International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are globally recognized principles developed by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) to ensure financial reporting consistency and openness. Singapore accepted IFRS Standards with minor changes, resulting in the Singapore Financial Reporting Standards (SFRS).
According to PWC, as the deadline for IFRS-based climate reporting approaches, the SBF conducted a survey and roundtable with 40 small- and mid-cap companies to gauge their readiness. This aligns with Singapore’s adoption of IFRS, ensuring consistent and transparent financial reporting under SFRS.
This alignment enables Singapore enterprises to publish credible financial reports, which boosts investor confidence and facilitates cross-border operations. In Singapore, the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) requires all publicly traded firms to follow SFRS, guaranteeing consistency with worldwide financial norms and improving the city-state’s status as Asia’s premier financial hub.
- IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) is a comprehensive global set of accounting rules that govern global financial reporting.
- The Purpose and Benefits of IFRS include simplifying reporting with automated processes, standardized templates, and consistent, transparent financial statements, and more.
- Key Features of IFRS ensure global consistency, flexibility through principles-based standards, and are required for many entities to promote transparency and reliable reporting.
- ScaleOcean’s accounting system offers an innovative accounting system created exclusively for Singapore firms to ensure seamless compliance with IFRS.

1. What Are IFRS?
IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) is a comprehensive global set of accounting rules that govern global financial reporting. IFRS, which covers issues such as revenue recognition, leasing, and financial instruments, ensures consistency, transparency, and comparability in accounting methods across businesses and nations.
With over 140 nations adopting IFRS, including Singapore, it is the most widely accepted framework for international financial reporting standards.
IFRS is the accounting standard that corporations in the European Union and other countries must adopt, showing its global relevance. In Singapore, IFRS adoption promotes transparency and comparability, which are critical for attracting foreign investment and sustaining the country’s competitiveness as a global financial hub.
2. IFRS Compliance in Singapore
In Singapore, the Accounting Standards Council (ASC) is in charge of overseeing the adoption and implementation of SFRS to ensure compliance with IFRS. The Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) monitors compliance and requires correct financial reporting, including the accurate management of accounts receivable.
Adherence to IFRS improves company credibility, facilitates access to foreign markets, and simplifies reporting for multinational firms based in Singapore.
According to Allen and Gledhill, beginning in FY 2025, the Singapore Exchange Regulation (SGX RegCo) will require climate-related disclosures that are consistent with the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards, reinforcing Singapore’s commitment to global reporting rules.
3. Key IFRS Standards Relevant to Singaporean Companies
Singaporean enterprises must focus on numerous essential IFRS standards to ensure compliance with both local and international obligations. These Singapore financial accounting standards handle complicated financial reporting difficulties by establishing a systematic approach that improves accountability and investor confidence.
Proper adoption of these standards also makes audits easier and promotes financial transparency for stakeholders.
a. IFRS 16 – Leases
Companies are required to recognize lease assets and liabilities, which provides a more complete financial picture. This standard eliminates the distinction between operating and finance leases for lessees, guaranteeing that all leases appear on the balance sheet. The ERP finance module can assist in automating and managing this process, ensuring compliance with the latest accounting standards.
For Singaporean enterprises with large leasing agreements, such as those in retail and logistics, IFRS 16 improves financial transparency. It also helps with financial planning by giving a more accurate picture of a company’s long-term responsibilities.
b. IFRS 17 – Insurance Contracts
Establishes consistent reporting for insurance contracts, which improves compatibility. This standard replaces antiquated processes with a standardized way to recognize revenue and quantify liabilities in insurance companies.
Singapore’s strong insurance sector, which includes both foreign and indigenous businesses, benefits from more transparency in analyzing risks and earnings. Furthermore, IFRS 17 increases investor trust by guaranteeing that reported financial information accurately reflects the economic realities of insurance contracts.
c. IFRS 9 – Financial Instruments
Determines the classification and measurement of financial assets and liabilities. This standard establishes an expected credit loss model, which requires businesses to account for probable future losses on financial instruments, while also providing insights that can be used to calculate the financial leverage formula for assessing capital structure.
For Singaporean banks and financial institutions, IFRS 9 improves risk management by making credit loss reserves more forward-looking. It also improves the transparency of financial statements, allowing investors to better comprehend the institution’s credit and market risks by analyzing key metrics like the accounts payable (AP) turnover ratio.
4. Purpose and Benefits of IFRS
The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) offer a global set of guidelines for financial reporting, promoting clarity, consistency, and comparability across businesses worldwide. Adopting these standards helps companies align with international norms, building trust with investors and enhancing decision-making.
Here are the key benefits of IFRS that help businesses improve their financial reporting and meet global expectations:
a. Automated Reporting
One of the biggest advantages of IFRS is the ability to automate financial reporting, saving time and effort. Automation streamlines the process, allowing businesses to generate accurate reports quickly, making it easier to meet IFRS deadlines and stay compliant.
