Supply chain management includes all actions necessary to convert raw resources into completed goods and distribute them to customers. This sophisticated process comprises sourcing, design, production, warehousing, shipping, and distribution, all of which play critical roles in guaranteeing smooth operations.
The basic purpose of supply chain management is to increase efficiency, quality, productivity, and, ultimately, customer satisfaction. By managing these interconnected processes, organizations may build a strong and adaptable supply chain that can satisfy changing market demands while maintaining a competitive advantage.
Based on the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (LPI), Singapore is recognized as a key logistics hub in Asia, consistently ranking among the top performers globally for its advanced logistics infrastructure, efficient customs processes, and strategic connectivity to global markets.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the ongoing process businesses use to optimize and streamline their supply chains for peak efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Key phases of SCM cover planning, sourcing, production, distribution, returns, inventory, IT, and risk management to optimize efficiency and resilience.
- SCM benefits enhance collaboration, agility, profitability, risk management, and sustainability, driving efficiency, cost savings, and long-term growth.
- ScaleOcean SCM software optimizes the supply chain with integrated modules, improving visibility, coordination, and responsiveness to market demands.

1. What is Meant by Supply Chain Management?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the ongoing process businesses use to optimize and streamline their supply chains for peak efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It strategically oversees the flow of goods, services, information, and finances, from raw materials through delivery.
SCM’s core goal is to streamline processes, reduce operational costs, and boost productivity across the entire chain. By integrating functions like production and distribution, it enables businesses to meet customer demands effectively while maintaining profitability.
2. What is the Importance of Supply Chain Management?
Effective supply chain management provides various benefits to firms, including flawless operations and improved customer experiences. According to Barton International, SCM improves efficiency while also lowering operational costs and increasing profitability, making it an essential component of current corporate strategies.
It establishes a coherent approach that brings together resources, technology, and stakeholders. It also improves resilience by handling disturbances and ensuring consistent operations. The following are the primary reasons why SCM is essential:
a. Enhancing Efficiency
By optimizing operations, SCM lowers waste, delays, and ensures smooth workflows. This includes optimizing inventory management to avoid overstocking or shortages, as well as ensuring effective resource allocation. Additionally, streamlined processes promote improved collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, resulting in shorter response times and higher customer satisfaction. Understanding the value chain through SCM can significantly improve coordination between these processes.
b. Cost Optimization
SCM identifies cost-cutting opportunities throughout the procurement, production, and distribution processes. This includes using technology to examine spending trends, supplier performance, and general ledger data to ensure efficient resource allocation. Furthermore, cost savings are realized through bulk purchasing, improved logistics, and waste reduction in manufacturing processes.
c. Boosting Customer Satisfaction
A well-managed supply chain ensures on-time deliveries and high-quality items, which boosts customer loyalty. It reduces errors in order processing and inventory management, reducing delays and increasing reliability. It also creates consumer trust by constantly achieving expectations and responding quickly to service difficulties.
d. Supporting Scalability
SCM enables firms to effectively scale their operations by efficiently managing resources and processes. This scalability enables firms to respond to rising demand while maintaining quality and speed. Furthermore, it enables the smooth integration of new markets, suppliers, or technologies, ensuring that firms remain competitive and nimble.
3. Components and Phases of SCM
Supply chain management is made up of interconnected components and phases that ensure effective and smooth operations. These components form a systematic framework for managing resources, processes, and activities throughout the supply chain. Each phase is critical for synchronizing operating objectives, optimizing efficiency, and addressing difficulties in order to maintain a resilient and adaptable supply chain. The following are the main components and phases:
a. Planning
Planning involves forecasting demand and strategically allocating resources to guide purchasing and production. Accurate market prediction helps organizations avoid inventory issues and enhance responsiveness to market shifts while aligning actions with core corporate goals.
