Navigating Singapore’s competitive business environment demands more than just a great concept. Understanding the statistics is critical, and financial metrics provide insights into your company’s true health. These measurements are essential for better decision-making.
Understanding financial indicators is required to navigate Singapore’s corporate environment and make informed judgments. The MAS Annual Report FY 2024/2025 addresses financial sector growth, digital resilience, artificial intelligence, sustainability, and anti-scam efforts, providing useful business insights.
This article provides key financial metrics and KPIs to help you evaluate profitability, liquidity, and efficiency. It discusses how to apply these measures in strategic planning. Understanding these concepts is critical for any business leader who wants to make informed decisions and achieve long-term success.
- Financial Metrics and KPIs track a company’s performance, offering insights into strengths and weaknesses to maintain financial health and meet goals.
- Key Financial Metrics and KPIs cover Gross Profit Margin, Net Profit Margin, Operating Cash Flow Ratio, and more, providing a measuring view of the business’s performance.
- Using Financial Metrics Effectively means selecting the right KPIs, setting tracking systems, and interpreting data to make informed, strategic decisions.
- ScaleOcean accounting software automates real-time tracking of key financial metrics, ensuring accurate data for decision-making and improving financial reporting efficiency.

What are Financial Metrics and KPIs?
Financial metrics are quantitative measures that track a company’s performance and health, offering insights into strengths and areas for improvement. Understanding financial metrics helps in making informed decisions.
KPIs, on the other hand, are key metrics that reflect a company’s financial and operational health. These indicators focus on important business data, such as revenue growth, profit margins, or customer acquisition costs, to track progress and help companies align with their strategic goals.
What Are Financial Key Performance Indicators (KPI)?
Financial KPIs are key metrics used to measure profits, revenue, expenses, and other financial results, focusing on the relationships derived from accounting data. These indicators are typically linked to a specific financial value or ratio to assess performance.
Most KPIs are grouped into five main categories based on the data they measure:
1. Profitability Metrics
Profitability metrics assess a company’s ability to generate profit relative to its revenue, assets, or equity. Common indicators include gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, which show how well a company controls its costs and expenses.
These metrics are crucial for understanding how efficiently a business is converting sales into actual profits. A higher profitability ratio generally reflects effective management, stronger market positioning, and the ability to withstand financial challenges.
2. Liquidity Metrics
Liquidity metrics measure a company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations using its liquid assets. The current ratio and quick ratio are common liquidity indicators, showing how easily a company can cover its debts with available assets.
Maintaining strong liquidity is vital for business operations, as it ensures the company can handle unexpected expenses and continue day-to-day activities without financial disruption. Poor liquidity can signal potential cash flow problems or financial instability.
3. Efficiency Metrics
Efficiency metrics help businesses assess how well they utilize their assets and resources to generate revenue. Common efficiency indicators include asset turnover and inventory turnover, which measure how effectively the company uses its assets and inventory to generate sales.
These metrics are essential for identifying operational improvements and ensuring resources are not wasted. High efficiency leads to reduced costs, increased productivity, and better overall performance, all of which enhance the company’s profitability.
4. Valuation Metrics
Valuation metrics are used to determine a company’s market value relative to its financial performance. Key indicators such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio and price-to-book (P/B) ratio provide insights into whether a company is undervalued or overvalued in the market.
These metrics help investors assess whether a company’s stock is fairly priced, based on its earnings and assets. Accurate valuation allows investors to make informed decisions, aligning with market expectations and the company’s growth potential.
5. Leverage Metrics
Leverage metrics evaluate the extent to which a company uses borrowed funds to finance its operations. Ratios like the debt-to-equity ratio and debt-to-assets ratio assess the company’s financial risk and reliance on debt for growth.
While leverage can boost returns, high leverage also increases the company’s exposure to risk, particularly in economic downturns. Proper management of leverage ensures a company can sustain operations without jeopardizing financial stability.
Why These Metrics are Crucial for Singaporean Businesses
In Singapore’s changing market, having a fantastic product is insufficient for success. Businesses must be agile, which requires an awareness of crucial financial measures. These indicators provide the data required for effective financial management process, which is vital to success in this situation.
