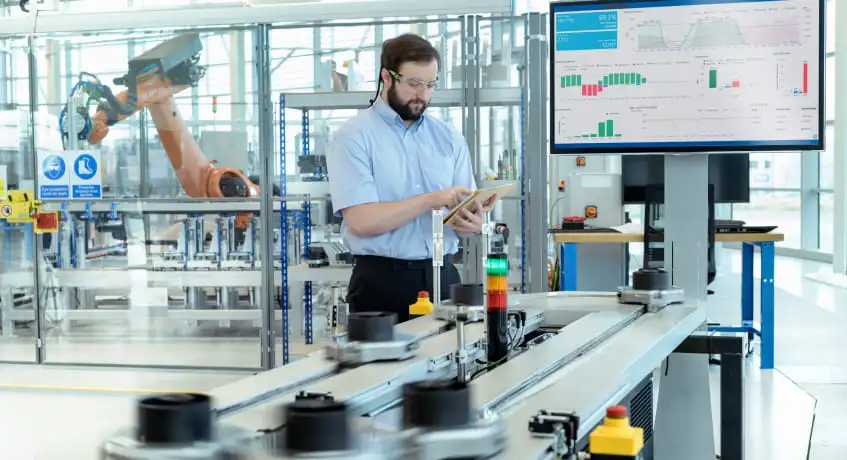
As manufacturing changes, old factories are finding it hard to keep up. Without live data or automation, daily work stays slow and full of mistakes. That is exactly where smart factories step in, offering a much faster and more flexible way to handle modern production.
Smart factories are proving their value, especially in places like Singapore. Companies adopting these technologies report impressive returns, like a 20% jump in output and 22% energy savings, according to the May Planning. These numbers really show how much of a difference modern tech can make.
In this article, we will explore the essentials of smart factories, such as what they are, how they function, how to build one, and a smart factory example. We’ll also look at the big benefits they bring to your business, helping you boost efficiency and drive long-term growth for your company.
- A smart factory is a fully digital and connected manufacturing workspace that uses tech like AI, IoT, and big data to study live info.
- Smart factory technologies like IIoT, AI, and digital twins support real-time data use and process automation.
- The smart factory levels progress through four stages, from data collection to full automation, improving efficiency and adaptability.
- ScaleOcean’s smart manufacturing software is built to link up perfectly with any equipment on your factory floor.

What Is a Smart Factory?
A smart factory is a fully digital and connected manufacturing workspace that uses tech like AI, IoT, and big data to study live info. This setup allows your production to run smoothly and flexibly on its own, making it much easier to keep your operations optimized and efficient.
The idea behind it is to create more responsive and reliable operations, with fewer delays and manual steps along the way. This approach tends to work well for manufacturers looking to adapt quickly and stay competitive without constantly overhauling everything.
According to the International Trade Administration, as Singapore’s manufacturing sector aims to grow from 20% to 30% of the GDP over the next decade, adopting smart factory technologies will play a key role in achieving this goal.
Smart Factories Explained
Smart factories are the heart of Industry 4.0, blending automation and AI to make manufacturing much smoother. By using smart sensors and IoT, they gather live data to make faster, sharper decisions. Tools like AI predictive maintenance and manufacturing cost estimating software really help keep productivity high.
At the core of these factories are things like machine learning and cloud computing. These tools let machines and workers communicate perfectly, leading to faster production and better quality. By analyzing data constantly, they can spot problems before they even happen.
Next, let’s dive into the differences between Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing:
Smart Factory vs. Smart Manufacturing
People often confuse smart manufacturing with a smart factory, but they refer to different things. Smart manufacturing is a broad approach or mindset. It involves the integration of advanced planning, interconnected systems, and real-time data flow across the entire supply chain, extending beyond just the factory.
In contrast, a smart factory is the physical embodiment of smart manufacturing principles. It refers to a factory where equipment, automation, and software work together in real time on the production floor. This makes the concept of smart manufacturing more tangible and operationally real.
