In Singapore, businesses of all sizes rely on accurate financial reporting to stay competitive. The Income Statement, or P&L, reviews a company’s financial performance and helps businesses navigate market challenges. According to the Premia TNC, ACRA monitors compliance through the Financial Reporting Surveillance Programme.
Transparent financial records are required by law in Singapore. The Income Statement reveals key insights into profitability and operational efficiency, helping businesses make strategic decisions while ensuring compliance with ACRA standards. Let’s explore its key components and best practices.
- An income statement is a financial report that summarizes a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits or losses for a specific period.
- The importance and uses of the Income Statement for businesses include assessing performance, optimizing operations, forecasting growth, and ensuring compliance.
- Best practices for preparing an income statement include consistency, accuracy, compliance with accounting rules, and automation to ensure reliable and error-free reporting.
- ScaleOcean accounting software automates income statement preparation, reducing errors, minimizing manual work, and providing accurate, real-time data for better decision-making.

What Is an Income Statement?
An income statement is a financial report that summarizes a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits or losses for a specific period, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually. It measures financial performance and helps businesses assess operational success, identify areas for growth, and make informed decisions.
This financial reporting type is critical for stakeholders like management, investors, and creditors to assess profit, expense control, and overall financial health. It informs strategic decisions by providing insights into success, growth potential, and risks. To fully understand it, let’s explore the key components below:
1. Revenue
Revenue is defined as the total income generated by a company’s sales of goods or services. It’s the starting point for an Income Statement and reflects the company’s ability to generate income from its core operations. Revenue comes from various sources, like product sales and service fees.
Understanding the net sales formula helps businesses accurately calculate the revenue retained after returns, allowances, and discounts. This offers a clearer picture of actual income and is a key measure of market demand and a company’s growth potential.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to direct costs involved in producing goods or services sold by the company. It includes expenses like raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overheads directly tied to the production process, impacting overall financial performance.
COGS is deducted from revenue to calculate gross profit, reflecting the effectiveness of a company’s manufacturing processes. It also shows the company’s ability to manage production costs, helping assess profitability and operational efficiency in the production cycle.
3. Gross Profit
Gross Profit is the remaining amount after subtracting COGS from total revenue. It reflects how efficiently a company produces and sells its products or services. A higher gross profit indicates effective control over production costs in relation to sales.
A lower gross profit may point to issues with pricing, manufacturing, or cost control strategies. Analyzing gross profit helps businesses identify areas for improvement, ensuring better profitability and operational effectiveness in their production and sales processes.
4. Operating Expenses
Operating Expenses are the costs associated with day-to-day operations, excluding COGS. Examples include salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative charges. These expenses are essential for running the business but don’t directly impact production.
Efficient management of operating costs is crucial for long-term profitability. While necessary for business continuity, controlling these costs ensures the business remains financially healthy and competitive in the market, supporting overall success and growth.
5. Operating Income
Operating income is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. This metric highlights how well the company manages its core operations, excluding non-operational income or costs. It reflects the profitability of the primary business activities.
Understanding the operating margin formula is crucial here, as it helps stakeholders evaluate the company’s ability to generate profit from its major business operations. This provides a clearer view of the company’s operational efficiency and overall performance.
6. Other Income/Expenses
Other income and expenses refer to non-operational financial activities that affect a company’s financial performance. These include investment gains or losses, interest income, and other irregular items not part of the core business operations, influencing profitability.
Although these figures aren’t part of regular business activity, they still impact a company’s total profitability. Tracking other income and expenses is essential for a comprehensive understanding of a company’s overall financial health and performance.
7. Net Income
Net income is calculated by subtracting a company’s total expenses, including costs of goods sold, operating expenses, interest, taxes, and other losses, from its total revenue. This formula provides a comprehensive view of profitability, reflecting the company’s financial performance over the period.
According to IRAS, the total income listed in the tax assessment is already reduced by allowable expenses. Net income is a key metric for investors, creditors, and management when evaluating a company’s financial health and its capacity to generate profits.
8. Marketing and Promotion Costs
Marketing and promotion costs include all expenses related to advertising, public relations, and other activities aimed at increasing brand awareness and sales. These costs are crucial for businesses to attract new customers and retain existing ones, directly impacting revenue.
These expenses can cover various channels, including digital ads, social media campaigns, and traditional media. While necessary for growth, it’s essential to track and manage them effectively to ensure a positive return on investment for marketing efforts.
