Managing cash flow in a business in Singapore companies can often feel like an overwhelming task. Many business owners struggle to keep track of every financial transaction, leading to stress and confusion. The general ledger in accounting is a powerful solution to this problem.
A general ledger (GL) serves as a comprehensive record of a company’s financial transactions, categorizing them according to account types such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. This organization aids in the preparation and analysis of financial statements.
By understanding the ledger in accounting and how it functions, You can improve the team’s decision-making, manage expenses, and remain compliant with financial regulations. In this article, we’ll explore what is a general ledger and the different types available and provide some handy templates to help you get started!
- General Ledger (GL) provides a summary of all transactions recorded using the double-entry bookkeeping system.
- Thegeneral ledger with the double-entry bookkeeping method, in which each transaction is documented as both a debit and a credit, with this balance: (Assets = Liabilities + Equity)
- Thetypes of general ledger include income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity.
- The general ledger records all financial records, starting from centralized financial, transaction records, income statements, balance sheets, cash flow, and Summarized Financial

What Is a General Ledger (GL)?
A general ledger (GL) provides a summary of all transactions recorded using the double-entry bookkeeping system. It records the impact of every transaction on at least two accounts: one account receives a debit, while a different account receives a credit. The total amount debited must always equal the total amount credited.
The ledger also serves as a comprehensive accounting record that aggregates all activities and financial transactions of a business, consolidating all accounts into a single location. It is utilized to generate financial statements, including balance sheets and income statements.
The general ledger categorizes transactions according to account types, such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. In accounting, a general ledger is crucial because this is primarily utilized for generating various accounting records, and also provides a centralized and detailed record of all financial activities, enabling you to track some types of general ledger.
Therefore, all of the transactions in the company are initially recorded in a general journal as journal entries, which are subsequently transferred to the general ledger. GL accounts include all debit and credit transactions related to them, along with detailed information about each transaction, such as the date, description, and possibly a brief explanation of the transaction.
This comprehensive tracking ensures that your financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement, are accurate and reliable. The ledger in accounting works by recording each transaction in two accounts: a debit in one and a credit in another, maintaining the accounting equation. This double-entry accounting book helps detect errors and ensures that the books are balanced.
In the context of financial management, the general ledger is a key component that organizes financial data into accounts, each representing specific types of financial transactions. The Chart of Accounts provides a comprehensive list of all the accounts within the general ledger, helping businesses categorize their financial activities.
Additionally, the general ledger often incorporates data from sub-ledgers, such as accounts payable or accounts receivable, which offer detailed insights into specific financial areas, ensuring accurate tracking and reporting of transactions.
What Are the Types of General Ledger?
A general ledger is divided into multiple accounts to provide a structured and detailed view of a company’s financial transactions, enhancing both accuracy and clarity. To have a better understanding, let’s have a look at each type of GL in accounting, including:
1. Assets
Assets in the ledger such as cash, inventory, accounts receivable, buildings, and equipment is crucial in accounting. Keeping track of these is key for knowing how much the company is worth and gaining investor trust. Prepaid expenses are also considered assets, as they represent payments made in advance for goods or services to be received in the future. These are classified as current assets and gradually recognized as expenses as the service is used.
For instance, cash is a current asset recorded at its real-time value, while equipment might depreciate over time. You won’t want to overlook intangible assets like intellectual property—they add major value, especially in tech sectors. A well-kept record of assets shows financial stability and growth potential.
2. Liabilities
The liabilities in the general ledger example, loans, expenses, and accounts payable, cover the company’s owes. Companies in Singapore’s liabilities in the ledger accounting help keep an eye on debts and manage cash flow effectively.
Based on Investopedia, loans, for example, are long-term liabilities, while accounts payable are short-term due to quicker repayment periods. Accurate records help you stay prepared for financial obligations and aid in planning future payments. It also reassures investors and creditors that your business is financially responsible.
3. Equity
Equity such as retained earnings, and capital contributions are stake in the business, also calculated as the difference between total assets and liabilities. Showcasing equity entries highlights the business’s financial value after debts are settled, crucial for attracting investors.