Financial performance metrics must be tracked by any Singapore-based business. It enables educated decision-making, assures compliance with local legislation, and promotes long-term sustainability. This technique is not only advantageous. It is a necessity for serious business owners.
1. Make Data-Driven Strategic Decisions
Metrics convert abstract business feelings into solid facts, assisting in the identification of trends, inefficiencies, and growth prospects through data analysis. This facilitates strategic decision-making by eliminating guesswork and enabling more specific, actionable choices for your company.
Consistently measuring financial metrics results in proactive management. It aids in forecasting future performance, allocating resources efficiently, and setting achievable goals. This strategy creates a resilient business capable of thriving in Singapore’s competitive market.
2. Secure Funding from Investors or Banks
When requesting capital from investors or banks, you must show precise, data-driven financial metrics. These figures demonstrate your company’s success and development potential, making them critical in convincing investors that your business is a good investment.
To ensure compliance with local regulations, businesses should align their financial reporting with Singapore financial accounting standards, ensuring transparency and accuracy in all financial statements.
A good financial track record increases confidence and trust among potential funders. Understanding crucial financial data demonstrates your ability to lead effectively. This instills investor trust in your potential to deliver returns, which is their ultimate objective.
3. Monitor Financial Health in a High-Cost Environment
Financial measurements are critical for enterprises in Singapore due to the high operational costs. Metrics such as cash flow, profitability, and debt levels serve as early warning systems, allowing businesses to stay on top of their financial health in a pricey market.
Companies can use a robust financial and accounting ERP system to help centralise these metrics in one integrated platform. Tracking important parameters like burn rate and profit margins enables firms to alter their budgets and strategy.
Proactive monitoring prevents cash flow crises and guarantees long-term financial sustainability, both of which are critical for success in Singapore’s high-cost economy.
4. Ensure Compliance with ACRA (Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority)
Every company in Singapore is required to follow ACRA requirements, which include maintaining correct financial records. Proper recording of financial indicators ensures that your records are well-organized and ready for audits or reviews, which is required for legal compliance.
Accurate data is critical for tax preparation and financial reporting. Consistently monitoring metrics helps you avoid penalties, legal hassles, and stress caused by noncompliance, allowing you to focus on running your business efficiently and without interruptions.
5. Benchmark Performance Against Competitors
Understanding your company’s success is critical, but comparing it to that of your competitors is even more important. Financial metrics enable you to compare your performance to industry averages and competitors, giving vital context for strategic planning and growth.
This comparison identifies strengths and drawbacks, highlighting factors such as profit margins and inventory turnover. Identifying these gaps allows you to create realistic improvement goals, which will drive your company’s performance and competitiveness.
32 Key Financial Metrics and KPIs to Measure Success in 2026
Tracking the right financial metrics and KPIs is key to understanding your business’s performance in 2026. With so many data points, it’s important to focus on the ones that offer the most meaningful insights into your financial health. Using tax software can help streamline the tracking of these metrics, ensuring accurate financial data and reporting.
Here are the key areas to keep an eye on:
1. Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin is the percentage of revenue that remains after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). A higher margin shows greater efficiency in managing production costs, which helps pay other corporate expenses. It is a major indicator of financial wellness. The formula is:
Gross Profit Margin = (Net sales – COGS) / Net sales x 100%
2. Return on Sales (ROS)/Operating Margin
Return on Sales (ROS) reflects how much operating profit a company generates from each dollar of sales after accounting for operating costs. It is calculated by dividing operating income by net sales revenue. ROS indicates a company’s ability to convert revenue into operating profit. The formula is:
Return on sales = (EBIT / Net sales) × 100%
3. Net Profit Margin
Net profit margin is the proportion of income remaining after all expenses, including taxes and interest, have been removed. A greater margin suggests that costs and expenses are well under control while profit is generated, indicating effective management. Here is the formula:
Net profit margin = (Net income / Revenue) × 100%
4. Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE assesses how effectively a company leverages shareholder equity to produce profits. A greater ROE shows that investment capital was effectively used, resulting in excellent returns and efficient business management. It reflects how effectively equity contributes to business growth. Here is the formula:
Return on Equity = Net Income / Shareholder Equity
5. Return on Assets (ROA)
