In today’s competitive business world, making quick, informed decisions is crucial for success. How can you ensure your choices lead to the best outcomes without wasting resources? This is where Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) helps—by evaluating the financial and non-financial consequences, ensuring efficient resource allocation and clear decision-making. Similarly, CBA can guide government policy, as seen in Singapore’s government budget, according to Trading Economics, which was -1.6% of GDP in December 2023, a decrease from -0.8% the previous year and a significant improvement from -10.8% in 2020.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, where decisions need to be data-informed and prompt, CBA plays a vital role. It allows businesses to navigate complexities by providing a structured way for evaluating options. By depending on CBA, companies can make well-informed choices that align with both short-term aims and long-term strategic goals.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) is a strategic tool used to evaluate costs against expected benefits, helping organizations make informed decisions and assess whether the benefits outweigh the expenses.
- The CBA process involves defining objectives, identifying costs and benefits, assigning monetary values, performing the analysis, and conducting sensitivity analysis to assess decision impact.
- CBA offers advantages like providing a structured decision-making framework and comparing alternatives but also has limitations, such as difficulties with intangible factors and the need for accurate data.
- ScaleOcean’s accounting software streamlines the CBA process by automating data tracking, simplifying computations, and integrating with financial reports, improving accuracy and efficiency in decision-making.

Understanding Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA)
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) is a process for weighing the entire estimated costs against the anticipated benefits of a choice. This approach assists organizations in determining whether the advantages outweigh the expenses, enabling them to make more informed decisions. By assessing all associated costs and potential gains, CBA provides a clear decision-making framework.
To provide a thorough examination, it is critical to measure both tangible and intangible aspects. Tangible aspects, such as direct costs and revenue, are easy to quantify, whereas intangible factors, like customer satisfaction or employee morale, can be more difficult to estimate. By incorporating both types of data, businesses can achieve a well-rounded evaluation that supports better decision-making and resource allocation.
The CBA Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) approach is critical for making sound business decisions in any context. Businesses can determine the financial viability of their decisions by weighing the costs and rewards. It aids in the establishment of defined objectives, the comprehension of potential consequences, and the implementation of a systematic decision-making process. This guide will take you through the key phases in completing a CBA:
1. Define Objectives and Scope
The first stage in any cost-benefit analysis is to establish defined objectives. What decision needs to be made? What are the precise goals of the analysis? This step also includes establishing the parameters, such as timelines and essential stakeholders, to ensure that all areas of the analysis are addressed.
2. Identify Costs and Benefits
Next, organizations should assess all potential costs and benefits.
These are classified as direct costs (e.g., production expenses), indirect costs (e.g., overhead), operating costs (e.g., daily expenses related to running the business), and opportunity costs (e.g., missed advantages from selecting one option over another).
It’s also important to consider other financial aspects, such as prepaid expenses, which represent payments made in advance for goods or services to be received in the future, helping to better manage cash flow and financial planning.
3. Assign Monetary Values
Allocating a monetary value to each recognized cost and benefit is an important undertaking. Accurate valuation enables organizations to evaluate the true financial impact of their decisions. This process can involve various methods such as market comparison, historical data analysis, or expert judgment, depending on the nature of the costs and benefits being assessed. Ensuring the right approach is used is crucial for obtaining accurate results.
4. Perform the Analysis
After setting values, it is time to conduct the actual analysis. Calculating the net present value (NPV), benefit-cost ratio (BCR), and other related metrics will reveal whether the action is financially feasible.
In addition to these methods, using techniques like standard costing can help in estimating the expected costs of production, which is crucial for comparing actual performance with expected outcomes. The cost-benefit analysis metrics obtained in this step will help you make decisions.
5. Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis enables firms to understand how changes in assumptions or factors may affect the outcomes. By varying key inputs and assumptions, businesses can identify which factors have the most significant impact on their analysis. This approach helps companies assess the robustness of their decisions and prepare for a range of potential scenarios, leading to more informed and adaptable decision-making.