This includes retained earnings and reinvested profits, reflecting growth over time. Tracking equity signals financial stability and growth potential, making it vital for evaluating shareholder wealth and company value. For businesses in Singapore, it might mostly reflect initial investments, while established firms show accumulated profits.
4. Revenue
Revenue, for example, sales income and service fees, reflects all income from the operations of businesses. Under the accrual accounting method, sales revenue is logged when goods are delivered, while service revenue is noted upon completion.
Monitoring revenue helps identify which areas drive growth and which need improvement. This aids in budgeting, forecasting, and performance evaluation, enabling strategic adjustments to achieve revenue targets.
5. Expenses
Expenses such as rent, salaries, and utilities are incurred in running your business and fall under expenses. Tracking these helps identify where to optimize or cut costs. Salaries are operating expenses, while loan interest is a financial expense.
Clear expense records are crucial for budgeting and resource allocation. Analyzing trends helps you adjust budgets and reduce unnecessary costs, boosting profitability and promoting sustainable growth.
What Information Does a General Ledger Provide?
Every financial step will be recorded in the ledger to make it easier for you to manage it. With this, you can organize data systematically, monitor financial health, and ensure its accuracy, as well as generate important reports for decision-making. These are the things the pieces of information recorded in the general ledger:
1. Centralized Financial Data
A ledger serves as the central repository for all financial data. By consolidating financial information in one place, it simplifies the tracking and planning of business needs.
This centralization helps in making informed decisions, such as pricing products based on absorption costing or determining the financial resources required to achieve business goals. Having all data in one location makes it easier to monitor and analyze financial performance.
The ledger in accounting pulls together data from various sources, ensuring that every financial transaction is accounted for. This comprehensive approach allows businesses to maintain a clear and organized record of their financial activities, which is essential for accurate financial planning and reporting.
2. Comprehensive Transaction Records
Every financial transaction your business undertakes, whether it’s a purchase, sale, or payment, is recorded chronologically in the ledger in accounting. These transactions often start from records like the purchase journal before being transferred to the ledger. This chronological recording ensures that all transactions are documented in the order they occur, providing a detailed history of financial activities.
This data forms the foundation for all subsequent accounting processes and reports. By maintaining a complete record of transactions, the ledger in accounting supports the creation of accurate financial statements and helps in tracking the financial stability of the business. This detailed record-keeping is crucial for transparency and accountability in financial management.
3. Income Statement Preparation
To generate an income statement, you need a summary of all income and expenses over a specific period. The ledger records all sales revenue, operating costs, and non-operating income and expenses, providing the necessary data to create this summary.
The ledger in accounting detailed records ensures that all income and expenses are accurately captured, allowing for precise financial analysis. This helps businesses understand their profitability and make informed decisions to improve financial performance.
4. Balance Sheet Compilation
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your business’s financial position at a specific point in time. It includes assets, liabilities, and equity account balances, all of which are recorded in the ledger in accounting.
By summarizing these balances, the ledger in accounting helps create a comprehensive balance sheet that reflects the resources available to the business and its financial obligations.
The balance sheet is an essential tool for assessing the economic resilience of a business. It provides insights into the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, helping stakeholders understand the overall financial stability and make strategic decisions.
5. Cash Flow Statement Creation
The ledger plays a crucial role in creating cash flow statements report by tracking all cash-related transactions. It provides insights into how cash is moving in and out of the business from operating, investing, and financing activities.
This information is vital for effective cash flow management, ensuring that the business has sufficient liquidity to meet its obligations. Additionally, incorporating a cost breakdown structure within cash flow analysis allows businesses to understand the specific costs associated with each activity.
So, the ledger in accounting could help businesses monitor their cash flow and make proper decisions about managing their finances. This is essential for maintaining financial stability and planning for future growth.
6. Summarized Financial Reports
The transaction details within a ledger, including accounts receivable, are summarized at various levels to produce trial balances. These trial balances are used to create multiple financial reports that assess the performance of your business.
Summarizing transactions helps in identifying trends, analyzing financial data, and preparing accurate financial statements. The ledger in accounting ability to summarize detailed transaction data into meaningful financial reports is crucial for effective financial management.
It provides a clear and concise overview of the business’s financial activities, helping stakeholders make informed decisions based on accurate and reliable information.