With automated reporting, companies reduce the risk of human error and improve efficiency. This also ensures they can quickly adjust to any updates or changes in IFRS, maintaining compliance without delays or hassle.
b. Standardized Templates
IFRS helps businesses follow standardized templates for financial statements, ensuring consistency in how reports are presented. This makes it easier for stakeholders to compare financial data across different companies and industries, fostering better understanding and analysis.
Using standardized templates also simplifies the reporting process. Instead of spending time formatting, businesses can focus on entering accurate data, ensuring that reports are clear, consistent, and easy to interpret for all involved parties.
c. Transparency & Consistency Across Reports
IFRS increases transparency by providing clear guidelines for how financial data should be presented. This clarity removes uncertainty, ensuring that companies present reliable and comparable financial information that stakeholders can trust.
The consistency that IFRS ensures across reports makes it easier for investors and regulators to analyze financial data. With a uniform approach, stakeholders can more confidently compare financial performance across companies and industries, leading to better-informed decisions.
d. Instant Access to Data
IFRS enables businesses to access real-time financial data, allowing key decision-makers to stay informed at all times. Instant access to accurate, up-to-date information means businesses can act quickly in response to changes and emerging trends in the market.
Having real-time access to financial data also helps companies keep their records current. This proactive approach to financial management helps businesses spot issues early, making it easier to correct discrepancies and avoid potential mistakes.
e. Global Consistency in Financial Language
One of the main benefits of IFRS is that it creates a universal financial language. Companies across the world can report their financial performance using the same terminology and standards, making it easier for global investors to compare and understand financial data.
This consistency helps break down language barriers in financial reporting. With a common approach to reporting, international businesses can communicate more effectively, which strengthens cross-border trade and attracts global investment, contributing to greater market stability.
5. Key Features of IFRS
The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) were created to bring consistency and transparency to financial reporting worldwide. These standards help companies present their financial health clearly, so stakeholders can make more informed decisions.
Here are some key features that define IFRS and its impact on global financial reporting:
a. Worldwide Standard
IFRS is recognized across many countries, making it a global standard for financial reporting. Its widespread adoption allows multinational companies to report their financials consistently, making it easier to compare data across borders.
By adopting IFRS, countries aim to make financial reporting more transparent. This global standard helps investors and regulators easily compare financial statements, contributing to a more stable global financial environment.
b. Based on Principles
Unlike more rigid, rule-based accounting standards, IFRS is principles-based. This gives companies more flexibility in applying the standards to suit their unique situations. The focus is on capturing the true nature of transactions rather than just following detailed rules.
This approach allows for more accurate reporting in cases where strict rules might not be sufficient. It helps ensure that financial statements reflect the real economic picture, making them more relevant and reliable for users.
c. Required for Numerous Entities
IFRS is mandatory for public companies and many other organizations worldwide, especially those listed on stock exchanges. This requirement helps ensure transparency and consistency in how companies report their financial performance.
For businesses operating in several countries, IFRS makes financial reporting easier. By following one unified set of standards, companies can simplify their reporting process, reducing costs and improving clarity across global markets.
d. Overseen by IASB
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) is in charge of developing and updating IFRS. This independent body ensures that the standards evolve to meet the changing needs of the global economy, keeping them relevant and up to date.
The IASB works with national standard-setters to maintain consistency in IFRS across different regions. By overseeing these standards, the IASB helps uphold fairness and transparency in global financial reporting.
e. Addresses Extensive Areas
IFRS covers a wide range of financial topics, from revenue recognition to lease accounting. Its broad scope means that it provides clear guidance on almost every aspect of financial reporting, helping businesses stay consistent in how they present financial information.
This comprehensive coverage ensures that companies in different industries, whether in banking, retail, or manufacturing, can follow the same standards. It helps create uniformity in reporting, making it easier to compare financial performance across various sectors and markets.
6. Important Requirements for IFRS Reporting
Under IFRS, companies need to share key financial reports that show how they’re really doing. These statements keep things clear and consistent for investors everywhere. Let’s take a look at the essential reporting requirements you’ll need to know:
- Balance Sheet: Under IFRS, your balance sheet should give a crystal-clear snapshot of where your business stands. By organizing assets, liabilities, and equity in a structured way, you keep things transparent for stakeholders while staying fully compliant with the standards.
- Income Statement: An IFRS income statement shows exactly how profitable a company is over time. It’s all about reporting your revenue and costs in a way that truly reflects your performance, following clear guidelines so that your results are easy to compare with others.
- Statement of Equity Changes: In IFRS reporting, the equity statement gives you a clear look at how your funds move. It shows exactly how things like earnings and extra capital change your equity over time. This breakdown is great for transparency and keeping everyone on the same page.