Components of a Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA)
The elements of a Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) offer a thorough breakdown of the aspects needing consideration when assessing a choice. Both costs and advantages are essential to the analysis, and comprehending them ensures that companies can make informed decisions. Following, we present the key components of a CBA that will direct the analysis procedure:
1. Costs
Costs are an important component of any Cost-Benefit Analysis because they provide information about the financial resources needed for a project or decision. Understanding these costs enables firms to determine if the anticipated benefits justify the expenses. In this part, we will break down the various expenses associated in a decision:
a. Direct Costs
These costs are directly related to the manufacturing or development of a product. They cover expenses such as raw materials, labor, and manufacturing costs. For example, according to DOS Singapore, in Singapore’s manufacturing sector, the cost of materials in 2023 amounted to $207,841,284 thousand, which reflects a significant portion of direct expenses in production. These costs are directly traceable to the product, making them an essential component of any cost study.
b. Indirect Costs
Indirect costs, sometimes known as overhead, are expenses that benefit the manufacturing process but cannot be directly traced to a specific product. Examples include rent, utilities, and administrative pay. These expenses must be included in the overall study for an informed financial assessment.
c. Opportunity Costs
Opportunity costs refer to the possible benefits lost by choosing one choice over another. For example, if a company invests in one project, it loses the option to invest in a more profitable project. These expenses should be considered, even if they are not always measurable.
2. Benefits
Grasping the advantages of a decision is a vital part of the Cost-Benefit Analysis process. By assessing both tangible and intangible benefits, companies can better comprehend the real value of their selections. These benefits aid in determining the long-term effect on the company’s expansion and success. Below, we investigate the different kinds of advantages that companies must contemplate:
a. Tangible Benefits
Measurable advantages relate to tangible gains that have a clear financial impact. These can involve boosted revenue, cost control processes, and reductions, or improved operational effectiveness. These gains are easier to quantify and immediately affect the financial standing of the company. Recognizing and maximizing tangible benefits helps businesses assess the return on investment (ROI).
b. Intangible Benefits
Intangible gains, conversely, are non-measurable, though equally important. These include enhancements like improved customer satisfaction, heightened employee morale, and a more robust brand reputation. Although these benefits may not be immediately quantifiable, they contribute to long-term business success and sustainability. Pinpointing these factors ensures that businesses capture their full potential value.
Advantages and Limitations of Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA)
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) presents several benefits, rendering it a useful instrument for businesses. Nevertheless, some constraints must be considered for the analysis to be effective, particularly when evaluating the expense in business and ensuring that costs are accurately accounted for in decision-making. Subsequently, we investigate both the advantages and disadvantages of CBA:
1. Advantages
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) provides several benefits, making it a useful tool for organizations. Nevertheless, there are certain constraints that require consideration for the analysis to be successful. Subsequently, we examine both the advantages and disadvantages of CBA:
a. Structured Decision-Making Framework
CBA provides businesses with a clear and organized method for making decisions. It helps ensure that all important costs and benefits are taken into account before a choice is made. By following a structured approach, companies can make confident decisions that are in their best interest.
b. Identifying and Quantifying Costs and Benefits
Via CBA, businesses are able to identify both tangible and intangible costs and advantages. This allows firms to gain a complete understanding of the entire financial and strategic impact of their choices.
c. Comparing Alternatives
CBA allows businesses to compare various options effectively. By quantifying the expenses and advantages, companies can weigh each alternative against the others, making it simpler to select the most beneficial option. This approach also helps with the expense management process, ensuring that businesses are optimizing their spending and maximizing returns.
2. Limitations
Although Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) is a very valuable tool for decision-making, it isn’t without its difficulties. These constraints can affect the accuracy, reliability, and effectiveness of the analysis if they are not correctly addressed. Comprehending these potential impediments is crucial for ensuring the conclusions derived from a CBA are well-informed and actionable. Here are the main limitations that businesses should know about:
a. Challenges with Intangible Factors
Measuring abstract elements like customer happiness and staff motivation may be tricky in conventional CBA. ScaleOcean SG’s software resolves this by providing analytics tools like sentiment analysis, customer feedback monitoring, and employee involvement metrics. This allows organizations to better capture and assess these factors, leading to a more precise and thorough Cost-Benefit Analysis.
b. Dependence on Accurate Data
CBA greatly depends on the availability of precise data and trustworthy forecasts. Should the data utilized in the analysis be inaccurate or incomplete, the resulting conclusions might not be reliable, potentially causing poor decision-making.
c. Potential Bias in Valuation
Imputing monetary values to both costs and advantages can occasionally be subjective, introducing potential biases. Various individuals or departments might value specific factors differently, potentially influencing the analysis’s objectivity. To reduce these biases, utilizing standardized valuation methodologies and data is essential.