How Is a General Ledger Organized?
What is general ledger is a systematic arrangement that simplifies reporting but also helps businesses maintain control over their finances. Understanding how the GL is structured is essential to making sound financial decisions and ensuring compliance with accounting standards in Singapore.
1. The Accounts in a GL are Organized into Five Main Categories
It includes assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. This classification provides a clear financial framework, ensuring that every transaction is properly categorized. By maintaining this structure, businesses can effectively assess their financial health and prepare accurate reports for stakeholders.
2. Each Category Helps Organize and Track Financial Transactions Systematically
By categorizing transactions into five main categories, you can maintain a structured and transparent financial record. It also simplifies financial reporting examples, enabling businesses to track growth, identify spending patterns, and comply with accounting standards. A well-organized ledger is crucial for effective financial management.
3. The Ledger is Broken Down into Accounts, Account Balances, and Financial Transactions
A ledger in accounting consists of individual accounts that store financial information, including account balances for assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. Each financial transaction, such as a sale or expense, is recorded in the relevant account to keep the ledger updated.
How Does the General Ledger in Accounting Work?
Acting as the central record-keeping system, the ledger can track every transaction that flows in and out, ensuring accuracy and transparency. It is important to understand what a general ledger is and how it works to maintain financial stability and ensure that every number adds up correctly.
1. Recording Transactions
Every financial transaction your business makes is recorded in the accounting ledger. This includes sales, expenses, asset purchases, and liabilities. Each transaction is documented with a date, description, and the amounts debited and credited to the relevant accounts. This ensures that all financial activities are accurately tracked.
By keeping detailed records, you can easily monitor your business’s financial performance and make better decisions. Accurate transaction recording also helps in preparing financial statements and complying with regulatory requirements. Regularly updating your ledger in accounting with each transaction is essential for maintaining the integrity of your financial data.
2. Double-Entry Bookkeeping
The ledger operates on the double-entry bookkeeping system. This system helps maintain the accounting equation and ensures that the numbers are always balanced, forming a core part of understanding bookkeeping vs. accounting. Double-entry bookkeeping is fundamental to detecting errors and preventing fraud.
By ensuring that debits and credits are equal, you can quickly identify discrepancies and address them. This method provides a comprehensive view of your financial activities, making it easier to analyze and report on your business’s financial health.
3. Categorizing Accounts
Transactions are categorized into different accounts, such as revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. This categorization helps in organizing financial data and makes it easier to prepare financial statements. Each account has its own ledger, which is a subset of the ledger in accounting.
By categorizing transactions, you can gain insights into specific areas of your business, such as the profit and loss statement report and cost management. This organization also simplifies the process of auditing and reviewing financial records. Properly categorized accounts ensure that your financial statements accurately reflect your business’s financial position and performance.
4. Posting Entries
Once transactions are recorded in the journal, they are posted to the ledger in accounting. Posting involves transferring the journal entries to the appropriate accounts in the ledger. This step is crucial for updating account balances and ensuring that all financial data is current.
Regular posting helps maintain the accuracy of your financial records and provides a real-time view of your business’s financial status. By keeping your ledger in accounting up to date, you can make timely and wise financial decisions. Consistent posting also facilitates the preparation of accurate financial statements and reports.
5. Trial Balance
Periodically, you will prepare a trial balance to ensure that the total debits equal the total credits. This step helps in identifying any discrepancies or errors in the ledger. A balanced trial balance indicates that the ledger in accounting is accurate and ready for the preparation of financial statements.
Preparing a trial balance is an essential part of the accounting cycle, as it verifies the integrity of your financial records. By regularly conducting trial balances, you can detect and correct errors early, ensuring the reliability of your financial data. This practice also supports compliance with accounting standards and regulations.
6. Preparing Financial Statements
The information in the ledger is used to prepare key financial statements such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. These statements provide a comprehensive view of your business’s financial performance and position, helping you make informed decisions.
Accurate financial statements are essential for stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and management, to assess the financial viability of your business. You can ensure that your financial statements are precise and reflective of your business’s true financial status. This transparency builds trust and supports strategic planning.