- Cash Flow Statement: An IFRS cash flow statement is your best tool for seeing exactly how money moves in and out of your business. It’s essential for checking your liquidity and making sure your financial reporting stays spot-on and fully compliant with IFRS standards.
7. Challenges in IFRS Implementation
Applying IFRS is difficult due to the technical complexity of the standards and the resource requirements for compliance. SMEs may struggle to match their operations with global needs. ERP modules with IFRS-compliant capabilities can simplify procedures, automate reporting, and make compliance easier.
a. Complexity
The complexities of IFRS can overwhelm firms without committed accounting resources. Each standard consists of complex rules and calculations that require a high level of skill to grasp and apply appropriately.
For example, the use of IFRS 16 for lease accounting necessitates extensive data collection and analysis of all leasing agreements. Smaller enterprises in Singapore may struggle with technical aspects, necessitating the use of external consultants to overcome expertise gaps.
b. Cost of Transition
Transitioning to IFRS necessitates training, technology changes, and compliance monitoring. Companies must invest in specialized accounting software and train their employees to meet the new reporting standards while also aligning with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles to ensure holistic corporate accountability.
In Singapore, where personnel and technology expenses are rather high, this transformation could have a substantial impact on operational budgets. Furthermore, firms may need to set aside resources for external audits to verify compliance during the first adoption phase.
c. Ongoing Updates
Businesses must keep up with continuous changes to IFRS standards. The IASB regularly revises guidelines to reflect changing financial practices, forcing businesses to adapt swiftly.
In Singapore, businesses must ensure that their accounting professionals are regularly taught to understand and apply these revisions. Failure to keep up with developments can lead to noncompliance, lowering investor trust, and result in regulatory penalties.
8. Differences Between IFRS and GAAP
IFRS focuses on principles, giving businesses the room to adapt standards to their specific needs. Unlike the more rigid, rules-based GAAP, this flexibility is a big reason why so many countries use it, because it easily fits different markets and regulations.
Unlike GAAP’s strict rules, IFRS lets you use more professional judgment when reporting. This helps your financial statements show a truer picture of your business’s health while keeping things consistent and clear for investors all around the world.
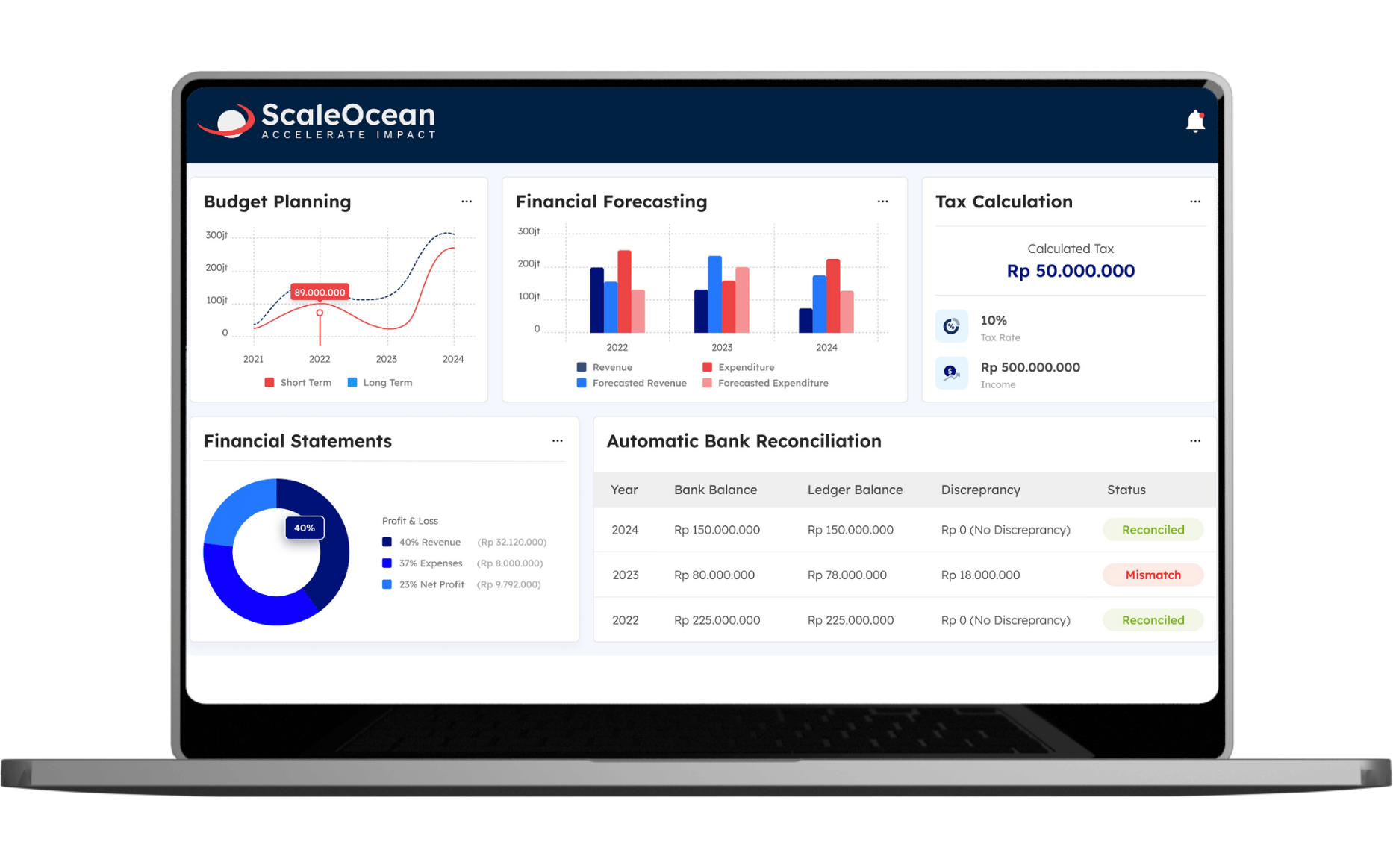
9. ScaleOcean: Tailored Accounting Solutions for IFRS Compliance
ScaleOcean’s top accounting system offers an innovative accounting system created exclusively for Singapore firms to ensure seamless compliance with IFRS. Its complete platform provides accuracy and efficiency while eliminating the burden of manual reporting.
ScaleOcean automates IFRS compliance, allowing businesses to focus on strategic growth rather than administrative responsibilities. Businesses interested in learning more about ScaleOcean’s capabilities can take advantage of a free demo to see the benefits for themselves.
a. Key Advantages
ScaleOcean’s strong features handle the specific demands of Singaporean firms, assuring compliance while streamlining financial procedures. Its easy tools decrease the problems of adhering to complicated standards, giving both precision and efficiency.