One such method is to account for significant expenses, such as capital expenditure, which involves large investments in assets that are expected to benefit the organization over the long term. This helps ensure that all financial considerations are factored into the analysis consistently.
Real-World Applications of CBA
Businesses have successfully utilized Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) in numerous ways to make informed choices. For instance, a retail chain applied CBA to assess the potential return on investment from growing its store network. By comparing the expenses of launching new locations with the anticipated growth in revenue, the company could prioritize the most advantageous expansion opportunities, a process that is deeply intertwined with capital budgeting to ensure optimal resource allocation for long-term growth.
CBA also has a crucial function in strategic planning, project management, and resource allocation. It helps companies ascertain the financial feasibility of projects and initiatives by clearly identifying potential expenses and returns. This enables businesses to allocate resources effectively, ensuring that capital and time are invested in projects that present the greatest return.
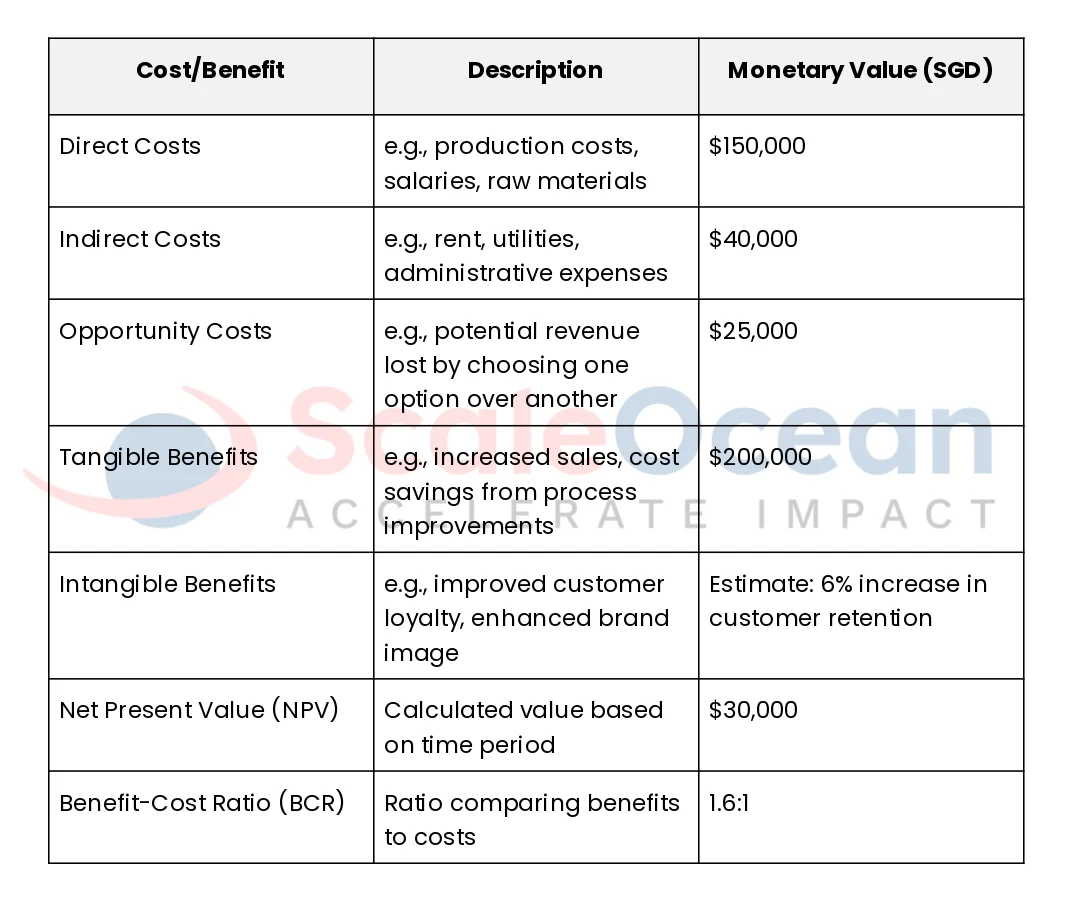
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) Template
An organized Cost-Benefit Analysis Template can assist businesses in streamlining the decision-making process by methodically tracking costs and advantages. Utilizing a template ensures consistency and helps maintain clarity throughout the analysis. Below is a comprehensive template to guide your CBA procedure:
To utilize the template efficiently, begin by pinpointing all expenses and advantages linked to your choice. Classify each cost and benefit as direct, indirect, or opportunity costs for costs, and tangible or intangible benefits for benefits.