While smart manufacturing may incorporate technologies like digital twins or AI-powered scheduling that can be applied off-site, a smart factory 4.0 focuses on upgrading the factory floor itself, integrating automation, real-time data, and AI to optimize operations at the core of production.
It’s all about improving how products are built, moved, and managed on the ground level, and adopting the best manufacturing execution system in Singapore can enhance these operations even further.
How Does a Smart Factory Work?
Picture a space where machines, sensors, and software aren’t just working, they’re constantly talking to each other, and to the people on the floor, too. In a smart factory, this real-time flow of information means things can adjust almost instantly, ensuring machine availability when every second counts.
You’ll see predictive maintenance happening before issues even show up, or automated systems doing quality checks without slowing things down. The whole setup is built for quicker reactions, less material waste, and just more room to shift when things change, which they often do.
The 3 Structure of a Smart Factory
A smart factory runs on three main pillars, which are gathering data, analyzing it, and using smart factory automation. These parts work together to sharpen production, keeping everything smooth and helping you make better decisions.
Let’s take a closer look at how each of these structures works:
1. Data Acquisition
This is basically the starting point, where machines, tools, and systems start collecting raw info through sensors, scanners, or even manual logs in some cases. Data acquisition is what sets the stage for everything else, so if this part isn’t solid, the rest tends to fall apart too.
What usually helps here is making sure the input is clean and steady, because without reliable data capture, even the smartest factory setup can start making clumsy decisions.
2. Data Analysis
After collecting the data, the real value shows up when you start digging into it, finding out what’s working and what’s just wasting time or energy. Data analysis gives context to the raw numbers, which helps teams react faster and adjust the line if something’s off.
This step tends to be the eye-opener, especially when trends or recurring bottlenecks emerge, as it reveals what you wouldn’t catch just by looking at reports on the surface.
3. Intelligent Factory Automation
Once you’ve got those insights, that’s when automation kicks in to make things smoother, such as robotics, auto-scheduling, and all of it. Smart factory automation helps reduce manual guesswork and keeps the workflow predictable, which is especially useful when scaling or switching product lines.
It’s not about removing people, but allowing them to focus on strategic tasks while machines handle repetitive work. ScaleOcean’s software also powers this automation, improving efficiency and ensuring precision across your factory operations, driving better overall performance.
4 Smart Factories Levels
The journey to a smart factory happens in four stages, each enhancing the factory’s ability to respond and adapt to changing conditions. From the initial stage of data collection to full automation, these levels improve efficiency and help factories stay ahead in a competitive market.
Let’s take a closer look at these four levels:
1. Basic/Available Data
At this first stage, the factory collects data, but it’s not actively used just yet. The data is available, but decisions are still made mostly based on experience or gut instinct. This is where factories usually begin, with data collection in place but not yet tied into daily operations.
Factories typically start at this level, where data is gathered but hasn’t yet impacted how decisions are made. The focus here is more on simply having the data available rather than using it to guide actions or optimize processes day to day.
2. Proactive/Accessible Data
At this stage, things start to get more interesting. Dashboards begin appearing, and alert systems are set up to catch problems early. The data is now more visible, making it easier for teams to plan. While full automation isn’t in the picture yet, the increased visibility makes planning more accurate and grounded.
Data becomes more accessible, and with it comes greater opportunity for improvement. Teams now have the tools they need to make better decisions based on available information, setting the stage for more refined operations in the future.
3. Active Data
By this stage, the system does more than just show data. It starts analyzing it and giving real-time suggestions. The system may flag trends or suggest actions before problems become bigger issues. This is where real-time data starts to play a more active role, connecting the dots between information and action.
Now, the system is working smarter, offering suggestions that help teams make decisions faster and more efficiently. The ability to spot patterns and make predictions before problems escalate makes this stage particularly valuable in streamlining operations and improving decision-making processes.
