In Singapore’s competitive economy, many businesses face challenges in staying focused and managing resources efficiently. Without setting clear financial goals for the business, tracking progress becomes difficult, leading to stagnation. The solution is establishing precise financial goals, guiding businesses toward sustainable growth and long-term success.
According to EDB Singapore, Southeast Asia is expected to become the world’s fourth-largest economy by 2030, with ASEAN nations fostering open and integrated trade. This economic shift presents opportunities and challenges for businesses, urging them to adapt their financial strategies.
In this article, we’ll define financial goals for business and explore their different types. We’ll cover 12 key financial goals, including boosting cash flow, improving profitability, increasing revenue, reducing debt, and more, all essential for achieving long-term success and stability.
- Financial goals are targets set by businesses to improve financial health, focusing on areas like revenue growth, cost reduction, and profitability.
- Short-term financial goals for business focus on cash flow, profit margins, cost reduction, revenue targets, debt management, and creating a budget.
- Long-term financial goals for a business target sustainable growth, innovation, capital structure, exit strategies, long-term profitability, and building financial reserves.
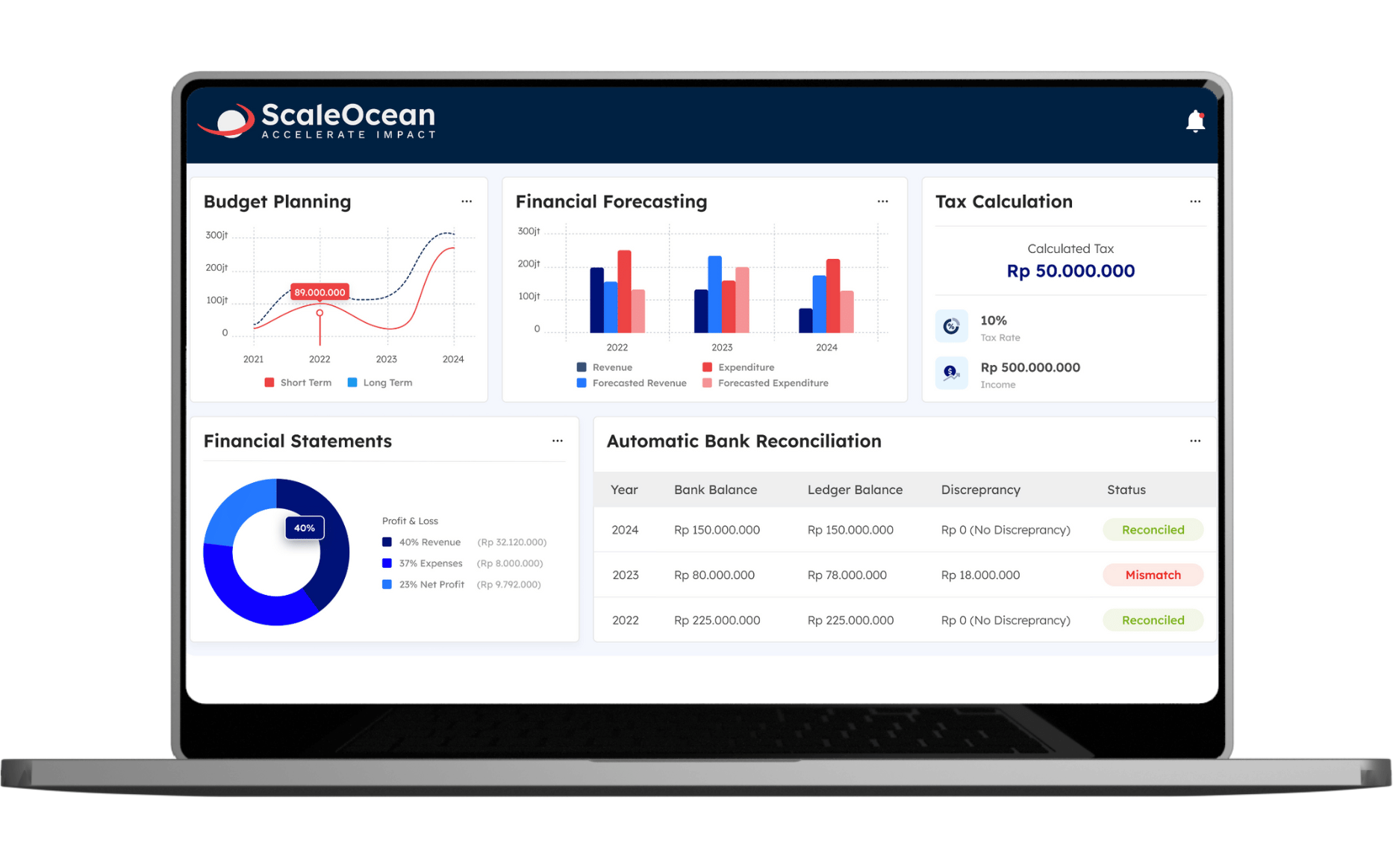
- ScaleOcean ERP and accounting software in Singapore support businesses by automating financial tracking, providing real-time data, and ensuring compliance.