Effective planning prepares businesses for shifts in consumer demand, preventing costly overstocking or stockouts. It ensures that the supply chain strategy robustly supports long-term goals, cultivating seamless operations and driving sustainable growth for the company.
b. Sourcing
Sourcing involves strategically finding and selecting suppliers for materials and services. To ensure consistency, businesses evaluate partners based on reliability, cost, and quality, fostering long-term relationships that secure a dependable supply chain.
Optimizing sourcing practices helps businesses lower procurement costs, guarantee timely deliveries, and increase supply chain flexibility. A strategic sourcing approach strengthens supplier relationships, delivering mutual benefits and greater efficiency.
c. Production
Production efficiently transforms raw materials into finished goods using advanced technology and lean methods. Strict quality control ensures products meet all customer and industry standards, effectively minimizing operational waste and costly delays.
Streamlined production increases output while upholding high product quality. By enhancing operational efficiency, businesses can meet customer demands promptly and reduce costs, directly improving overall profitability and customer satisfaction levels.
d. Distribution
Distribution, or logistics, centers on the efficient delivery of products to customers. This core function involves managing transportation, warehousing, and inventory to ensure goods reach their final destination on time and in optimal, ready-to-use condition.
An efficient distribution network minimizes operational costs while significantly boosting customer satisfaction. Well-managed logistics enables businesses to quickly adapt to market demands, improving service delivery and solidifying long-term customer loyalty.
e. Return Process
The return process manages product returns due to defects or dissatisfaction. This phase is crucial for preserving customer trust and satisfaction by ensuring returns are handled efficiently, thereby minimizing any negative impact on the business.
An organized return process ensures swift handling of returned products for restocking, repair, or disposal. By defining clear policies and efficient logistics, businesses can significantly reduce costs and enhance the overall customer experience.
f. Inventory Management
Inventory management involves tracking optimal stock levels to reliably meet demand without excess. Optimizing this crucial process minimizes waste, reduces holding costs, and improves cash flow, while ensuring customers always have timely access to products.
Efficient inventory control is vital to prevent costly overstocking or stockouts, leading to smoother operations and significantly enhanced customer satisfaction. Integrating systems like warehouse execution software further strengthens control and streamlines order fulfillment efficiency.
g. Information Technology (IT) Systems
IT systems are pivotal for modern supply chain management, offering crucial real-time data visibility. Technologies like ERP, IoT, and AI enhance resource allocation, improve demand forecasting, and sharpen decision-making across all supply chain activities.
Integrating advanced IT systems connects departments and stakeholders, ensuring accurate information sharing. This technological foundation enhances overall efficiency, minimizes errors, and allows quicker market adaptation, ultimately driving superior business outcomes.
h. Risk Management
Risk management centers on identifying and addressing potential threats like supply chain disruptions, economic volatility, and transport issues. By proactively tackling these challenges, businesses can effectively safeguard their core operations and ensure the continuity of service delivery.
Implementing mitigation strategies, such as alternative sourcing and robust contingency planning, significantly enhances resilience. This ensures supply chains remain functional during disruptions. A solid risk management approach minimizes financial exposure and protects the company’s vital reputation.
4. What Are the Benefits of Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management provides numerous benefits that promote business growth and sustainability. Businesses may increase efficiency, save costs, and improve customer satisfaction by optimizing each stage of the supply chain.
According to Indeed, professionals in supply chain management, such as supply chain managers, earn an average salary of $86,594 per year in the United States, making it a lucrative career path. These benefits, taken together, create a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic marketplace. Here are the main benefits:
a. Improved Collaboration
SCM improves communication and coordination among stakeholders, suppliers, and customers. This collaboration promotes openness throughout the supply chain, resulting in faster decision-making and problem resolution. Furthermore, enhanced communication lowers misconceptions and builds trust, resulting in a more resilient and adaptable supply chain network.
b. Enhanced Agility
An efficient supply chain enables organizations to react rapidly to market developments and consumer expectations. It enables firms to change production levels, improve inventories, and streamline logistics to meet changing priorities. Furthermore, by evaluating real-time data, organizations may predict trends and align their strategy with client expectations.