4. Action-Oriented Data
At this final stage, the system steps up by acting on data without needing a human hand. Machines adjust their own settings and processes, meaning people are less involved in the nitty-gritty. This is where the smart factory truly comes alive, as actions happen automatically.
Now, the system is on autopilot, with machines keeping everything running smoothly. The factory hits its full potential when tasks are automated, letting your team move away from daily chores and focus on big-picture strategy instead. It’s all about working smarter, not harder.
Smart Factory Technologies
Smart factories rely on advanced technologies that help make factory operations smarter and more efficient. These technologies work together to improve communication, automate tasks, and provide real-time data that helps businesses adapt quickly and optimize production.
Let’s take a closer look at these key smart factory technologies:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): IIoT devices connect machines, sensors, and systems, gathering data continuously. They monitor performance, detect issues early, and create a real-time communication network on the factory floor.
- AI (Artificial Intelligence): AI processes fast-moving data, predicts problems, and optimizes operations. It helps identify inefficiencies and eliminate redundant tasks, improving productivity and supporting better decision-making.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning, part of AI, learns from data over time, recognizing patterns even humans might miss.
- Sensors: Sensors measure variables like heat, pressure, and movement to support automation.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms store and process large data volumes, removing the need for physical server infrastructure.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR offer immersive training environments, allowing workers to practice tasks safely.
- Blockchain: Blockchain ensures secure, traceable data in manufacturing. It provides tamper-proof records, enhancing transparency in supply chains and improving data security, especially in regulated industries.
- Modern Database: Modern databases handle real-time manufacturing demands, enabling quick access to insights and preventing bottlenecks. Integrating the best manufacturing ERP software in Singapore can further streamline this process, ensuring efficient data management and seamless operations.
- Big Data and Analytics: Big data uncovers long-term patterns, helping forecast maintenance needs and prevent equipment breakdowns.
- Automation and Robotics: Automation and robotics handle repetitive, high-precision tasks. Robots perform work without fatigue or mistakes, reducing errors and ensuring consistent, reliable production at a steady pace.
- Digital Twins: A digital twin is a virtual replica of the factory that allows manufacturers to simulate and test changes without affecting real production.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing is perfect for quick prototypes and small-batch custom parts. While not for mass production, it reduces lead times, cuts excess inventory, and enables on-demand manufacturing of specialized components.
Also Read: 2026 Top 15 Manufacturing Industry Trends
Smart vs. Traditional Factories
Many old-school factories depend on fixed systems and manual labor, making it hard to see what’s really happening live. This lack of flexibility makes it tough to pivot quickly, often causing delays because even tiny changes can throw off the whole workflow.
Smart factories, on the other hand, act like living systems. They learn and make quick choices using real-time data. By using automation and live analysis, they react instantly to any changes, giving your business a huge edge in today’s fast-moving market.
Here’s a comparison between traditional and smart factories:
| Aspect | Traditional Factory | Smart Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Systems operate in isolation with limited interaction. | Devices and systems are integrated, continuously exchanging data through IIoT. |
| Data Availability and Use | Data is scattered and often requires manual work to gather, limiting immediate access. | Data is centralized across operations and instantly available for analysis. |
| Downtime | Equipment failures are hard to foresee, resulting in unplanned downtime and higher costs. | Predictive maintenance helps minimize unplanned downtime and lowers costs. |
| Manufacturing Flexibility | Making adjustments to production processes is slow and difficult. | The system is highly responsive, adapting quickly to changes in demand. |
| Product and Process Development | Development is slow, costly, and involves multiple iterations of physical prototypes. | Digital twins allow rapid testing and adjustments to virtual models, speeding up development. |
| Quality Control | Quality checks are manually performed, consuming time and resources. | Automated quality control is fast, cost-effective, and can adjust processes automatically. |
| Analysis and Decision-Making | Data processing is slow and requires manual aggregation, making decisions more labor-intensive. | Analysis is quicker, powered by advanced tools that enable faster, data-driven decisions. |
Benefits of Smart Factories
Smart factories offer numerous advantages, transforming traditional manufacturing by integrating advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and automation. These innovations create more efficient, flexible, and data-driven environments, significantly improving operations and outcomes.