ROA compares profitability to total assets, allowing you to examine how efficiently assets are used to generate earnings. A greater ROA indicates that the company is making better use of its resources and earning more money with fewer assets. Here is the formula:
Return on assets = Net income / Total assets
6. Current Ratio
The current ratio compares a company’s current assets and current liabilities. A ratio greater than 1 shows that the corporation can meet its short-term obligations, indicating financial soundness. It provides a brief overview of the company’s short-term health. Here is the formula:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
7. Quick Ratio (Acid-Test Ratio)
The quick ratio is a stricter measure of liquidity that excludes inventory from assets. It provides a more conservative assessment of a company’s capacity to satisfy short-term obligations. A ratio greater than one indicates that the company is liquid and doesn’t rely on inventories. Here is the formula:
Quick ratio = (Current assets – Inventory) / Current liabilities
8. Operating Cash Flow Ratio
The operating cash flow ratio indicates how successfully a company’s operations can cover current liabilities. A greater ratio indicates that the company can satisfy its obligations without the need for external financing, hence ensuring liquidity. Here is the formula:
Operating Cash Flow Ratio = Operating Cash Flow / Current Liabilities
9. Debt-to-Equity Ratio
This ratio compares a company’s debt to its shareholder equity, reflecting financial leverage. A high ratio suggests a higher risk due to heavy borrowing, while a low ratio indicates more conservative financing with less reliance on debt. Here is the formula:
Debt-to-equity ratio = Total liabilities / Total shareholders’ equity
10. Debt-to-Asset Ratio
The debt-to-asset ratio indicates the percentage of assets financed with debt. A smaller ratio suggests a lesser financial risk and a more stable financial position, whereas a higher ratio indicates a greater reliance on debt to fund assets. Here is the formula:
Debt-to-Asset Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets
11. Interest Coverage Ratio
Interest coverage measures a company’s ability to meet its interest payments on debt using operating profit. A higher ratio indicates the company has a greater ability to service its debt and is less at risk of defaulting on interest payments. Here is the formula:
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expenses
12. Inventory Turnover Ratio
Inventory turnover measures how often a company sells and replenishes its inventory. A higher ratio indicates efficient inventory management and strong sales, while a low ratio suggests excess inventory or slow-moving goods, which could impact cash flow. Here is the formula:
Inventory Turnover Ratio = COGS / Average Inventory
13. Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
The AR turnover ratio measures how often a company collects its average accounts receivable balance over a period. A higher turnover ratio suggests efficient credit management and faster cash collection, improving liquidity and reducing credit risk. Here is the formula:
Accounts receivable turnover = Net credit sales / Average accounts receivable balance
14. Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
Accounts payable turnover ratio shows how quickly a company pays its vendors. A high ratio may indicate good financial health, but an overly high ratio could suggest underuse of supplier credit. Accounts payable automation software can help streamline and optimize this process. Here is the formula:
Accounts payable turnover = Net Credit Purchases / Average AP balance
15. Asset Turnover Ratio
The asset turnover ratio assesses how effectively a corporation uses its assets to produce revenue. A higher ratio demonstrates greater efficiency in using assets to generate income, indicating effective asset utilization and the potential to generate more sales with fewer resources. Here is the formula:
Asset Turnover Ratio = Net Sales / Average Total Assets
16. Sales Growth Rate
Sales growth rate is the percentage increase in sales over time. Consistent sales growth implies a solid business trajectory, demonstrating robust demand and effective marketing, both of which are critical for long-term corporate expansion and investor confidence. Here is the formula:
Sales Growth Rate = (Current Sales – Previous Sales) / Previous Sales x 100
17. Earnings Per Share (EPS)
EPS measures the portion of a company’s profit allocated to each outstanding share of stock. A rising EPS signifies increased profitability and greater value for shareholders, often used to assess a company’s performance and investment attractiveness. Here is the formula:
Earnings per share = Net income / Weighted average shares outstanding
18. Working Capital
Working capital reflects the difference between current assets and current liabilities, showing a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. Low working capital may suggest cash flow problems, while high working capital can indicate inefficiency. The formula is:
Working capital = Current assets – Current liabilities
19. Gross Burn Rate
Burn rate measures how quickly a company is using its available cash to cover operating expenses, particularly useful for startups. A high burn rate means the company will need additional funding soon, while a lower burn rate indicates a longer runway before funding is required. The formula is:
Gross burn rate = Company cash / Monthly operating expenses
20. Average Invoice Processing Cost
This metric tracks the average cost of processing each invoice, including labor, systems, and overhead. Lower processing costs indicate a more efficient accounts payable process, while higher costs suggest inefficiencies or reliance on manual systems.