9. EBITDA
EBITDA, or Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization, provides a clear picture of a company’s operational profitability. It reflects how well the core business is performing without the influence of financing or accounting decisions.
This metric is often used by investors to assess the health of a business because it focuses solely on operations. By excluding non-operational costs, EBITDA helps determine whether the company is generating enough profit from its primary activities.
10. Overhead and Admin Costs
Overhead and admin costs include the necessary expenses to run a business that aren’t directly tied to production. This category covers things like office rent, utilities, and salaries for administrative staff, which support day-to-day operations.
While these costs are essential for keeping the business running, they don’t directly contribute to revenue generation. Managing these costs efficiently is key to maintaining profitability, as they can accumulate quickly without generating direct returns.
11. Asset Depreciation Costs
Asset depreciation costs represent the reduction in value of a company’s tangible assets over time, such as machinery or buildings. These costs are recorded to reflect the aging and wear of assets, which helps businesses budget for future replacements or upgrades.
Depreciation is a non-cash expense, but it plays a crucial role in understanding the long-term cost of ownership. By accounting for it, companies can spread out the financial impact of large capital investments, making them more manageable over time.
12. Earnings Before Tax
Earnings Before Tax (EBT) is a financial metric that indicates a company’s profitability before tax obligations are deducted. It reflects how well a business is performing at an operational level, excluding the impact of tax policies.
EBT is an important indicator of a company’s financial health and efficiency. It allows stakeholders to compare companies within the same industry, as it removes the effects of differing tax rates and structures that may skew profitability.
13. Tax Expenses
Tax expenses are the amounts a company must pay in taxes based on its taxable income. These costs are an inevitable part of doing business and must be factored into financial planning and budgeting.
Managing tax expenses involves understanding applicable tax laws and minimizing liabilities through deductions and credits. A strategic approach to tax planning can significantly impact a company’s net income and cash flow statement, affecting overall profitability.
How do Income Statements Work?
The income statement shows how the company’s revenue is converted into net profit or loss, by reporting four essential factors such as sales, expenses, gains, and losses. It begins with sales figures and works its way down to compute net income and, if applicable, earnings per share (EPS).
This financial statement does not make a distinction between cash and non-cash transactions, like credit versus cash sales or credit versus cash payments. This approach provides a simplified view of profitability, focusing solely on the company’s financial outcomes.
The time period covered by the income statement is clearly stated in the heading. For example, it could say “for the year ending December 31, 2024,” representing the company’s full fiscal year, or “for the three months ending March 31, 2025,” indicating a specific quarterly period.
What is the Importance and Uses of the Income Statement for Businesses?
The Income Statement plays a crucial role in helping businesses assess their financial performance and make informed decisions. It provides a clear breakdown of a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits or losses, allowing businesses to monitor their financial progress over time.
This statement is essential for both internal management and external parties, like investors and regulators. It helps evaluate the company’s ability to generate profit, control costs, and meet legal requirements, making it a key tool for strategic planning and maintaining financial transparency. Below here is where we are gonna discuss the details, take a look:
1. Internal Operations Management
Internal Operations Management involves using the Income Statement to assess how well a company’s resources are being utilized. By tracking expenses, businesses can identify inefficiencies, reduce waste, and optimize their operations to increase profitability. Understanding the bookkeeping and accounting differences also helps ensure the underlying financial data is accurate and reliable.
This process allows management to make data-driven decisions on cost control, resource allocation, and pricing strategies. Monitoring the income statement regularly ensures that operations stay aligned with business goals, improving long-term sustainability and operational efficiency.
2. Stakeholder Assessment
Stakeholder Assessment focuses on using the Income Statement to evaluate a company’s financial performance from the perspective of shareholders, investors, and creditors. It provides transparency into profit margins, expenses, and overall financial health.
By analyzing key figures like net income and gross profit, stakeholders can gauge the company’s ability to generate consistent profits, repay debts, and fund future growth. This evaluation builds trust and informs investment or lending decisions.
3. Performance Comparison
Performance Comparison involves using the income statement to compare a company’s current performance with past results or industry benchmarks. This comparison reveals trends and helps businesses measure growth, profitability, and operational efficiency over time.