Let’s explore the key benefits of smart factories:
- Improved Flexibility: Smart factories are highly adaptable, quickly responding to shifts in demand, production needs, or market changes. With automated systems and real-time data, these factories can easily adjust schedules and workflows to stay aligned with evolving priorities.
- Quicker, More Informed Decisions: With instant access to real-time data and advanced analytics, smart factories allow decision-makers to act quickly. This enables businesses to respond to issues or changes without delay, ensuring they stay ahead and make the best possible choices.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation and streamlined processes in smart factories improve overall efficiency. Tasks are completed faster, resources are used more effectively, and downtime is minimized, ultimately boosting productivity and ensuring operations run smoothly.
- Optimized Warehouse Operations: Smart factories help improve warehouse operations by using automation and real-time tracking. With accurate data, warehouses can optimize inventory levels, reduce the chances of overstocking or running out of stock, and speed up order fulfillment.
- Accelerated Product Design: Digital tools like CAD and digital twins allow for rapid design, testing, and prototyping. This significantly shortens the time it takes to bring a new product to market, and teams can easily make design changes when needed to improve the final product.
- Ongoing Enhancements in Process and Product Quality: Smart factories continuously gather data to monitor and improve both processes and products throughout the product life cycle. With real-time insights, automation ensures that quality control is built into every stage of production, leading to more consistent results.
ScaleOcean’s Manufacturing software brings the benefits of smart factories to life by integrating AI, IoT, and automation. With real-time data, automation, and advanced analytics, ScaleOcean helps enhance flexibility, efficiency, decision-making, and product quality, driving improved outcomes across operations.

How to Create a Perfect Smart Factory
Creating the perfect smart factory involves a strategic approach that aligns your needs, goals, and available technologies. It’s about ensuring that your factory operates with maximum efficiency, adaptability, and sustainability through the integration of advanced solutions.
Let’s explore the key steps to building the ideal smart factory:
- Evaluate Requirements and Objectives: Start by clearly defining what your factory truly needs and the specific goals you want to achieve. Having well-defined objectives helps guide your technology choices and ensures they align with your long-term vision.
- Understand Available Possibilities: Take the time to explore the range of technologies that could enhance your operations. Knowing what’s available allows you to make informed decisions and select solutions that best fit your factory’s needs and goals.
- Engage Your Workforce: Involve your team from the start to get their input and buy-in. When employees understand the changes and feel part of the process, it makes the transition smoother and leads to a more successful implementation of new systems.
- Streamline System and Data Integration: Ensure all your systems and data are well-connected to enable real-time information flow across your factory. This integration not only boosts efficiency but also supports faster decision-making and better overall performance.
- Begin with Small Steps: Start with manageable pilot programs to test the new technologies. By implementing gradual changes, you can evaluate their impact, make adjustments as needed, and ensure everything works as expected before expanding further.
- Prioritize Investment in Essential Technologies: Focus your investment on technologies that will provide the most immediate benefit to your factory. By concentrating on the essentials, you can optimize resources and avoid unnecessary spending while improving operations.
- Leverage AI and Machine Learning: Make use of AI and machine learning to automate routine tasks, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes. These technologies help increase the efficiency of your factory, making it more agile and responsive to change.
Real-Industries Examples of Smart Factories
Some of the bigger car manufacturers are already deep into smart factory technology, especially for just-in-time production. What’s interesting is how they rely on real-time sensors to tweak things as they go, which helps avoid delays or overstocking.
Smaller setups, like food packaging lines, are also starting to catch on with smart factory examples that help them cut down waste and keep quality checks moving fast. It’s a practical shift, especially when margins are tight, and speed really matters.