Companies can adopt the best invoicing software, businesses can streamline the invoicing process, reduce manual errors, and lower overall processing costs, leading to greater efficiency. The formula is:
Average invoice processing cost = Total AP processing costs / Number of invoices processed
21. Selling, General and Administrative (SG&A)
The SG&A ratio calculates the proportion of revenue used to cover selling, general, and administrative expenses. A lower SG&A ratio indicates that the company is managing its operational costs efficiently, leading to better profitability. The formula is:
SG&A ratio = (SG&A expenses) / Net sales revenue
22. Budget Variance
Budget variance compares actual financial performance with the budgeted figures. A positive variance indicates better-than-expected performance, while a negative variance suggests that the company is overspending or underperforming in certain areas. The formula is:
Budget variance = (Actual result – Budgeted amount) / Budgeted amount × 100
23. Budget Creation Cycle Time
This efficiency metric tracks how long it takes to complete the organization’s budget creation process. Shorter cycle times indicate better efficiency in planning and execution, enabling quicker decision-making and resource allocation. The formula is:
Budget creation cycle time = Date budget finalized – Date budgeting activities started
24. Line Items in Budget
The number of line items in a budget represents the level of detail and granularity in financial planning. A higher number of line items reflects a more detailed approach, while fewer line items may indicate a broader view or less specificity.
25. Number of Budget Iterations
This metric measures how often a budget is revised during the creation process. A higher number of iterations can indicate inefficiencies or internal disagreements, leading to delays in finalizing the budget and affecting business planning. The formula is:
Number of budget iterations = Total versions of the budget created
26. Current Accounts Receivable
This ratio indicates how effectively a company is managing its receivables. It’s calculated by comparing unpaid but current sales to total accounts receivable. A higher ratio reflects timely payments, reducing the risk of bad debts and improving cash flow. The formula is:
Current accounts receivable ratio = (Total AR – Past due AR) / Total AR
27. Current Accounts Payable
The AP ratio shows how much of the company’s accounts payable is not yet due. A high ratio indicates that the company is paying its bills on time, while a low ratio might indicate financial strain or slow payments, which could harm supplier relationships. The formula is:
Current accounts payable ratio = (Total AP – Past due AP) / Total AP
28. Payroll Headcount
The payroll headcount ratio measures how many full-time employees are supported by each HR or payroll specialist. This efficiency metric helps assess the productivity of the HR department and its ability to manage a growing workforce. The formula is:
Payroll headcount ratio = HR headcount / Total company headcount
29. Days Sales Outstanding
DSO measures the average number of days a company takes to collect payments from customers. A lower DSO indicates faster collections, which improves cash flow and reduces the risk of overdue payments, benefiting the company’s liquidity. The formula is:
Days’ sales outstanding = 365 days / AR turnover
30. Days Payable Outstanding
DPO shows the average time it takes for a company to pay its suppliers. A higher DPO means the company is taking longer to pay its bills, improving short-term liquidity but potentially affecting supplier relationships. Managing this balance is crucial for financial health. The formula is:
Days payable outstanding = (Accounts payable × 365 days) / COGS
31. Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio measures the price investors are willing to pay for a company’s earnings. A higher P/E indicates that investors expect higher future growth, but it could also suggest overvaluation. A lower P/E may indicate undervaluation or slower growth prospects. The formula is:
Price-to-earnings ratio = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share (EPS)
32. Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The P/B ratio compares a company’s market value to its book value. A ratio above 1 suggests that the market values the company higher than its book value, while a ratio below 1 could mean the stock is undervalued. It helps investors assess if a company is over- or underpriced. The formula is:
Price-to-book ratio = Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share
How to Effectively Use Financial Metrics
Financial metrics, well, just tracking them is only the beginning, isn’t it? The real power, the true value, comes from actually knowing how to put these numbers to work, using them to push your business ahead. Otherwise, honestly, they’re just numbers sitting there, not really doing anything useful.
