational disruptions.
Example of MRP Implementation
Consider a mid-sized electronics manufacturer that produces printed circuit boards (PCBs) as an example of how MRP software works. The company uses the software to track all the components required for each PCB, such as microchips, resistors, and capacitors, while ensuring these materials arrive on time to meet production schedules.
The best manufacturing execution system (MES) operates with real-time data updates, helping the company identify when to reorder materials, avoid overstocking, and adjust production schedules if customer demand changes.
This streamlined approach ensures the necessary materials are always available exactly when needed, reducing inventory costs, minimizing delays, and increasing productivity, all while maintaining high product quality and customer satisfaction.
Improve Capacity Planning Accuracy Using ScaleOcean MRP Software
In manufacturing, proper capacity planning is essential to meet production goals and keep operations running smoothly. ScaleOcean MRP Software is an effective system for Singaporean manufacturing businesses looking to improve resource management and production scheduling.
With advanced tools and real-time data, it helps manufacturers adapt quickly to market changes, offering a free demo to showcase its transformative capabilities. Key Features of ScaleOcean MRP Software:
- Demand Forecasting: Leverage historical data and predictive analytics to anticipate production needs accurately.
- Material Requirement Planning: Automatically calculate material needs based on production schedules and inventory levels.
- Production Scheduling: Optimize workflows by generating efficient, conflict-free production plans.
- Capacity Analysis: Evaluate available capacity against demand to identify bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement.
- Real-Time Reporting: Access live dashboards and reports to monitor key metrics and make informed decisions quickly.
- Supplier Collaboration Tools: Streamline communication with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of materials and components.
By adopting ScaleOcean MRP Software, Singaporean businesses can achieve significant advantages in a highly competitive manufacturing landscape. With its ability to adapt to fluctuating demand and optimize resource utilization, the software supports consistent on-time delivery, reduces operational costs, and minimizes production waste.
Furthermore, its intuitive interface and localized features align with the needs of Singapore’s forward-thinking manufacturers, enabling them to stay ahead in an increasingly dynamic market.
Conclusion
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) emphasizes the connection among demand forecasting, inventory management, and production scheduling to sustain smooth operations. From a simple control concept, MRP has evolved into a robust solution that refines inventory oversight, improves scheduling, and cuts costs.
MRP’s core value remains data-driven decision-making. By reducing waste and boosting collaboration, MRP helps businesses stay competitive in diverse industries.
ScaleOcean MRP Software implements these principles through features such as real-time reporting and predictive analytics, allowing for efficient capacity planning and demand forecasting.
By adopting it, companies adapt quickly to shifting markets, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing production waste. A free demo highlights seamless integration and resolves future production issues. Embracing ScaleOcean fosters sustained efficiency and long-term profitability.
FAQ:
1. What are the two types of MRP?
There are two primary categories of MRP types: one designed for deterministic planning and the other for consumption-based planning. This distinction helps manufacturers decide the best approach depending on their production needs and inventory control methods.
2. What skills are needed to work with MRP?
To excel as an MRP specialist, a strong grasp of supply chain management, inventory control, and production planning is essential. Typically, these skills are backed by a degree in business, engineering, or a related field, ensuring a solid foundation for the role.
3. Is MRP a type of inventory?
MRP systems help businesses track dependencies and determine the required number of products by the dates specified in the master production schedule. It functions as both a control and inventory management system to track and order materials for product manufacturing.
4. What does an MRP planner do?
An MRP planner is responsible for optimizing production schedules by analyzing customer orders, inventory levels, and production capacity. The MRP system ensures production aligns with demand, keeping operations on track and meeting customer expectations efficiently.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