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a term you’ll frequently see used in these smart manufacturing spaces. It gives a solid read on whether your machines are actually helping or just taking up space.
Smart Factories as the Future of Manufacturing
When manufacturers put their resources into smart tech early on, it tends to pay off in flexibility later. Being able to shift quickly as markets change isn’t just useful, it’s starting to feel necessary.
The direction of manufacturing now leans heavily on being adaptable, and smart factory 4.0 makes that shift easier to handle without the usual spike in overhead or confusion.
Manufacturing process upgrades are already showing up across the board, and much of that’s coming from better systems that actually work together, such as smarter setups, not just newer ones.
ScaleOcean is the Best Technology to Perfect Smart Factories
ScaleOcean’s smart manufacturing software is built to link up perfectly with any equipment on your factory floor. Thanks to its industrial IoT tools, you get live insights into how things are running, making it much easier to keep track of your operations and overall performance in real time.
The system plugs directly into your machines to monitor performance, status, and energy use. This tight connection gives you all the data you need to sharpen your processes, cut down on waste, and make sure your production line is running as efficiently as possible.
ScaleOcean is also eligible for the CTC grant, helping you get financial support for new tech. This grant makes it much cheaper for your business to go digital, making the switch to smart factory solutions a lot more affordable and accessible for your team.
Here are the unique features of ScaleOcean’s manufacturing software:
- Platform Integration Customization: ScaleOcean easily connects with existing software and hardware, ensuring smooth data flow between smart factory tools and management modules.
- Connected Manufacturing Modules: ScaleOcean integrates smart MRP, BOM management, SCM, and warehouse management for seamless production operations.
- Predictive Maintenance and Monitoring: ScaleOcean uses sensor technology for real-time machine performance tracking and preventive maintenance management.
- Smart Energy Management: ScaleOcean optimizes energy usage across the entire factory, monitoring and controlling energy consumption in real-time to reduce waste and enhance operational efficiency.
- Automated Quality Control: ScaleOcean uses computer vision and AI for automatic inspections to ensure consistent quality.
- Multi-Factory Management: ScaleOcean integrates operations across multiple factories for seamless coordination and efficiency.
In addition to the key features mentioned above, ScaleOcean offers many more capabilities tailored to meet your unique system and software needs. You can explore all of ScaleOcean’s powerful features with a free demo, giving you firsthand experience of its capabilities.
Conclusion
Smart factories are no longer just a concept because they’re a real, measurable advantage for manufacturers ready to adapt. Whether you’re dealing with rising costs, skill gaps, or unpredictable markets, smart factory solutions help you respond faster and perform better. As technology matures, the edge goes to those who integrate early and strategically.
With the right tools in place, like ScaleOcean’s intelligent manufacturing system, you’re not just automating, you’re transforming. To help you experience this transformation firsthand, ScaleOcean offers a free demo so you can explore all its features before making a decision.
FAQ:
1. What is the goal of the smart factory?
The primary objective of a smart factory is to create a digitally connected and automated manufacturing environment that utilizes IoT, AI, and real-time data to optimize production processes, enhance efficiency, and respond quickly to changes.
2. What are the three components of a smart factory?
A smart factory is built on three key elements, which are industrial connectivity that links machines and systems, real-time data analysis to drive decisions, and flexible automation that allows production to adapt swiftly to changing requirements.
3. What are the pillars of a smart factory?
1. Connectivity: that allows machines, systems, and devices to communicate seamlessly.
2. Intelligence: through the use of AI and data analytics for informed decision-making.
3. Flexibility: enabling the factory to adjust quickly to production changes.
4. What makes a factory smart?
A factory becomes smart when it integrates real-time data from connected sensors and systems, automating tasks, predicting maintenance needs, and making data-driven decisions to boost efficiency, minimize waste, and adapt to changes.









 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