To truly make a difference, we need to move past just collecting data and actually use it effectively in our business. This means choosing the right KPIs, setting up a reliable tracking system, and understanding the story behind the numbers. This is the point where your data becomes a strategic asset, truly.
1. Selecting the Right KPIs for Your Business Stage and Industry
Not all financial measures are equivalent. Startups concentrate on capital expenditures, but established enterprises value profitability. According to EDB Singapore, the technology sector provides US$450 billion (S$579.4 billion) in opportunities, emphasizing the importance of adjusting KPIs by company stage.
Taking the effort to understand what drives success in your industry is critical. Aligning your financial KPI metrics with these criteria guarantees that resources and attention are directed to the data that has the most impact on your company’s performance and growth.
2. Setting Up a System for Tracking
Using manual spreadsheets to maintain financial data frequently leads to errors and wastes time, particularly as your firm grows. What you truly need is a dependable system for rapidly gathering and organizing financial data to improve accuracy and decision-making.
The best accounting software automates most of the tracking process, ensuring that your data is accurate, up to date, and easy to access. This allows more time to focus on analysis and strategy, making it an essential tool for effective metric tracking and business management.
3. Interpreting the Numbers
Having the data is important, but understanding it is critical. Looking at a single metric yields little knowledge. It is critical to monitor changes over time and compare data to industry standards. For example, a regular reduction in profit margin shows the need for further investigation.
Understanding how measurements connect is essential. While rapid sales growth is desirable, it is less valuable if operational profit margins are decreasing. When appraising future projects, you should take into account elements such as the Net Present Value (NPV).
4. Avoiding Common Pitfalls
One common issue is focusing on “vanity metrics” that appear attractive but may not promote genuine business success, such as high internet traffic without conversions. To ensure effectiveness, focus on a few critical criteria that steer decisions and activities.
Another issue is “analysis paralysis,” which occurs when decision-making is hampered by an overwhelming amount of facts. Ensuring data accuracy is also critical; making judgments based on inaccurate data can be detrimental to your organization. Regularly assessing data collection methods is vital for making informed decisions.
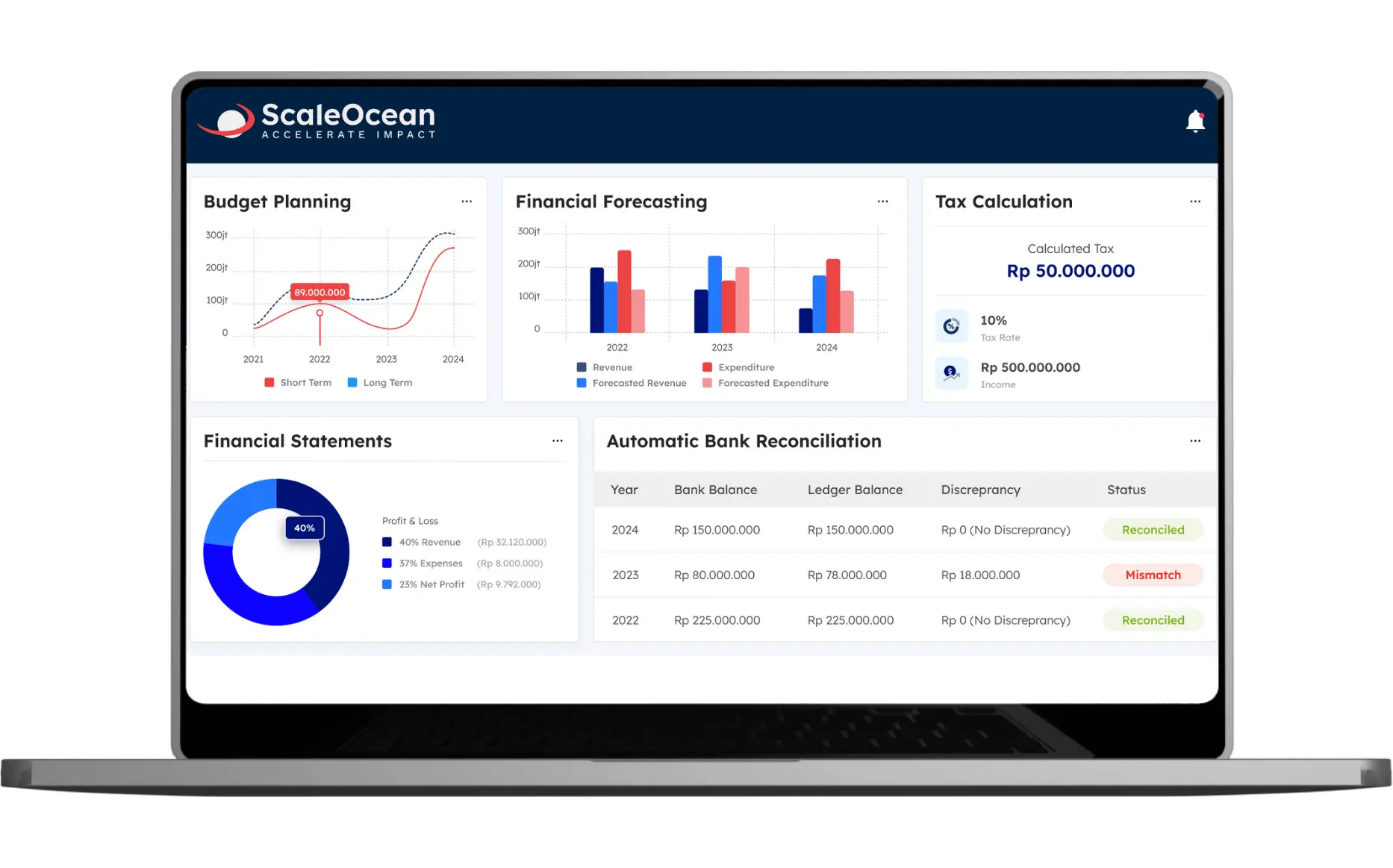
Automate Your Financial Tracking with ScaleOcean’s Accounting Software
