In today’s fast-paced business environment, choosing the right accounting software can make all the difference in staying ahead of the competition. Whether your business is a startup or an established enterprise, having efficient accounting software in Singapore is crucial for streamlining your financial processes.
Choosing the wrong accounting software can impact the stability of business processes, such as difficulty in improving the accuracy of financial reports, slowing cash flow, and increasing the risk of errors in tax and regulatory management.
Therefore, companies must consider many aspects when selecting the right accounting software that meets their needs, so that the system can be optimally implemented to manage business finances comprehensively.
This article will discuss accounting software in depth, including 23 recommendations for the best accounting software for you to consider, including definitions, functions, comprehensive features, and tips for choosing the most suitable software. Learn more here.
- Accounting software automates financial tasks like bookkeeping, invoicing, and payroll, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
- Key features of accounting software include invoicing, expense tracking, financial reporting, and multi-currency support for easy financial management.
- Best accounting software for businesses in Singapore includes ScaleOcean, Xero, Zoho Books, QuickBooks, and NetSuite, each offering pricing models to suit different business needs.
- ScaleOcean is an all-in-one solution that integrates with other business modules, offering real-time reporting and customizable insights.

What Is Accounting Software?
Accounting software is a digital tool designed to help businesses manage and streamline their financial processes. It automates tasks in accounting systems such as bookkeeping, invoicing, payroll, and tax calculations, ensuring accuracy and reducing human error.
The rising demand for automation in financial management process is one of the key factors driving the growth of ERP software in Singapore. According to a report by TechSci Research, the Singapore ERP software market is expected to grow significantly due to the increasing adoption of digital transformation by businesses of all sizes.
Accounting software Singapore gives businesses real-time financial insights through capabilities including spending tracking, financial reporting, and interaction with other systems.
It simplifies accounting procedures, which helps companies keep organized, adhere to rules, and make wise financial decisions. It also increases productivity and saves time while managing financial operations, making it ideal for small to large enterprises.
Key Benefits of Accounting Software
Implementing an accounting system is a strategic step in streamlining operations, ensuring compliance, and supporting your decision-making. Especially in a fast-growing global hub like Singapore, using this software is the right solution for your company. Here are some of the benefits:
1. Streamlined Financial Processes
Automated Data Entry that can record real-time transactions and eliminate manual spreadsheets and repetitive bookkeeping tasks. Efficient Report Generation, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, is just a click away.
By implementing an accounting system, companies can also easily track their financial metrics without getting bogged down in complicated calculations.
2. Regulatory Compliance Made Easier
Automatically calculate Singapore Special Taxes such as Goods and Services Tax (GST). This helps ensure your company complies with Singapore’s IRAS (Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore) regulations.
If regulations are subject to change, accounting software Singapore can perform automatic updates and reflect the latest regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance and costly fines.
3. Time and Cost Efficiency
Automating routine accounting tasks frees up employees to focus on strategic activities such as business analysis and development rather than day-to-day bookkeeping. By streamlining processes, you’ll likely reduce the need for external accounting services.
4. Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Accounting system uses a double-entry accounting bookkeeping system, which ensures that every transaction is balanced. This helps catch inconsistencies early and maintain financial accuracy. Additionally, the system can align with Singapore’s financial accounting standards to ensure compliance with local regulations.
In addition, the software can also perform Automatic Bank Feeds, so transactions are updated in real-time. This reduces manual data entry and helps you reconcile bank statements more quickly and accurately.
5. Enhanced Data Security and Backup
The Application accounting has a Secure Cloud solution using strong encryption methods to protect your financial data from unauthorised access. Frequent data backups reduce the risk of losing critical information. In the event of a system failure or cyber threat, you can quickly restore your data and resume normal operations.
6. Financial Insights and Better Decision-Making
Real-Time Financial Dashboard and accessible anytime, anywhere. With a clear picture of cash flow, expenses, and income, you can make decisions quickly. The accounting system also provides a forecasting module that predicts future income and expenses.
Types of Accounting Software in Singapore
Accounting software is crucial for businesses to streamline financial management and ensure accurate reporting. There are several types of accounting software available, each offering unique features suited to different business needs.