7. Regular Review and Reconciliation
Regularly reviewing and reconciling the ledger in accounting is essential for maintaining accurate financial records. This involves comparing the ledger entries with bank statements and other financial documents to ensure consistency and accuracy. Regular reconciliation helps in detecting and correcting errors promptly.
By conducting regular reviews, you can ensure that your financial records are up-to-date and free from discrepancies. This practice also helps in identifying any unusual transactions or potential fraud.
Maintaining accurate and reconciled records supports effective financial management and decision-making, ensuring the long-term success of your business.
How a General Ledger Functions With Double-Entry Bookkeeping
The general ledger employs the double-entry bookkeeping method, in which each transaction is documented as both a debit and a credit. This practice guarantees that the accounting equation stays in equilibrium. You can balance the double-entry data by using the following formula:
(Assets = Liabilities + Equity)
This system meticulously documents each transaction by ensuring that debits and credits are equal, thereby maintaining balanced accounts. For instance, when a business completes a sale, it credits revenue and debits cash. It monitors financial activities across different accounts, including inventory and accounts payable, offering a comprehensive overview of assets and liabilities.
The Function of General Ledger in Singapore’s Businesses
The general ledger is the backbone of a company’s financial records, acting as a single source of truth for all transactions. What is ledger is a crucial role in ensuring accuracy, compliance, and strategic financial planning? But what exactly does it do, and why is it indispensable for businesses?
1. Financial Reporting
The ledger is essential for preparing financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, financial leverage, and cash flow statement. These reports provide valuable insights into your company’s financial performance, helping stakeholders make informed decisions.
Accurate financial reporting is important for maintaining transparency and trust with investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies. By ensuring that all transactions are correctly recorded in the ledger in accounting, you can produce reliable financial statements that reflect your business’s true financial position.
2. Budgeting and Forecasting
Analyzing the data in your ledger in accounting allows you to create accurate budgets and forecasts. This helps in planning for future expenses, setting financial goals, and making strategic decisions to achieve those goals.
Budgeting and forecasting are essential for managing cash flow, allocating resources efficiently, and anticipating financial challenges. These practices support informed decision-making, helping you to allocate resources efficiently and adapt to changing financial conditions, ultimately fostering a stable and growth-oriented financial environment for your business.
3. Internal Controls
Your ledger in accounting plays a crucial role in maintaining internal controls by ensuring that all financial transactions are accurately recorded and accounted for. This helps prevent fraud, errors, and discrepancies in financial records.
Strong internal controls are vital for safeguarding assets, ensuring compliance with laws and regulations, and promoting operational efficiency. By regularly reviewing and reconciling the GL, you can detect and correct any irregularities, thereby enhancing the integrity of your financial data.
4. Tax Compliance
An accurate and up-to-date ledger in accounting records is essential for tax compliance. They provide the necessary information for preparing tax returns and ensure that businesses meet their tax obligations. Proper tax compliance, especially with IRAS tax Singapore regulations, helps avoid penalties, interest charges, and legal issues.
The ledger in accounting tracks all taxable transactions, making it easier to calculate tax liabilities and claim deductions. By maintaining detailed and organized records, you can streamline the tax filing process and ensure that you comply with all relevant tax laws.
5. Performance Analysis
The ledger allows businesses to analyze their financial performance over time. By comparing current and past financial data, you can identify trends, measure progress, and make data-driven decisions to improve operations.
Performance analysis helps understand strengths and weaknesses, optimize resource allocation, and enhance profitability. The ledger in accounting provides a comprehensive view of financial activities, enabling in-depth analyses and developing strategies for growth and improvement.
6. Audit Preparation
Having a well-maintained ledger in accounting simplifies the audit process. Auditors rely on the ledger to verify the accuracy of financial statements and ensure compliance with accounting standards. A detailed and organized ledger facilitates the audit process by providing a clear and complete record of all financial transactions.
This helps auditors assess the reliability of financial data, identify any discrepancies, and provide recommendations for improving financial practices. By maintaining accurate records, you can ensure a smooth and efficient audit process.
7. Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management is critical for the survival and growth of any business. The ledger helps track all cash inflows and outflows, providing a clear picture of your company’s liquidity position.