- Pre-Built IFRS Templates: ScaleOcean eliminates the need for accounting staff to manually update templates, allowing them to focus on analytics. These templates are intended to meet the most recent IFRS and SFRS criteria, ensuring compliance without additional customization.
- Integrated Features: The software integrates accounts payable, receivable, and general ledger administration to streamline operations. This connectivity maintains uniformity across all financial activities, allowing teams to collaborate more effectively and efficiently.
- Ease of Use: Accounting experts can prepare compliant reports with ease thanks to an accessible UI. The user-friendly design lowers the learning curve, allowing teams to maximize production from the start.
b. Benefits
ScaleOcean is designed to meet the unique regulatory environment of Singapore, ensuring businesses remain competitive and compliant. Its solutions are scalable and configurable, making it an excellent alternative for businesses of all kinds, from startups to huge organizations.
- Compliance Guarantee: Automated updates assure compliance with the most recent IFRS and SFRS standards. Businesses no longer have to worry about manual adjustments or missed regulatory changes. Accounting teams can rest easy knowing that ScaleOcean is committed to compliance.
- Scalability: Adaptable to increasing transaction volumes, enabling both small and large organizations. ScaleOcean expands with your organization, providing capabilities that scale seamlessly as operations increase.
- Time Savings: Reduces manual effort, allowing accounting teams to focus on strategic responsibilities. Automated procedures improve workflow efficiency, allowing firms to focus on innovation and growth rather than repeated tasks.
10. Conclusion
IFRS compliance is crucial for Singapore businesses seeking to retain transparency, attract international investors, and compete on a global scale. Using accounting software such as ScaleOcean streamlines the compliance process, eliminates human modifications, and ensures correct reporting.
It also improves decision-making by delivering real-time information about financial performance, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to market needs. Learn how ScaleOcean can improve your financial reporting by signing up for a free demo now and experiencing seamless IFRS compliance firsthand.
FAQ:
1. Who Uses IFRS?
IFRS is implemented in over 140 countries, including regions in Europe, Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Oceania. It is either required or permitted for public companies to ensure global consistency in financial reporting.
2. Does Singapore use IFRS or GAAP?
Singapore follows the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) with slight adjustments, known as the Singapore Financial Reporting Standards (SFRS), aligning closely with IFRS to ensure global consistency while catering to local needs.
3. What are the 4 pillars of IFRS?
The four core pillars of IFRS S1 and S2 are governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics & targets, which outline how sustainability-related disclosures should be structured in line with global standards.
4. How many rules are in IFRS?
There are 17 core IFRS standards, from IFRS 1 to IFRS 17, addressing different aspects of financial reporting. The total number may change as new standards are introduced or older ones are updated or replaced.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