Choosing the right types depends on factors such as business size, industry, budget, and technical requirements. Below, we explore the different types of accounting software and how they cater to various organizational demands, including:
1. Manual Accounting Systems
Manual accounting systems rely on traditional paper-based methods for tracking financial transactions. For example, small businesses with limited financial activity often use a Spreadsheet. While it offers low upfront costs, it is highly time-consuming, prone to human error, and lacks scalability as the business grows.
2. Computerized Accounting Software
Computerized accounting software automates basic accounting tasks such as ledger management, invoicing, and payroll. It improves accuracy, speeds up processes, and allows for easier financial reporting. However, it still requires manual data entry and can be limited by the features provided in the software.
3. Cloud-Based Accounting Systems
Cloud accounting systems store financial data on remote servers, allowing businesses to access their accounts from anywhere. These systems offer scalability, real-time updates, and automatic backups. They typically require a subscription but offer increased flexibility and reduced IT maintenance costs.
4. ERP-Based Accounting Software
ERP-based accounting software integrates accounting with other enterprise functions like supply chain, HR, and customer relations. It provides a comprehensive solution for larger businesses by centralising all data in one platform.
Integration with financial ERP systems improves accuracy and efficiency but can be expensive and complex to implement.
5. Hybrid Accounting Software
Hybrid accounting software combines the features of both cloud-based and desktop solutions. It allows businesses to store data on-site while accessing certain features through the cloud. This offers flexibility and greater control over sensitive financial data while still benefiting from cloud computing features like remote access and updates.
6. Commercial Off-the-Shelf Software
Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) accounting software is a ready-made solution designed for general use across multiple industries. It offers essential accounting features at a lower cost than custom software but may lack the flexibility to meet specific business needs. Examples include QuickBooks and Xero.
7. Custom Accounting Software
Custom accounting software is built specifically for a company’s unique needs, offering high flexibility and scalability. While it can be expensive and time-consuming to develop, it provides tailored features that perfectly align with the business’s operations and can integrate seamlessly with other internal systems.
8. Desktop Accounting Software
Desktop accounting software is installed directly on a computer and operates without an internet connection. It is typically more affordable than cloud-based systems and offers a one-time payment option. However, it lacks the convenience and remote access features that cloud-based systems provide.
9. Open-Source Accounting Software
Open-source accounting software is freely available and allows businesses to modify the software’s source code to fit their specific needs. It offers high customization but requires technical expertise to implement and maintain. Popular examples include GnuCash and LedgerSMB.
Essential Features in Accounting Software
Accounting software offers key features that simplify these tasks, making your business finances easier to manage, more accurate, and much more efficient. So companies in Singapore need to choose software with some of these features. Here are 8 key features of software for your company:
1. Invoicing and Billing
The capability to generate, issue, and manage invoices is a necessity for every accounting program. Reduced errors, time savings, and on-time client payments are all benefits of automated invoicing.
For businesses learning about invoice vs receipt, it is also important that notifications of past-due bills and payment reminders are generated by the program.
2. Expense Tracking
Tracking expenses is important for maintaining financial health. Application accounting should allow users to categorize expenses, attach receipts, and monitor spending. This feature ensures businesses stay on top of their cash flow and helps in preparing for tax deductions.
3. Online Payments
Online payment integration allows businesses to accept payments directly through their accounting software. It streamlines the payment process, offering customers multiple payment options such as credit cards, e-wallets, and bank transfers.
This feature of accounting software can also improve cash flow by accelerating payments, reducing administrative tasks, and enhancing the customer experience.
4. Tax Compliance
Tax compliance features help businesses stay up-to-date with the latest tax regulations and ensure accurate tax reporting. The software automatically calculates taxes, generates tax reports, and provides necessary documentation for tax filing.
This feature can reduce the risk of errors, penalties, and the need for manual calculations, streamlining the tax process for businesses.
5. Snapshot Reports
Snapshot reports provide real-time, visual overviews of a company’s financial status. These reports offer quick insights into key metrics such as revenue, expenses, and profit margins, allowing business owners and managers to make informed decisions.
Companies can customize the accounting system to meet specific business needs and help track performance against goals.
6. Enhanced Cash Flow Management
Enhanced cash flow management tools within accounting software allow businesses to track and predict their cash inflows and outflows. By integrating with the best invoice software, businesses can streamline their invoicing process, track outstanding invoices, and manage upcoming bills, ensuring that they stay on top of expected payments.