c. Increased Profitability
Profit margins increase as processes are optimized and costs are reduced. Businesses can increase returns by streamlining procedures and avoiding unnecessary expenses. Furthermore, implementing efficient production procedures and utilizing economies of scale helps to sustain profitability in the long run.
d. Better Risk Management
SCM detects and manages potential risks, providing operational continuity. This includes examining supply chain vulnerabilities such as supplier reliability, geopolitical risks, and transportation interruptions. Businesses can prevent disruptions and maintain consistent operations even when faced with unexpected problems by employing preemptive steps such as alternate sourcing and contingency planning.
e. Sustainability
Integrating eco-friendly techniques into SCM encourages environmental stewardship and long-term growth. This strategy entails lowering carbon emissions, implementing renewable energy sources, and optimizing transportation routes to minimize environmental impact. It also promotes sustainable procurement and waste reduction activities, which help businesses connect with global environmental goals.
5. Types of Supply Chain Models
Businesses use many supply chain models depending on their specific needs, market dynamics, and operational objectives. Choosing the correct model allows firms to maximize productivity, cut costs, and improve their capacity to adapt to client demands. Here are the common models:
a. Continuous Flow Model
This model assures a constant production process, making it appropriate for high-demand products that require minimal variance. It eliminates operational difficulties and production downtime by ensuring a consistent flow of resources and standardized procedures. This technique is especially effective in businesses where consistency and dependability are critical to achieving consumer expectations.
b. Agile Model
This concept is designed to be adaptable to changing market demands and trends. It enables organizations to respond quickly to changes in consumer behavior, supplier disruptions, and unanticipated market possibilities. This concept helps firms sustain competitiveness in highly variable industries by focusing on adaptability first.
c. Fast Model
The fast model focuses on delivering items swiftly in time-sensitive markets. It is especially effective in areas that require rapidity, such as fashion or technology, where items have a short lifespan. By emphasizing rapid manufacturing and distribution, this approach assures that enterprises can meet consumer wants before trends change or products become outmoded.
d. Flexible Model
This strategy accommodates firms with seasonal or unpredictable demand patterns and allows for expansion. It is especially useful in areas like retail and agriculture, where demand varies depending on the time of year or market trends. This strategy assures that firms can handle peak periods efficiently while reducing expenses during off-peak times by allowing for flexible resource allocation and production planning.
e. Efficient Model
This paradigm prioritizes cost-efficiency, reducing waste while increasing resource usage. It accomplishes this by utilizing lean manufacturing techniques and advanced analytics to detect and eliminate inefficiencies. It also focuses on resource allocation, ensuring that every component of the supply chain runs at optimal efficiency in order to cut costs while preserving quality.
f. Custom Model
This model is tailored to specific business demands and handles distinct operating constraints. It enables firms to create supply chain procedures that address specific difficulties, such as niche market demands or customized product requirements. Businesses that customize workflows can improve productivity and maintain a competitive advantage in their market.
6. Example of Supply Chain Management (SCM)
A retail company using SCM would source resources globally, manufacture products locally, and distribute them through regional hubs to ensure timely delivery. Each element, from procurement to delivery, is meticulously planned and executed to maximize efficiency and reduce costs.
By employing technology and solid supplier relationships, the organization ensures consistency in quality and delivery schedules, effectively fulfilling changing consumer expectations.