What Are Financial Goals in Businesses?
Financial goals are targets set by businesses to improve financial health, focusing on areas like revenue growth, cost reduction, and profitability. These goals help align strategies with measurable results, ensuring sustainable growth and long-term financial stability.
Business financial goals are divided into short-term and long-term categories. Short-term goals focus on immediate needs, like maintaining cash flow or increasing earnings within a year, helping businesses manage daily operations. According to the Technology Government, they control operating costs for businesses and ensure financial stability.
Long-term goals, on the other hand, are more strategic, focusing on growth, innovation, and transformation. These goals align business tactics with realistic expectations and serve as benchmarks for decision-making, guiding the company toward sustained success and growth.
Why Financial Goals Matter for Business Success?
Establishing financial goals for a corporation promotes profitability, sustainability, and investor trust. Clear goals provide firms with a solid direction for managing their money. This also enables organizations to detect potential hazards early on and embrace fresh opportunities. Financial goals, when well planned, contribute to long-term stability and growth.
They also help to keep the emphasis on key performance areas like revenue growth and business operational costs. Setting specific targets makes it easier to maintain a healthy profit margin. These goals serve as standards for monitoring progress and corporate performance. As a result, stakeholders acquire greater trust in the company’s future.
12 Types of Financial Goals in Business
Financial goals are essential for any business aiming to achieve long-term success and sustainability. Setting clear financial goals helps companies stay focused, improve their financial health, and navigate a competitive market. Here are 12 types of financial goals businesses should aim for:
1. Revenue Objectives
Revenue objectives focus on maximizing the income generated from sales and services. By setting clear revenue targets, businesses can track their performance and implement strategies to drive sales growth. These goals often involve expanding customer bases, launching new products, or increasing market penetration.
For example, a clothing retailer might set a revenue objective to increase sales by 15% over the next quarter. This could be achieved through targeted marketing campaigns or expanding into new geographic areas to reach more customers and boost overall sales.
2. Profit Objectives
Profit objectives aim to increase the difference between a company’s revenue and its expenses. Achieving these goals requires efficient cost management, improving operational productivity, and optimizing pricing strategies. Profit goals are critical for ensuring a business’s sustainability and long-term financial health.
A restaurant might set a profit goal by reducing food waste and renegotiating supplier contracts to lower ingredient costs. This would allow the business to increase its margins, improving profitability without needing to increase prices or sales volume.
3. Cash Flow Objectives
Cash flow objectives focus on maintaining a healthy cash position to meet daily operational needs. By managing cash inflows and outflows effectively, businesses can avoid cash shortages and ensure smooth operations. These goals often include optimizing collection processes and reducing payment delays.
For example, a subscription-based business might aim to improve cash flow by offering early payment discounts or implementing automated billing systems. This ensures that cash is consistently available to cover expenses and support growth initiatives.
4. Investment Objectives
Investment objectives are about strategically allocating resources to generate returns over time. These goals typically involve diversifying investments, such as funding new projects, purchasing assets, or investing in innovation.
Understanding the different types of financial instruments also helps businesses develop effective strategies for growth and increasing market value.
A tech startup might set an investment objective to allocate a percentage of its profits towards product development and technology upgrades. By investing in innovation, the company can stay competitive and capture a larger market share in the long run.
5. Debt and Financial Obligations Objectives
Debt and financial obligations objectives focus on managing and reducing liabilities. These goals are essential for maintaining financial stability and reducing the risk of insolvency. By prioritizing debt repayment, businesses can lower interest costs and free up resources for reinvestment into growth.
A manufacturing company might set a debt reduction objective by refinancing high-interest loans or paying off short-term debts. This can lower the overall cost of debt and improve the company’s financial health, allowing for greater flexibility in managing future investments.
6. Return on Investment (ROI) Objectives
ROI objectives focus on maximizing the returns from investments made in various areas of the business. By evaluating the effectiveness of different investments, businesses can ensure they allocate resources where they’ll yield the highest returns, improving profitability and overall performance.
For example, an e-commerce company could set an ROI objective by increasing the return from digital advertising. By tracking which ad campaigns lead to the most conversions and adjusting marketing strategies, the company can ensure its advertising budget generates optimal returns.