These tools provide insights into outstanding invoices, upcoming bills, and expected payments, helping businesses maintain a positive cash flow. This feature helps prevent liquidity problems and ensures that funds are available when needed.
7. Financial Forecasting
Financial forecasting tools allow businesses to project future financial outcomes based on historical data and current trends. This feature helps companies plan for growth, anticipate challenges, and make strategic decisions.
By forecasting revenue, expenses, and profits, companies can also allocate resources more efficiently and prepare for potential financial scenarios.
8. Bank Reconciliation
Businesses can link their bank accounts and accounting systems through bank reconciliation. This function makes it easy to identify discrepancies and maintain accurate financial records by comparing the software’s records with actual bank statements.
9. Multi-currency Support
Multi-currency support is essential for companies that conduct business internationally or interact with clientele from other countries. Software should be able to handle transactions in different currencies, automatically convert rates, and provide accurate reports.
10. Integration with Other Systems
Good software should integrate seamlessly with other business systems such as accounts payable automation systems, CRM, ERP, e-commerce platforms, and payment gateways. This guarantees that data flows seamlessly across all departments, hence increasing overall efficiency.
23 Best Accounting Software in Singapore
When choosing the right software for your business, it is important to understand which solution aligns best with your company’s needs. The list below includes the top 23 accounting software programs that may help firms enhance their operations and achieve maximum efficiency in accounting processes.
Here are the best accounting software that companies can compare and use for optimizing accounting processes, including:
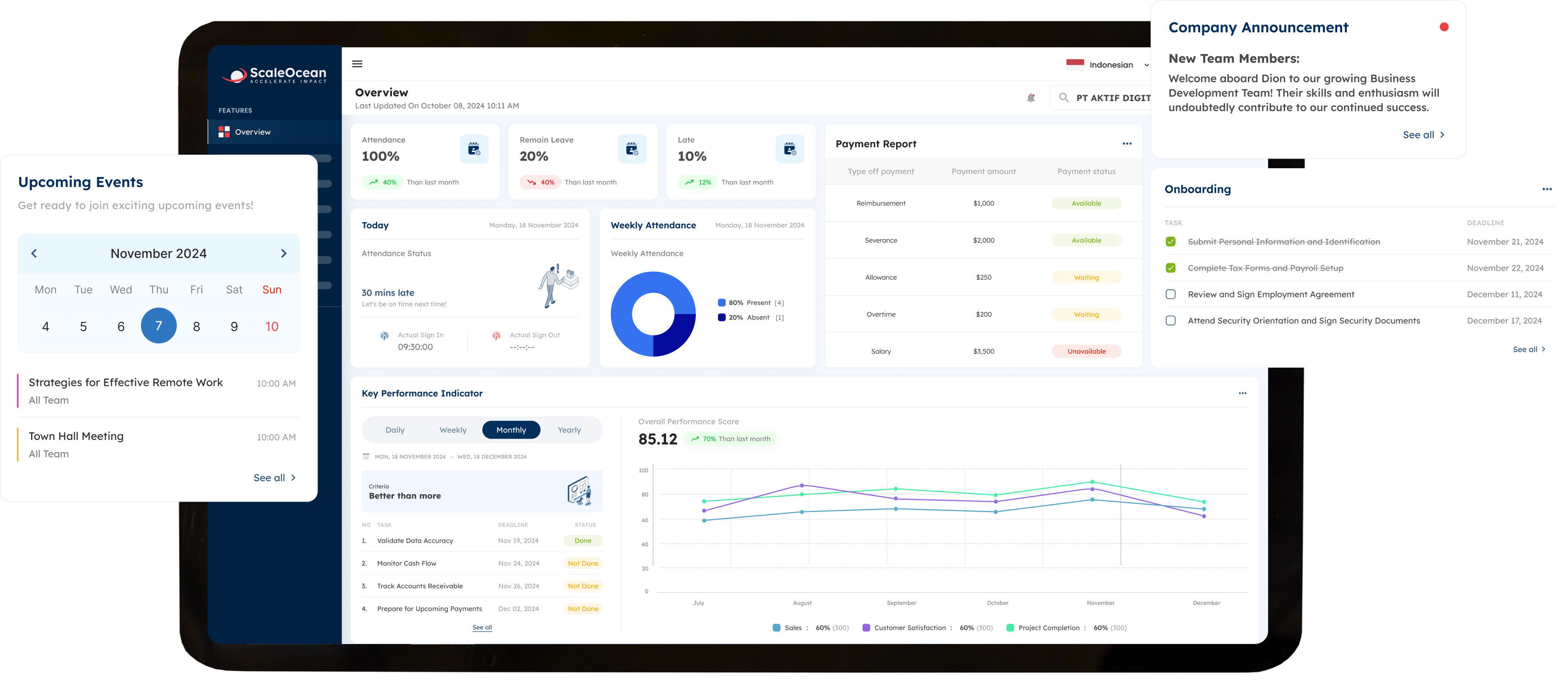
1. ScaleOcean
ScaleOcean accounting software is a system that manages a firm’s financial data with high efficiency and accuracy. It enables businesses to automate financial transaction recording and connects smoothly with other business modules, like as sales, purchasing, and inventory, maintaining a consistent flow of financial data between departments.