By tracking key metrics, businesses can identify areas of improvement, set realistic goals, and adjust strategies accordingly. This process enables continuous performance evaluation, fostering better decision-making and more effective resource allocation.
4. Strategic Financial Forecasting
Strategic Financial Forecasting uses historical data from the income statement to predict future financial performance. By analyzing trends in revenue, expenses, and profit margins, businesses can make informed decisions for growth and expansion, especially when supported by a clear accrual accounting strategy.
This forecasting helps companies anticipate challenges and plan for future investments, ensuring that financial targets are realistic and aligned with overall business goals. Accurate forecasting also allows for better risk management and resource allocation.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory Compliance ensures that businesses adhere to local and international financial reporting standards, such as those set by the ACRA or IFRS. Accurate income reporting ensures that companies avoid penalties and maintain transparency with regulatory bodies.
Regular submission of Income Statements is a legal requirement for businesses to operate ethically and legally. Compliance not only builds trust with regulators but also fosters a positive reputation among investors and stakeholders.
Structure of an Income Statement
The Single-Step Income Statement is a simple financial reporting method that combines all revenues and expenses before calculating net income. It’s a basic approach, ideal for smaller businesses seeking a straightforward view of their financial performance at a glance.
This format does not categorize revenues or expenses but presents them in total, making it easy for smaller enterprises to understand their overall financial results. A profit and loss statement is a prime example of using this format to display financial performance.
In contrast, the Multi-Step Income Statement offers a more detailed analysis, including gross profit and operating income. Larger companies prefer this style as it separates operational and non-operational activities, providing a deeper insight into profitability and long-term sustainability.
Who Prepares the Income Statement?
The creation of an Income Statement is an important task within a firm, and many parties may be involved in assuring its accuracy and compliance. The statement must accurately reflect the company’s financial performance while also meeting regulatory standards. The following are the major contributors to preparing an income statement.
1. Internal Teams
The Income Statement is prepared by the internal finance and accounting departments of many companies. These teams are responsible for gathering financial data through balance sheets, recording transactions, and ensuring the statement aligns with the company’s business objectives and goals.
Their role is crucial in maintaining accuracy and consistency in financial reporting. This is essential for internal decision-making and strategic planning, ensuring that the company’s financial health is properly understood and used for future business strategies.
2. External Auditors
Independent auditors may be involved in preparing or reviewing the income statement to ensure its accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Their role is crucial in ensuring financial statements meet both international standards, like IFRS, and local standards like SFRS.
External auditors provide an independent perspective on financial reporting, ensuring transparency and trust. Their third-party viewpoint ensures that companies adhere to the necessary financial reporting rules, promoting confidence in the financial statements.
3. Software Solutions
Accounting software has become a popular tool for automating Income Statement preparation, ensuring accuracy and efficiency. Solutions like ScaleOcean streamline data entry and report generation, saving time and reducing errors.
By automating these tasks, businesses can improve their financial reporting and focus on strategic activities while ensuring compliance with accounting standards. Additionally, financial ERP software integrates financial tasks into one platform, offering a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health.
Income Statement vs. Other Financial Statements
The Income Statement focuses on a company’s ability to generate profit over a specific period, offering insights into long-term profitability. Unlike the Balance Sheet, it highlights performance over time and helps assess the financial leverage ratio, showing the impact on capital structure.
The Income Statement shows how well a company manages revenue and expenses, providing a dynamic view of performance. While the cash flow statement focuses on liquidity, the Income Statement emphasizes profitability, showing how revenue turns into profit or loss. A cash flow statement example complements this by showing cash movements.
The Income Statement tracks profits and losses, offering insight into operational efficiency. It provides a view of profitability and evaluates how well a company manages expenses. Unlike the balance sheet or cash flow statement, it reflects operational success over time.
Steps to Create an Income Statement in a Financial Model
Creating an income statement in a financial model involves analyzing various financial aspects of a business to accurately reflect its profitability. The process includes estimating revenue, accounting for expenses, and adjusting for non-operating factors. Here’s how you can approach it:
1. Forecast Revenue
Forecasting revenue is the first crucial step in building an income statement. You need to project future sales based on historical data, market conditions, and anticipated business growth. This estimation provides the foundation for the entire financial model.
Accurate revenue forecasting helps businesses set realistic expectations and track performance over time. It’s important to consider both external factors, like market trends, and internal factors, such as sales strategies and product launches, when making these predictions.
2. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
The next step is calculating the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), which represents the direct costs involved in producing goods or services sold by the company. These costs include materials, labor, and overhead directly tied to production.
Properly estimating COGS is vital for understanding how efficiently a company uses its resources. By subtracting COGS from revenue, you can determine gross profit, which provides insights into the company’s operational efficiency and cost management.
3. Estimate Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the ongoing costs required to run a business, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing. Estimating these expenses ensures a comprehensive picture of how much it costs to operate the business.
These expenses should be categorized and estimated carefully to avoid underestimating costs. A clear understanding of operating expenses helps businesses maintain profitability and effectively allocate resources to different operational areas.
4. Account for Non-Operating Items
Non-operating items, such as interest payments, taxes, and one-time gains or losses, should also be considered when creating the income statement. These items may affect the company’s overall financial performance but are not part of regular operations.
Including these adjustments ensures a more accurate representation of net income. By deducting or adding non-operating items, you get the final net income, which reflects the true profitability of the company after all factors are accounted for.
Best Practices for Preparing an Effective Income Statement
When generating an Income Statement, best practices assure accuracy, dependability, and conformity with accounting rules. A well-prepared Income Statement not only assists in strategic decision-making but also provides stakeholders with reliable financial information. Implementing these best practices can improve process efficiency and reduce the likelihood of errors, which can lead to financial mismanagement.
1. Consistency
Consistent accounting systems and periods are required for reliable comparisons over time. Businesses maintain the comparability and reliability of their financial data by adopting the same accounting standards, such as revenue recognition and expense classification, over successive periods. This uniformity enables stakeholders to more efficiently monitor the company’s financial health, identifying patterns and opportunities for improvement.
2. Accuracy
To avoid providing false financial information, all income and expenses must be recorded accurately. Using a structured approach like the double-entry accounting method helps ensure each transaction is captured correctly on both sides of the ledger.
Small inaccuracies or omissions in the income statement can affect profitability data, causing inaccurate assumptions about a company’s performance. To ensure accuracy, all financial transactions should be documented, and double-checking can help avoid costly errors.
3. Compliance
Adhering to local accounting standards and rules guarantees that the Income Statement is legally correct and displays financial performance consistently. Companies in Singapore must prepare their income statements in accordance with Singapore Financial Reporting Standards (SFRS). This ensures business compliance with local regulations like ACRA, avoiding potential legal or tax concerns related to tax invoice management.
4. Automation
Automation in accounting software significantly streamlines the preparation of the Income Statement by automating tasks like data entry and calculations, which reduces the risk of errors and speeds up the reporting process. This allows businesses to dedicate more time to analysis and decision-making rather than spending it on manual tasks.
With the added benefit of ensuring consistency and accuracy, accounting software like ScaleOcean also helps businesses stay compliant with local financial regulations, such as those established by ACRA, simplifying the process of meeting reporting requirements.
Example: Income Statement for a Singapore-Based Business
To further understand how the Income Statement is structured, consider this example for a Singapore-based company. This example deconstructs major financial components that are critical for evaluating a company’s financial success over a certain period.
The Income Statement gives information on the business’s profitability, cost management, and general financial health. For a deeper understanding, explore the general ledger examples to track transactions contributing to the Income Statement. Here’s an example based on a hypothetical company’s financial data:
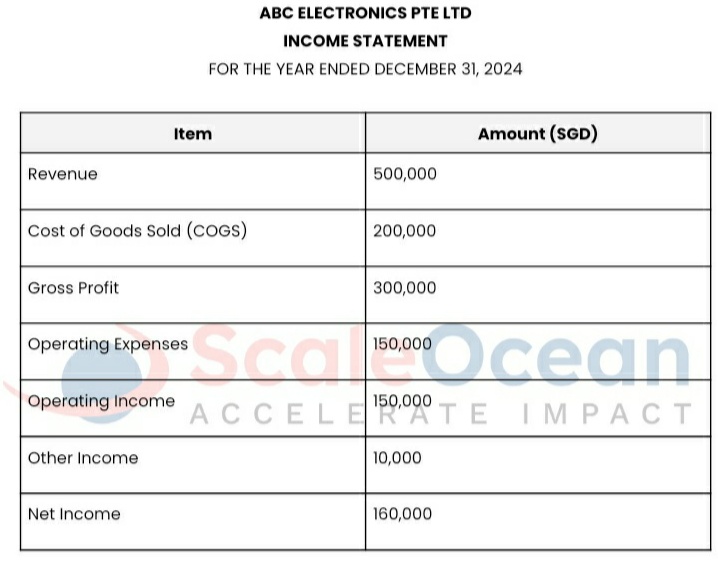
ABC Electronics Pte Ltd’s Income Statement for the year ending December 31, 2024, shows the company’s financial performance. Revenue is SGD 500,000 from electronics sales, with COGS of SGD 200,000 for production costs like raw materials and labor. Subtracting COGS from revenue yields a gross profit of SGD 300,000.