By monitoring cash flow, you can ensure sufficient funds to meet obligations, invest in growth opportunities, and avoid cash shortages. The ledger provides detailed information on cash transactions, enabling better management of cash flow and informed financial decisions.
8. Decision Making
The GL provides valuable financial information that supports decision-making processes. By analyzing the data in the ledger, you can make informed decisions about investments, cost-cutting measures, and strategic initiatives.
Accurate financial data is essential for evaluating the potential impact of different decisions and choosing the best course of action. The ledger offers a comprehensive view of your company’s financial integrity, helping assess risks, identify opportunities, and develop effective strategies.
9. Compliance and Governance
Maintaining a detailed ledger is essential for compliance with financial regulations and corporate governance standards. The ledger provides a transparent record of all financial transactions, ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Compliance with financial regulations helps protect the company from legal issues, fines, and reputational damage. The ledger also supports corporate governance by providing accurate and reliable financial information to stakeholders, promoting accountability and transparency.
10. Historical Record
The GL serves as a historical record of all financial transactions conducted by your business. This historical data is valuable for analyzing past performance, identifying trends, and making accurate decisions about the future.
By maintaining a comprehensive and accurate ledger in accounting, you can preserve your financial history and use it as a reference for future planning and decision-making.
Examples of General Ledger Entries
A general ledger (GL) serves as a comprehensive record of all financial transactions occurring within an organization. It encompasses accounts related to assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses. Entries in the ledger are created to formally record these transactions. Below are several examples:
In the following scenario, a company acquires office supplies valued at $500 on credit. The accountant will subsequently augment the office supplies account (an asset) by $500 and correspondingly raise accounts payable (a liability) by $500. This transaction ensures that the accounting equation remains balanced, as both the asset and liability components are impacted equally by the same amount.
Each entry documented in the ledger consists of the transaction date, description, amount involved, account affected (either debit or credit), and vendor name, if relevant. These data are also used to prepare financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Example of Ledger in Accounting Implementation
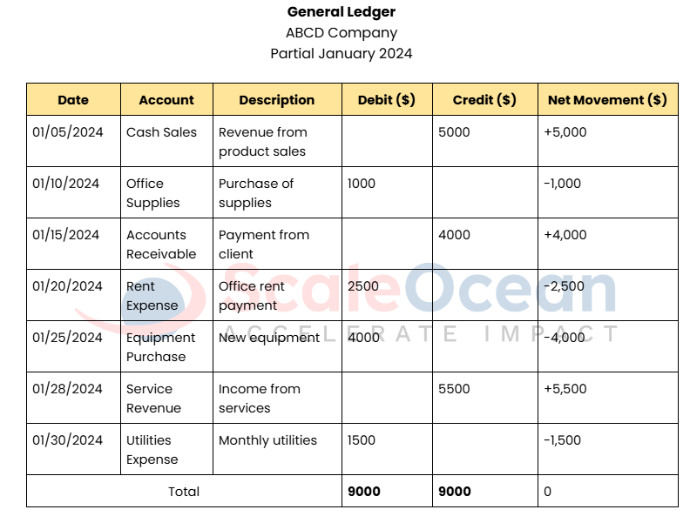
The implementation of a ledger in accounting is essential, providing a structured way to track financial activities. Businesses in Singapore can rely on it to consolidate accounts, monitor cash flow, and produce accurate financial reports. Here is an example to make it easier for you to create one:
This ledger records both income and expenses, categorizing each transaction as a debit or credit to ensure a balanced outcome with a net movement of zero. Income entries, such as Cash Sales and Service Revenue, are recorded as credits, reflecting revenue growth and increasing the company’s cash flow.
On the other hand, expenses like Office Supplies, Rent Expense, Equipment Purchase, and Utilities Expense are recorded as debits, representing operational and capital costs that reduce the balance. The Accounts Receivable entry, recorded as a credit, highlights cash flow improvement through client payments.
With both the debit and credit totals matching at $9,000, this balanced ledger provides a detailed view into cash flow, supporting regulatory compliance, and aiding in strategic decision-making.
Using technology can greatly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of your GL. Modern accounting software, like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), simplifies data entry, automates calculations, and minimizes human errors, allowing you to record transactions in real-time and categorize them effortlessly.