The ScaleOcean accounting system assists businesses in creating financial reports, including cash flow reports, profit and loss vs budget reports, and balance sheets.
Additionally, ScaleOcean, which has become IRAS-approved accounting software, can ensure these reports are generated accurately and in real-time, providing valuable insights into your company’s financial health.
With its user-friendly interface, even complex financial data can be presented in an easy-to-understand format, enabling business owners and finance teams to make informed decisions quickly.
The ability to customize reports allows businesses to tailor financial statements according to their specific needs, ensuring compliance with local accounting standards in Singapore. You can get a free demo for more information and maximum implementation
Key Features:
- Bank Integration with Auto-Reconciliation: Automatically compares internal records and transactions entered into the bank, guaranteeing correctness and cutting down on human entry.
- Bank Integration with Auto-Payment: Automates scheduled payments to vendors, ensuring timely payments.
- Multi-Level Financial Analysis: Facilitates branch or project-level analysis as well as comparisons of financial statements across several parameters.
- Forecast Budgeting: Provides tools for predicting future expenses and revenue based on historical data.
- Customizable Printouts for Invoices:
Adapts invoice forms to the needs of the client. - Tax Invoicing: Facilitates the automatic generation and printing of tax invoices directly from the system.
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
2. Xero
Xero accounting app is a cloud-based accounting solution designed for small to medium-sized businesses, also the preferred choice for accountants. The system offers a user-friendly interface, essential financial management tools, also integration capabilities.
Key Features:
- Invoicing
- Bank Reconciliation
- Multi-Currency
- Financial Reporting
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
3. FreshBooks
FreshBooks accounting app is a cloud-based solution primarily designed for freelancers and small businesses, and service-based industries. It offers intuitive tools for accounting, managing invoicing, expenses, and time tracking.
Key Features:
- Invoicing
- Expense Tracking
- Time Tracking
- Payments
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
4. QuickBooks Online
QuickBooks is a cloud-based accounting system that is commonly used for financial management by small and medium-sized businesses, offering features like invoicing, expense tracking, and bank reconciliation to handle their accounting needs with ease and efficiency.
It provides a range of features that can manage finances, including invoicing, payroll processing, and tax reporting. This system, as part of the finance module in ERP, also ensures compliance with local regulations.
- Invoicing
- Bank Reconciliation
- Payroll Integration
- Financial Reporting
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
5. Zoho Books
Zoho accounting system is a cloud-based financial management solution with a user-friendly interface and is designed for small to medium-sized businesses. It offers a range of features for accounting, invoicing, and financial reporting, also time tracking and role-based access.
Features:
- Invoicing and Estimates
- Expense Tracking
- Bank Reconciliation
- Multi-Currency
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
6. NetSuite
NetSuite Accounting Software Singapore is a cloud-based financial management solution for enterprises and a good fit for medium-sized businesses that need a robust interface to connect with other systems. It offers a full set of tools for managing accounting, financial planning, and reporting.
Key Features:
- General Ledger
- Accounts Payable & Receivable
- Multi-Currency Support
- Financial Reporting
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
7. Wave Accounting
Wave Accounting is an accounting solution for small businesses and freelancers that offers essential accounting features and can simplify financial management through functions such as invoicing, bookkeeping, and tax reporting. The system also offers an easy-to-use interface for managing business accounting.
Key Features:
- Expense tracking with detailed reporting.
- Tax-friendly features for easy GST filing.
- Receipt scanning and document storage.