ScaleOcean’s accounting software generates and displays critical financial parameters like as profitability, liquidity, and efficiency ratios in real time. This eliminates the need for manual tracking, which is error-prone and time-consuming, allowing you to access trustworthy data at your fingertips.
ScaleOcean automates financial tracking, providing real-time data for ACRA compliance and reporting. Schedule a free demo to explore its features. Here are key features of ScaleOcean’s accounting software to help you track your financial metrics:
- Real-Time Financial Reporting: Provides instant access to key financial metrics for timely decision-making.
- Comprehensive Integration: Seamlessly integrates with other business functions to reduce manual data entry and errors.
- Automated Bank Reconciliation: Automatically matches internal transactions with bank statements for improved accuracy.
- Flexible Reporting: Customizable financial reports to meet specific business needs and ensure compliance.
- End-to-End Financial Workflow: Covers all aspects of financial management, ensuring accurate, real-time data across processes.
Conclusion
Financial indicators are critical for business success in Singapore, providing clarity and insights to assist in navigating problems and exploiting opportunities. They go beyond simple data crunching to tell the story of a company’s financial health and guide future decisions.
Companies need the necessary tools to turn financial tracking into strategic research. ScaleOcean’s accounting software automates financial tracking and analysis, delivering real-time insights and KPIs. This powerful tool enables firms to make more informed decisions and accelerate growth.
FAQ:
1. What is a financial metric?
A financial metric refers to a numerical measure used to evaluate a company’s financial performance and overall health. These metrics are essential for assessing various aspects such as profitability, liquidity, and solvency, and they help guide business decisions.
2. What is the best financial metric?
The most valuable financial metric varies by industry and business objectives. Key metrics commonly used to assess performance include Net Profit Margin, Return on Equity (ROE), and Operating Profit Margin, as they provide insights into a company’s profitability and financial efficiency.
3. What are the five key financial ratios?
The five key financial ratios often include:
1. Gross Profit Margin.
2. Operating Profit Margin.
3. Net Profit Margin.
4. Return on Equity (ROE).
5. Current Ratio.
These ratios are crucial for evaluating a company’s financial stability, profitability, and operational efficiency.
4. What are the financial metrics for KPI?
Common financial metrics used for KPIs include:
1. Revenue Growth.
2. Net Profit Margin.
3. Return on Investment (ROI).
4. Operating Profit Margin.
5. Cash Flow.
These metrics help businesses measure their financial performance and assess how effectively they are reaching their strategic goals.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