The operating expenses of SGD 150,000 include costs such as salaries, rent, and marketing. These are removed, leaving an operating income of SGD 150,000. The statement also includes Other Income of SGD 10,000 from non-operational operations, bringing Net Income to SGD 160,000. Net Income represents the company’s overall profit after all expenses and incomes are considered. This report provides stakeholders with an accurate picture of the company’s financial health and operational effectiveness.
ScaleOcean Accounting Software: Streamlining Income Statement Preparation
ScaleOcean Accounting Software is a comprehensive and user-friendly solution that streamlines financial management for organizations of all sizes. It assists businesses in reducing manual work, minimizing errors, and enhancing financial reporting efficiency through automation.
ScaleOcean is a critical tool for businesses across industries, boosting efficiency, financial transparency, and smooth operations. Firms may qualify for the CTC Grant, which can help cover the costs of implementing digital solutions like ScaleOcean. Here are the main advantages of ScaleOcean Accounting Software:
- Automation for Streamlined Income Statement Preparation: ScaleOcean Accounting Software automates the generation of Income Statements, significantly reducing the risk of errors and manual efforts in financial reporting.
- Customization for Tailored Reporting: The software allows businesses to customize their reports to meet specific business needs and comply with local regulatory requirements, offering flexibility for diverse industries.
- Seamless Integration with Financial Statements: ScaleOcean seamlessly integrates with other financial processes, enabling real-time data flow across various modules like sales, procurement, and inventory, ensuring consistency in reporting.
- Compliance with Singapore’s Accounting Standards: The system ensures full compliance with Singapore’s accounting standards, making it ideal for businesses operating in or with connections to Singapore, ensuring regulatory adherence and smooth audits.
Conclusion
Leveraging the Income Statement is critical for making educated strategic decisions. Regular analysis of the Income Statement helps businesses gain insights into profitability, cost structure, and efficiency. These insights assist managers and stakeholders in making informed decisions about spending, pricing strategies, and future growth. The Income Statement helps analyze financial performance and identify risks and opportunities to stay competitive and profitable.
Embracing technology is key to enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of financial reporting. Accounting software like ScaleOcean automates critical processes, reducing human error and ensuring compliance with local regulations. This streamlines financial operations, provides real-time updates, and delivers more reliable data, saving time and improving financial health. Businesses can explore ScaleOcean with a free demo to see how the software optimizes financial management.
FAQ:
1. What is the difference between a balance sheet and an income statement?
A balance sheet gives an overview of a company’s financial position, including assets, liabilities, and equity. In contrast, an Income Statement summarizes revenues, costs, and expenses, showing profitability over a period. The balance sheet reflects ownership and debt, while the Income Statement shows profit or loss.
2. How can I calculate an income statement?
To create an Income Statement, follow these steps:
1. Revenue: Record total income from sales or services.
2. COGS: Subtract direct production costs to calculate gross profit.
3. Operating Expenses: Deduct operating costs to find operating income.
4. Other Income/Expenses: Include additional financial activities.
5. Net Income: Subtract taxes and other expenses to determine final net income.
3. What is the basic income statement?
An Income Statement summarizes revenue, costs, and profits or losses. It includes revenue, COGS, gross profit, operating expenses, operating income, and net income. This statement helps assess financial health and supports informed decision-making.
4. What is the format of an income statement?
The typical format of an Income Statement includes:
1. Revenue: Total income from sales or services.
2. COGS: Direct production costs.
3. Gross Profit: Revenue minus COGS.
4. Operating Expenses: Costs like wages and rent.
5. Operating Income: Profit after operating expenses.
6. Other Income/Expenses: Non-operating financial items.
7. Net Income: Final profit or loss after deductions.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