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
8. MYOB
MYOB accounting app is a versatile financial management solution tailored for small to medium-sized businesses, offering both cloud-based and desktop options with essential functionalities for GST compliance and budgeting.
Key Features:
- Payroll Management
- Inventory Tracking
- Bank Feeds
- Multi-Currency
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
9. Invoice2Go
Invoice2Go is a cloud-based invoicing and accounting solution designed for small businesses and offering a simple setup and accounting functions with comprehensive features. Including invoicing, expense management, and financial reporting.
Key Features:
- Cloud-based with easy access from anywhere.
- Automated data entry for expenses and invoices.
- Tax calculations and reporting for GST.
- Integrates with PayPal and other payment systems.
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
10. Kashoo
Kashoo is a cloud-based accounting software tailored to help small to medium-sized businesses. It offers features like invoicing, expense tracking, and bank reconciliation, also provides essential tools for managing financial tasks with a focus on ease of use and affordability.
Key Features:
- Invoicing and Billing
- Expense Tracking
- Financial Reporting
- Payroll Management
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
11. Financio
Financio software is a cloud-based accounting solution designed for businesses of all sizes, offering a wide range of financial management tools for invoicing, expense tracking, and inventory management.
Key Features:
- Invoicing
- Inventory Management
- Bank Reconciliation
- Financial Reporting
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
12. Osome
Osome is an accounting platform to simplify accounting and tax procedures. This cloud-based platform allows you to access your financial information at any time. In addition, Osome can ensure compliance with Singapore tax laws and regulations.
Key Features:
- Automated accounting and bookkeeping.
- Cloud-based platform with anytime access.
- E-filing for GST and corporate taxes.
- Mobile app for on-the-go access.
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
13. TrulySmall Accounting
TrulySmall accounting system is a cloud-based accounting solution designed specifically for very small businesses and freelancers, focusing on simplicity and essential financial functions.
Key Features:
- Invoicing
- Expense Tracking
- Bank Reconciliation
- Financial Reporting
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
14. Sage
Sage accounting software is a cloud-based and leading supplier of accounting and financial management software designed for growing businesses. It focuses on helping products designed to meet the needs of start-ups, sole traders, and small businesses by providing robust accounting capabilities with flexible customization options.
Key Features:
- Project Accounting
- Multi-Entity Consolidation
- Revenue Recognition
- Reporting and Dashboards
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
15. GnuCash
GnuCash is an open-source accounting app that provides double-entry accounting and is ideal for small businesses in Singapore. It is highly customizable and features robust financial management tools, allowing businesses to manage everything from transactions to reporting while maintaining compliance with Singapore’s accounting standards.
Key Features:
- Double-entry accounting system for accurate reporting.
- Budgeting and forecasting tools.
- Multi-currency and multi-language support.
- Customizable reports for tax filing.
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
16. SAP Business One
SAP Business One Accounting Software is an integrated enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution designed for small to mid-sized businesses, providing complete financial management together with additional tools for corporate processes.
Key Features:
- Financial Management
- Sales and Customer Management
- Inventory and Distribution
- Multi-Currency Support
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
17. Serenic Navigator
Serenic Navigator accounting system is a cloud-based financial management solution specifically designed for non-profit organizations, NGOs, and public sector entities. It provides tailored tools to manage grants, fund accounting, and donor contributions.
Key Features:
- Fund Accounting
- Grant Management
- Donor Management
- Budgeting and Forecasting
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
18. ePromis ERP Cloud
ePROMIS ERP Cloud is a comprehensive cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution designed for businesses of all sizes. It integrates financial management with various business operations, offering a full suite of tools for accounting, inventory, and project management.
Key Features:
- Financial Management
- Project Accounting
- Inventory and Procurement
- Reporting and Analytics
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
19. Odoo Accounting
Odoo app is part of the broader Odoo ERP suite, offering a comprehensive, cloud-based financial management solution for businesses of all sizes. It integrates seamlessly with other Odoo modules, providing a unified platform for accounting and business operations.
Key Features:
- Invoicing
- Expense Management
- Multi-Currency
- Financial Reporting
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
20. Vic.ai
Vic.ai Software is an AI-powered accounting automation platform designed to streamline and optimize financial processes. It uses artificial intelligence to handle routine accounting tasks, offering enhanced accuracy and efficiency in bookkeeping and financial management.