7. Trends and the Future of Supply Chain Management Technology
The future of supply chain management is being defined by new technology and changing business requirements. As global supply chains become more complicated, firms are turning to innovative solutions to boost efficiency and responsiveness. The following are major trends:
a. The Value of ERP and SCM Integration
Integrating enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems with SCM enhances data sharing, streamlining operations, contract management, and decision-making. This interface provides real-time visibility into supply chain processes, resulting in more precise forecasting and resource allocation. It also helps to unify diverse systems, which improves collaboration and overall operational efficiency.
b. SCM and the Cloud
Cloud-based supply chain optimization software enables real-time data access, scalability, and collaboration for worldwide operations. By providing seamless integration of systems and data, these solutions enable businesses to make educated decisions rapidly. Furthermore, cloud technology enables remote access, which ensures continuity and flexibility in managing global supply chains.
c. The Impact of AI in Supply Chain Management
Artificial intelligence allows predictive analytics, process automation, and improved supply chain decision-making. By analyzing massive amounts of data, AI can find patterns and trends that assist proactive initiatives for reducing disruption. Furthermore, AI-powered automation boosts efficiency by reducing repetitive tasks and optimizing workflows across a variety of supply chain operations, including pharmaceutical distribution automation software.
d. SCM and Industry 4.0
The fourth industrial revolution introduces IoT, robotics, and smart technologies into SCM, increasing efficiency and innovation. IoT offers real-time tracking and monitoring of commodities, improving visibility throughout the supply chain. Robotics automates repetitive operations, lowering errors and boosting efficiency, whilst smart technologies use data analytics to improve decision-making and operational accuracy.
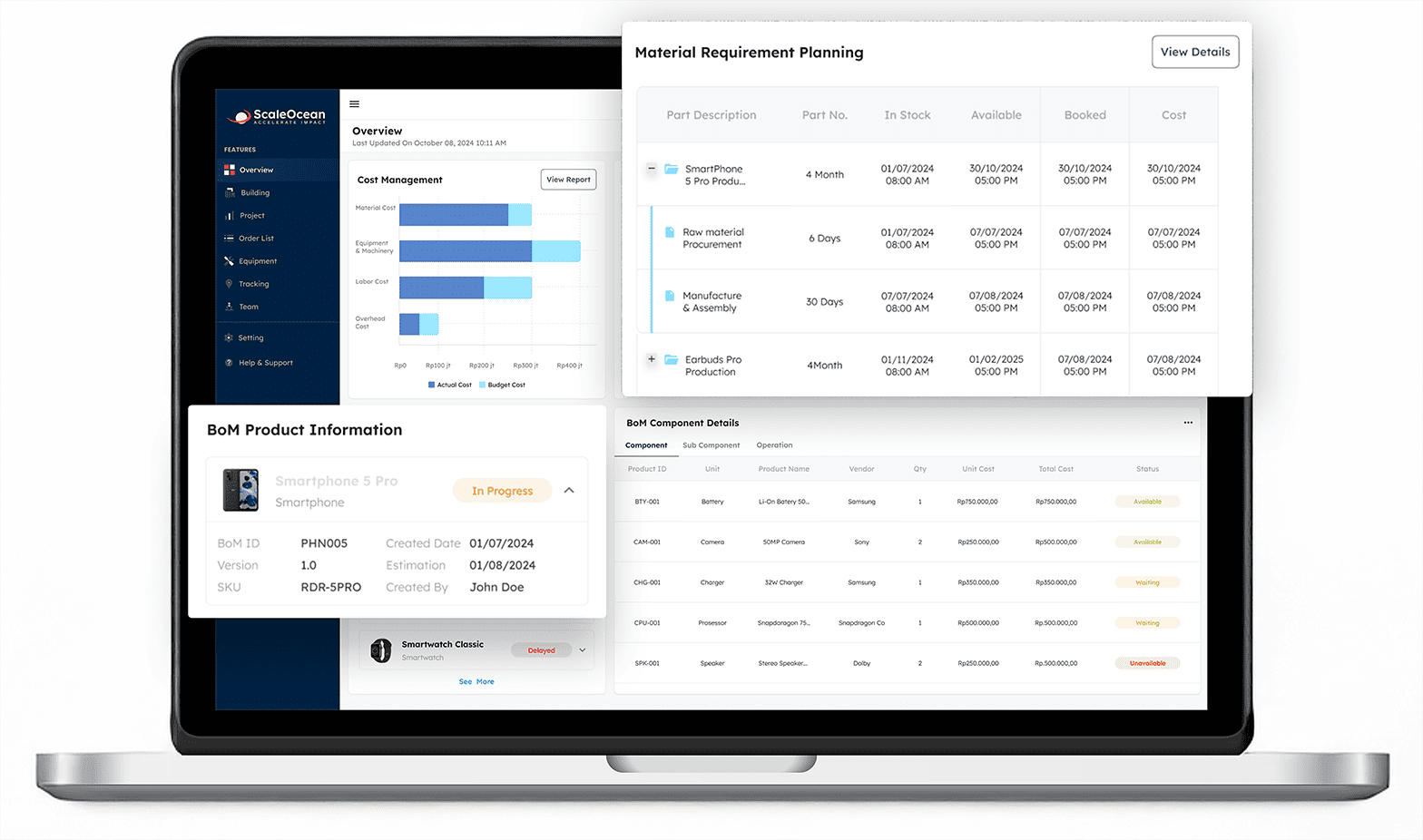
8. Manage All Supply Chain Processes with ScaleOcean SCM Software
ScaleOcean ERP offers integrated SCM software to optimize end-to-end supply chain operations. Its connected modules enhance visibility, improve coordination between procurement, warehousing, and distribution, and help businesses respond quickly to changing market demands.
ScaleOcean focuses on data-driven decision-making, unifying procurement, logistics, and inventory in a single platform. In Singapore, it helps companies use the CTC Grant to turn process improvements and workforce upskilling into measurable supply chain gains over time. The following are the key advantages of ScaleOcean SCM software:
- Enhanced Collaboration: Facilitates seamless communication and coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, ensuring transparency and improved decision-making.
- Real-Time Visibility: Provides instant insights into inventory levels, supply chain performance, and potential bottlenecks, enabling quicker corrective actions.
- Cost Reduction: Identifies inefficiencies, reduces waste, and optimizes resource allocation to significantly save costs and improve margins.
- Scalability: Supports business growth with flexible tools tailored to your specific operational and market needs.
- Automation: Automates routine tasks with precision, freeing up valuable resources and time for strategic initiatives and innovation.
- Sustainability: Promotes eco-friendly practices through optimized routes, waste reduction strategies, and the adoption of renewable energy solutions, driving long-term environmental and business benefits.
9. Conclusion
Supply chain management is a vital function for firms that want to optimize operations, increase efficiency, and satisfy customer expectations. Companies can promote growth and sustainability by knowing the phases, benefits, and technical advancements of supply chain management.
To be competitive, businesses require innovative technologies such as ScaleOcean SCM Software. ScaleOcean streamlines every part of your supply chain with innovative features and an easy-to-use UI. Try our free demo today to see how ScaleOcean can transform business operations, increase productivity, and enable better decision-making.
FAQ:
1. What does supply chain work do?
At its core, supply chain management (SCM) oversees the movement of goods, information, and finances related to a product or service. This process spans from sourcing raw materials to delivering the finished product to its final destination.
2. What is MBA in supply chain management?
An MBA in supply chain management is a graduate program that focuses on the strategic oversight of supply chains. It provides professionals with expertise in areas such as logistics, procurement, operations, and analytics, preparing them for leadership positions to enhance supply chain performance.
3. What are the 5 main functions of supply chain management?
The primary functions of supply chain management include procurement, operations, logistics, resource management, and the flow of information, each contributing to streamlined and effective operations.
4. What are the 7 C’s of supply chain management?
The 7 C’s are Connect, Create, Customize, Coordinate, Consolidate, Collaborate, and Contribute. These serve as a guiding framework to enhance supply chain reliability, efficiency, and sustainability, especially as technology advances and global challenges arise.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