6 Short-Term Financial Goals for Businesses in 2026
Short-term financial goals for businesses help them stay financially healthy while sustaining day-to-day operations. These objectives give a practical framework for managing resources efficiently and maintaining performance on track.
Businesses that focus on short-term goals can strengthen their financial position and plan for future growth. Regularly monitoring performance, including calculating net sales, allows businesses to make quick adjustments and data-driven decisions for revenue growth. Here are some important examples of short-term financial goals to consider:
1. Cash Flow Management
One of the most typical short-term financial goals for a corporation is to maintain positive cash flow. Proper planning ensures that there is enough liquidity to cover regular operations as well as unforeseen needs.
Using financial management tools allows organizations to gain real-time financial data. With a good financial management process system in place, teams can make quicker and more accurate judgments.
2. Profit Margins
Businesses frequently strive for specified earnings targets to preserve financial health each quarter. A specific aim makes it easier to measure progress and evaluate financial performance consistently.
A structured cost breakdown structure might help you uncover profit-maximizing opportunities. This strategy guarantees that resources are allocated properly across operations.
3. Cost Reduction
Short-term financial strategies continue to prioritize cost-cutting measures. This could include renegotiating supplier contracts or enhancing internal processes. Using tools such as bookkeeping and accounting allows you to quickly track and regulate your spending. These measures improve profitability and operational efficiency.
4. Revenue Targets
Setting specific monthly or quarterly revenue goals aids in measuring business performance. Companies can use these checkpoints to regularly examine their marketing and sales strategies. Regular monitoring ensures that adjustments may be made quickly if necessary. Consistent success toward revenue goals indicates a positive corporate picture.
5. Debt Management
Reducing short-term debt increases a company’s financial stability and flexibility. Managing liabilities responsibly improves cash flow management and lowers financial risks.
One important practice in maintaining financial stability is regular bank reconciliation, which ensures that cash records align with bank statements, preventing discrepancies. Disciplined debt management leads to stronger connections with lenders, opening up prospects for future funding and expansion.
6. Create a Budget
Developing a detailed budget is a crucial short-term financial goal. It helps businesses monitor their income and expenses, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. A strong budget allows companies to avoid overspending and ensures that they remain financially stable.
By setting realistic budgetary limits, businesses can ensure they have enough funds for both planned expenses and unexpected costs. Regular reviews and adjustments of the budget help businesses stay on course and maintain financial health.
6 Long-Term Financial Goals for Businesses in 2026
Long-term financial goals for businesses are focused on protecting the company’s future through sustainable strategy and rigorous financial planning. These objectives assist organizations in maintaining their competitive advantage while also planning for potential future problems.
In Singapore, both SMEs and businesses understand the importance of connecting long-term goals with development prospects. The following are some common areas where firms set their long-term financial goals:
1. Sustainable Growth
One of the most typical long-term financial objectives for a company is to maintain consistent, year-over-year growth. This includes entering new markets and improving consumer connections.
According to GovTech Singapore, the Singapore Green Plan 2030 outlines the nation’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, encouraging businesses to align their strategies with sustainability goals. Diversifying products or services also promotes ongoing corporate growth, which demands solid and continuous financial preparation.
2. Investment in Innovation
Successful organizations invest in R&D and technological upgrades for future growth. Innovation helps to generate new revenue sources and keeps businesses relevant. Staying ahead of opponents generally requires ongoing progress and inventive thinking. This strategy improves long-term resilience in a rapidly changing market.
3. Capital Structure Optimization
Balancing debt and equity promotes financial stability and reduces risks. A smart financial management strategy ensures that resources are allocated effectively to promote growth. This balance also leaves room for future investments and expansions. Careful preparation in this area improves a company’s financial situation.
4. Retirement or Exit Strategy
A clear plan for mergers, acquisitions, and business succession is essential. A well-planned exit strategy guarantees seamless leadership transfers and stability. Following IFRS standards promotes openness and increases investor trust. This preparedness ensures the business’s long-term prosperity.
5. Long-term Profitability
Consistent profitability ensures a solid market position and future opportunities. Businesses in Singapore link their financial goals with market demand and forecasts. To maintain profitability, strategies must be evaluated and refined on a constant basis with a financial audit. This concentration promotes resilience in the face of market volatility.
6. Build Financial Reserves
Building financial reserves is crucial for long-term financial stability. By setting aside funds for future uncertainties, businesses can ensure they remain resilient in the face of economic shifts or unexpected challenges. This strategy also promotes investor confidence and allows for strategic flexibility.