Key Features:
- AI-Powered Invoice Processing
- Real-Time Data
- Audit Trail
- Predictive Intelligence
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
21. ANNA
ANNA accounting app is a cloud-based financial management solution specifically designed for small businesses, freelancers, and sole traders. It simplifies accounting processes while offering integrated banking services.
Key Features:
- Invoicing
- Expense Tracking
- Tax Calculations
- Notifications
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
22. AccountsIQ
AccountsIQ accounting system is a cloud-based financial management solution designed for medium-sized businesses and multi-entity organizations. It offers advanced accounting features combined with business intelligence tools for enhanced financial control.
Key Features:
- Multi-Entity Consolidation
- Financial Reporting
- Budgeting and Forecasting:
- Accounts Payable & Receivable
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
23. Refrens
Refrens software is a cloud-based financial management platform designed primarily for freelancers and small businesses. It focuses on simplifying invoicing, expense tracking, and payments.
Key Features:
- Invoicing
- Payments
- Quotation and Estimates
- Financial Reporting
| Benefits | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|

What is the IRAS ASR+
IRAS ASR+ (Automated Submission and Reconciliation) is a system included in the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) that is designed to simplify and automate the submission and reconciliation process for businesses in Singapore. This system can facilitate efficient and accurate tax reporting so that businesses can submit their financial data directly to IRAS through electronic means.
This system can automate tax reconciliation, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing errors. With the use of IRAS ASR+, you can also simplify the reporting process for businesses by ensuring that all required data is submitted and reconciled accurately.
This will help companies ensure compliance with the complex tax regulations in Singapore. Companies can leverage ASR+ and the best tax software in Singapore to improve their operational efficiency and focus more on their core activities while meeting their tax obligations smoothly.
Best IRAS ASR+ Accounting Software
The IRAS ASR+ system has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses in Singapore do their tax reporting. As more businesses look for an easy-to-use accounting system to integrate with ASR+, several key players have emerged as top providers. Not only that, the system will also ensure accuracy and compliance with IRAS requirements.
Here are some of the best IRAS ASR+ accounting software Singapore providers that businesses can rely on to simplify their tax reporting and reconciliation processes, including:
1. Xion.AI Pte. Ltd
Xion. AI Pte. Ltd offers an innovative accounting system that works well with the IRAS ASR system. The software automates many tasks, reducing the need for manual data entry and ensuring accurate financial handling.
It helps businesses meet IRAS deadlines easily. Its user-friendly design and quick reporting make it ideal for companies looking for efficiency and compliance. With Xion. AI, businesses file taxes efficiently and gain valuable insights into their finances.
2. Autocount (S) Pte. Ltd
This software, Autocount (S) Pte. Ltd., offers comprehensive accounting solutions compatible with the IRAS ASR system. Their software handles invoicing, financial reporting process, and tax reconciliation, making it reliable for Singaporean businesses.
It automates accounting tasks, freeing up time for other business activities. The system supports multiple currencies, ideal for international companies. Autocount provides real-time data to help businesses stay compliant with tax requirements.
3. Metro Group Pte. Ltd.
Metro Group offers a user-friendly accounting software Singapore that integrates with IRAS ASR+, simplifies complex tasks like tax submission and reconciliation, and provides accurate financial data, automatic tax filing, and detailed reporting.
The solution from Metro Group gives companies precise financial data that satisfies the strict criteria of IRAS. Additionally, the software provides thorough financial reporting, enabling companies to make wise decisions while adhering to regional tax regulations.
4. Netiquette Software Pte. Ltd.
Netiquette Software Pte. Ltd. offers a reliable accounting solution for businesses integrating with the IRAS ASR+ system. It offers automated reconciliation, tax filing, invoice management, financial reporting, and multi-user access, allowing businesses to focus on growth.
With its user-friendly interface and emphasis on precise data processing, Netiquette makes sure that companies can concentrate on expansion while letting the software handle the hassles of tax filing.
Things to Consider When Choosing Accounting Software
In choosing the right accounting software, there are several things that you must consider carefully and according to your needs, such as financial reporting for accurate statements, tax compliance tools for easy filing, and bank reconciliation to match records with statements.
The accounting application chosen must also be capable of automated bookkeeping for routine tasks, real-time data access, invoicing and payment management, payroll management, and seamless integration with other business software.