Afterwards, allocate monetary values or estimations where suitable. Ultimately, compute the Net Present Value (NPV) and Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR) to gauge the financial feasibility of your decision. This systematic approach guarantees thorough analysis and informed choices.
Streamlining Your Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) with ScaleOcean’s Accounting Software
ScaleOcean’s Expenses Software is crafted to boost the efficiency and precision of conducting Cost-Benefit Analyses (CBA). By automating data tracking, simplifying computations, and integrating smoothly with financial statements, ScaleOcean’s cloud accounting software ensures that firms can perform thorough CBA with ease. These tools streamline the entire CBA process, permitting businesses to concentrate on decision-making rather than manual computations and data administration.
For companies seeking to explore ScaleOcean’s solutions, we offer a free demo to demonstrate how our software can assist with your cost-benefit analysis needs. Furthermore, businesses utilizing ScaleOcean may be eligible for the CTC (Cost-to-Company) grant, which provides financial aid for implementing HR and accounting technologies. Below is a list of key features of ScaleOcean’s software:
- Real-Time Data Tracking, ScaleOcean ensures real-time financial data updates, providing accurate and timely cost-benefit analysis without manual delays.
- Automated Calculations, The software automates complex financial calculations, reducing human errors and saving time for efficient CBA.
- Integration with Financial Statements, ScaleOcean integrates with financial reports, linking CBA results to overall financial performance for better decision-making.
- All-in-One Solution, Over 200 customizable modules are available, offering a comprehensive solution without the need for additional software, saving time and costs.
- Multi-Level Analytical Reporting, ScaleOcean enables multi-level financial analysis, comparing costs and benefits across departments or projects in real-time for thorough CBA.
Conclusion
Performing a thorough cost benefit analysis enables businesses to make informed choices by weighing both costs and advantages in a structured manner. It provides clarity on financial viability, assisting businesses avoid needless risks and optimize resources for maximum returns. This systematic method is crucial for effective decision-making in competitive markets.
ScaleOcean Singapore plays a key role in empowering businesses with the right tools for carrying out effective cost benefit analysis. Our software simplifies data gathering, analysis, and forecasting, enabling businesses to perform robust CBAs. Utilize ScaleOcean Singapore’s solutions to improve your decision-making and drive smarter business results.
FAQ:
1. How to calculate CBA?
To calculate CBA, subtract the total costs from the total benefits. A positive result indicates the decision is beneficial. You can use tools like net present value (NPV) or benefit-cost ratio (BCR) to measure the financial impact and determine if the benefits justify the investment.
2. What is the main goal of a cost-benefit analysis?
The primary goal of CBA is to determine whether the benefits of a decision outweigh its costs, ensuring resources are used efficiently. It helps businesses evaluate options based on both financial and non-financial impacts to make more informed choices.
3. What is the CBA method?
CBA is a systematic approach where costs and benefits are identified, measured, and compared. Key metrics like NPV or BCR are used to evaluate the financial feasibility of a decision, providing a clear framework for making effective business choices.
4. What is a cost-benefit analysis ROI?
ROI in cost-benefit analysis measures the return on a decision by comparing the benefits gained to the costs incurred. It’s calculated as the ratio of benefits to costs, allowing businesses to evaluate how much value they get from their investments.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