Strategic Approach to Achieving Financial Goals
Achieving financial goals for a firm takes more than just setting targets. It also necessitates a clear and planned approach. Businesses must transform these goals into daily actions in order to stay on track with their long-term strategy. A strategic strategy enables businesses to manage resources, foresee issues, and adapt as needed. Below are numerous practical strategies that help firms attain their financial targets:
1. Detailed Planning
Breaking down financial goals into smaller, more manageable tasks is a wise first step. This includes determining KPIs, streamlining inventory accounting, creating realistic timetables, and assigning tasks to the appropriate people.
A thorough plan helps businesses stay focused and minimize confusion. This strategy keeps everyone in sync and accountable.
2. Budgeting and Forecasting
Accurate budgeting helps organizations stay on track while planning for potential risks. Forecasting future performance provides a better understanding of financial health. Implementing a digital financial control system helps to provide exact and up-to-date data. With accurate forecasts, decision-making becomes more dependable.
3. Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular monitoring allows businesses to closely monitor their financial success. Reviewing financial data can help you uncover gaps and areas for development. Businesses can quickly modify methods to stay on pace with their goals. This behavior improves financial resilience in the long run.
4. Investment Strategies
Smart resource allocation promotes long-term growth and innovation. Companies frequently adjust their investment plans after learning from market developments. Recognizing the importance of opportunity cost helps businesses make more informed investment choices. Aligning corporate objectives with financial goals provides long-term investment benefits. This promotes future success and stability.
Using Accounting Software Like ScaleOcean to Achieve Financial Goals
ScaleOcean is a reliable source of accounting software in Singapore that helps businesses manage their money more efficiently. ScaleOcean, with features geared for both SMEs and larger enterprises, helps businesses track financial performance, optimize cash flow, and keep accurate records. Businesses that use an integrated system, such as ScaleOcean, can stay on track with their financial goals, improve decision-making through real-time data, and maintain compliance with local rules.
Companies interested in learning more about how ScaleOcean may improve their financial management should request a free demo. Additionally, eligible Singaporean enterprises can use the CTC grant to make implementation more reasonable. This opportunity offers businesses to understand how ScaleOcean may meet their demands while optimizing value. Here’s a summary of the main features from the ScaleOcean software:
- Real-time Financial Data: Instant access to real-time financial data for faster, more accurate decisions.
- Budgeting and Forecasting Tools: Automated budgeting and forecasting for precise financial planning.
- Automated Reports and Analytics: Instant, accurate reports to monitor financial progress effortlessly.
- Cash Flow Monitoring: Real-time tools to track income, expenses, and liquidity with ease.
- Strategic Financial Insights: Advanced analytics to reveal opportunities and risks for smarter decisions.
Conclusion
Setting specific short-term and long-term financial objectives is critical for guaranteeing corporate growth, stability, and sustainability. These goals provide direction, aid in progress measurement, and enable businesses to make informed decisions that are consistent with their strategic objectives. Without clear goals, firms risk losing focus, making it more difficult to manage resources effectively and achieve consistent development.
For Singapore firms, using the correct tools, such as dependable accounting software, can substantially ease the process of defining, tracking, and attaining financial goals. ScaleOcean provides an entire solution to assist businesses in managing their finances more efficiently, including real-time analytics, automation, and strategic analysis to ensure long-term success. Now is the moment to look into ScaleOcean and take charge of your company’s financial future.
FAQ:
1. What are examples of financial goals?
Below are several examples of financial goals commonly set by businesses:
1. Boosting profit margins within a specific period.
2. Strengthening cash flow to support smooth business operations.
3. Lowering unnecessary operating expenses to improve efficiency.
4. Reaching targeted monthly, quarterly, or yearly revenue milestones.
5. Building savings for future investments or company expansion.
6. Settling outstanding debts to improve overall financial health.
2. What is a financial goal in business?
A financial goal in business is a specific target aimed at improving how a company handles its finances. These goals serve as a guide for financial planning, budgeting, and investment decisions. Common objectives involve raising revenue, minimizing expenses, or keeping cash flow healthy. Meeting these goals helps maintain the company’s financial strength and competitiveness.
3. What are the goals of business finance?
Here are the main purposes of business finance:
1. Maximizing profitability through effective resource allocation and strategic planning.
2. Securing liquidity to ensure the company can meet short-term obligations smoothly.
3. Managing risks to protect the business from unexpected financial challenges.
4. Supporting sustainable growth to achieve long-term financial security and success.
4. What are the top 3 goals for business?
These are typically the top three goals that businesses prioritize:
1. Increasing profits to deliver returns and support reinvestment opportunities.
2. Maintaining healthy cash flow to meet operational needs and financial obligations.
3. Achieving steady growth for long-term stability and to remain competitive in the market.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