Choosing the right accounting software can significantly improve your company’s financial management, although it can be difficult to choose the software that suits your needs due to the many alternatives available. Furthermore, you can do the following to choose the right system.
1. Assess Your Business Needs
Start by evaluating your company’s specific accounting requirements. Consider your company’s size, industry, and the intricacy of its financial dealings. Are you managing payroll, handling inventory, or dealing with multiple currencies? Identifying these needs will help you narrow down your options.
2. Determine Your Budget
Create a defined budget for software purchases. Accounting app comes with varying price points, from free versions for small businesses to premium packages for larger enterprises. Determine whether you prefer one-time payments for desktop software or recurring subscriptions for cloud-based options.
3. Check for Essential Features
Make a list of must-have features based on your business needs, such as invoicing, expense tracking, financial reporting, and payroll management. Ensure that the software you select offers these functions to fulfill your day-to-day accounting needs.
4. Consider Cloud vs. Desktop
Decide whether you want a cloud-based or desktop accounting solution. Cloud-based software offers flexibility, remote access, and automatic updates, whereas desktop software provides more control over data and security. Evaluate which choice best fits your business operations and security needs.
5. Evaluate User-Friendliness
The software should be easy to use, especially if your team has limited accounting experience. Look for intuitive interfaces, easy navigation, and minimal learning curves. A user-friendly solution ensures that your staff can quickly adopt the software without requiring extensive training.
6. Check for Integration Capabilities
Ensure the software can integrate with other tools you use, such as CRM systems, ERP solutions, or payment gateways. Seamless integration will streamline your operations and prevent the need for duplicate data entry.
7. Look for Scalability
Select software that grows with your company. You might require more sophisticated features or the capacity to manage more transactions as your business grows. Make sure the program is expandable so it can accommodate your future expansion.
8. Test for Customer Support and Training
Verify whether the software provider offers trustworthy customer support, including phone, email, and live chat support. In addition, determine whether they offer lessons, webinars, or a knowledge base to assist you in getting started and troubleshooting issues as needed.
9. Consider Compliance and Security
Ensure the software complies with your local accounting and tax regulations, such as GST or VAT reporting.
Furthermore, look for strong security features like data encryption, backups, and user access limits, especially if you’re going with cloud-based software.
10. Trial the Software Before Purchase
Most software providers offer a free demo. Take advantage of these to test the software’s functionality, ease of use, and how well it fits your business processes. Involve your finance team in the testing phase to gather feedback before making a final decision.
Conclusion
Choosing the right accounting software in Singapore is key to effective financial management. Whether cloud-based or traditional, software options offer various capabilities to suit your business needs.
IRAS accounting software, with its flexibility, real-time access, and scalability, helps businesses stay competitive and streamline operations for growth.
Suppose you are looking for an all-in-one solution to streamline your financial management. In that case, ScaleOcean accounting software Singapore offers the perfect cloud-based platform that brings flexibility and seamless integration to your business.
With ScaleOcean, you can easily manage your financial data, automate accounting processes, and ensure real-time accuracy, all from a user-friendly interface. Whether you’re a small business or a growing enterprise, our software is designed to scale with your needs.
Curious about how ScaleOcean can transform your accounting processes? Try it out risk-free with a free demo and experience how it can simplify your financial management while giving you more control over your business decisions.
FAQ:
1. Which system of accounting is mostly used?
The double-entry accounting is the most widely used and recognized accounting method. It tracks all three account types—real, nominal, and personal—ensuring accuracy in financial records by recording each transaction in two accounts and maintaining balance.
2. What accounting standard does Singapore use?
Singapore primarily uses the Singapore Financial Reporting Standards (SFRS) for businesses and entities within its borders. Multinational companies based in Singapore adhere to both SFRS and IFRS, depending on the specific needs of their international operations
3. What is the accounting method in Singapore?
In Singapore, businesses typically use the accrual accounting method, a key principle of local accounting standards. This method records revenues when transactions occur, rather than when payments are received, ensuring accurate financial statements that reflect the company’s financial health
4. Which accounting qualification is best in Singapore?
Accounting qualification in Singapore, becoming a Chartered Accountant (CA) with ISCA, is highly recommended. It is widely recognized, and many accounting roles require this designation, making it a top choice for local and international career opportunities.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