Many industries can be reached with this technology, including construction ERP. With features like automated reminders for pending entries and smart cash flow insights, you can keep a timely, complete view of your finances.
General Ledger Template for Singapore Companies
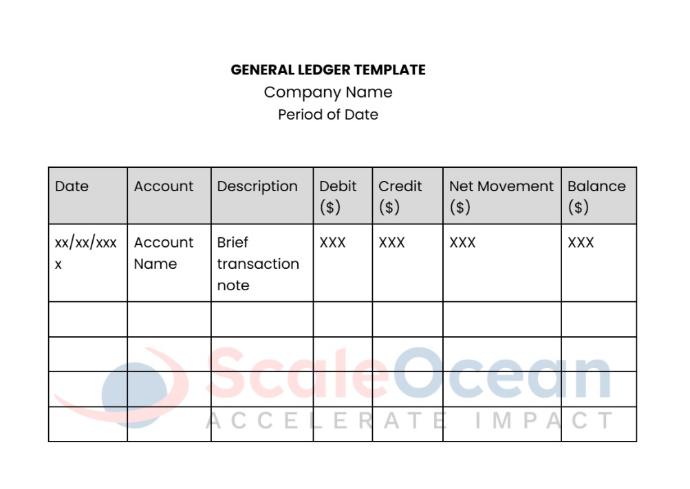
Setting up a ledger from scratch can be a hassle, especially when dealing with a lot of financial transactions. A well-structured ledger in an accounting format streamlines the process, ensuring consistency, and efficiency in financial tracking. Here’s a template you can use in Singapore’s Company:
Each column in the table is designed to capture specific details about every transaction, allowing for a clear and organized financial overview.
The Date column ensures that transactions are recorded chronologically, while the Account column categorizes each transaction by its type (e.g., revenue, expenses, assets). The Description column provides a brief note on each transaction, adding context for easy reference.
The Debit and Credit columns show the amounts that increase or decrease specific accounts, and the Net Movement column reflects the impact of each transaction on your cash flow. Finally, the Balance column keeps a running total, allowing you to see the cumulative effect of all transactions over time.
This template ensures that every income, expense, or adjustment is documented, promoting transparency and accuracy in financial reporting. As you fill in the table, you can track each account’s balance and easily prepare financial statements like the balance sheet and income statement.
Conclusion
We know that is general ledger is an indispensable tool for any business, encompassing all financial transactions in a structured format. This comprehensive record ensures accuracy, transparency, and organization in financial reporting. By providing a detailed overview of assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses, the ledger in accounting enables informed decision-making.
Creating and managing a ledger has become significantly easier and more efficient due to advancements in technology, particularly with the introduction of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. With ERP, various business functions can be integrated into a single platform, alleviating the challenges often faced when recording and tracking financial transactions.
In this context, the accounting module within a ScaleOcean ERP for accounting can allow for the automation of real-time transaction entries. You can simplify complex financial processes, reduce errors, and focus more on strategic goals. If you’re interested in seeing how this technology could enhance your business, feel free to try a free demo and consultation to experience its impact firsthand.
FAQ:
1. What are the 5 parts of the general ledger?
A general ledger organizes accounts into five categories: assets, liabilities, owner’s equity, revenue, and expenses. These classifications, listed in the chart of accounts, help businesses track financial activities, maintain accurate records, and ensure proper financial reporting.
2. What is an example of a GL account?
A GL account categorizes financial transactions in a general ledger. Examples include asset accounts like Cash, Accounts Receivable, and Inventory, as well as liability accounts such as Accounts Payable and Notes Payable, helping businesses track financial positions accurately.
3. Is general ledger debit or credit?
A general ledger records all business accounts and transactions using debits and credits. Debits, recorded on the left, increase assets and expenses, while credits, on the right, increase liabilities, equity, and revenue. Balancing requires subtracting total debits from total credits.
4. What are the 4 C’s of general ledger?
The 4 C’s in a general ledger refer to the Chart of Accounts, Calendar, Currency, and Accounting Convention. These elements define financial structure, reporting periods, transaction currency, and accounting system principles, ensuring consistency and accuracy in ledger processing and financial management.









 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















