Bank reconciliation is an important financial process that compares a company’s internal financial records to the bank statement to guarantee consistency. This approach is especially critical for Singapore enterprises, which require regulatory compliance and financial transparency. Accurate reconciliation enables firms to manage cash flow, uncover errors, and eliminate disparities that may influence financial reporting.
In today’s competitive company world, keeping correct financial records is essential for staying ahead. Regular bank reconciliation not only assures compliance with local rules, but it also gives useful information for cash flow management. Automating this process is becoming increasingly important for businesses to stay efficient and competitive by reducing errors, saving time, and making faster, more informed decisions.
- Bank reconciliation is the process of comparing a company’s financial records to the bank’s records to ensure consistency, preventing errors like missed deposits and mishandled payments.
- The steps for doing bank reconciliation include gathering necessary documents, comparing records, identifying discrepancies, making adjustments, and finalizing the reconciliation to ensure accurate financial reporting.
- The bank reconciliation template helps organizations match internal records with the bank’s statement, ensuring accuracy, reducing errors, and supporting better decision-making.
- ScaleOcean ERP software automates the bank reconciliation process by integrating financial data with bank statements, improving accuracy, efficiency, and timeliness while reducing manual errors.

What Is Bank Reconciliation?
Bank reconciliation is the process of comparing a company’s financial records to the bank’s records to guarantee consistency. This practice is critical for businesses to keep accurate financial data since it ensures that every transaction recorded in the company’s books corresponds to those shown in the bank statement. Reconciliation eliminates disparities, such as mishandled payments or missed deposits, which could lead to inaccuracies in financial reporting.
Bank reconciliation is crucial for managing a company’s financial records, ensuring transactions match the bank’s records. Regular reconciliation helps businesses quickly detect errors, maintain accurate financial reporting, and improve cash flow management. It enhances financial transparency and prevents misstatements that could affect decision-making. The timing and process of reconciliation depend on the firm’s size and transaction volume. The following are the main points of when to execute bank reconciliation:
1. Daily
Daily reconciliation is ideal for organizations with significant transaction volumes, such as retail or e-commerce. It enables the speedy detection of errors or fraud and keeps financial records up to date. Daily checks reduce disparities, providing firms more control over their cash flow and budgets. This frequency delivers real-time analytics, allowing organizations to respond promptly to financial changes.
2. Weekly
Weekly reconciliation is suitable for medium-sized organizations with moderate transaction activity. It strikes a balance between keeping track of finances and controlling workload. Businesses that reconcile weekly can spot anomalies early on and maintain financial records correctly without the pressure of daily reviews. Weekly reconciliation strikes an appropriate compromise between accuracy and efficiency, lowering the likelihood of errors developing over time.
3. Monthly
Monthly reconciliation is excellent for small organizations with few transactions. It is an effective method for keeping accurate financial records while managing limited resources. Monthly checks allow firms to keep track of their cash flow and identify any problems that may arise without frequent oversight. This strategy enables firms to better manage their time while maintaining financial transparency and the financial control process.
The Goal of Bank Reconciliation
The primary purpose of bank reconciliation is to guarantee that a company’s financial records, including the general ledger, correspond to those provided by the bank. This procedure entails comparing transactions such as deposits, withdrawals, and bank fees between the company’s accounting records and the bank statement.
This allows organizations to ensure that all transactions have been appropriately recorded on both sides, preventing mismatches. Reconciling these records also enables firms to detect errors and anomalies early on, helping them stay on track with their financial goals.
Detecting these issues enables organizations to resolve them before they damage financial statements or generate reporting errors. Finally, this process improves the overall accuracy of financial reporting by ensuring that the company’s financial records represent the genuine financial status of the organization.
Why Bank Reconciliation Is Important for Businesses
Bank reconciliation is an important activity for businesses since it guarantees that the company’s financial records match the bank’s records. This frequent practice assists firms in maintaining accounting accuracy, preventing errors, and mitigating potential financial hazards. Just as absorption costing accurately allocates costs to products, bank reconciliation ensures that all financial transactions are correctly recorded, preventing discrepancies and misstatements.
Without effective reconciliation, differences can easily go undetected, resulting in severe financial misstatements and operational inefficiencies. As a result, bank reconciliation is critical for seamless corporate operations and ensuring the accuracy of financial reports. The following are the main reasons why bank reconciliation is vital for firms:
1. Ensuring Accuracy in Financial Records
Reconciliation guarantees that organizations can track their financial flow accurately. Companies can avoid errors in their financial records by reconciling on a regular basis, ensuring that all receipts and payments match the bank transactions.
Examples of financial instruments, such as loans or bonds, are often included in these reconciliations, contributing to dependable and consistent financial reporting.
2. Preventing Fraud
Bank reconciliation is crucial to combating fraud. Discrepancies, mistakes, or unlawful transactions are rapidly identified, minimizing the likelihood of fraudulent activity being undetected. Regular checks make it easier to detect any questionable activity that may otherwise result in financial loss and damage to the company’s reputation.
3. Improving Cash Flow Management
Accurate reconciliation helps businesses manage and forecast cash flow by tracking deposits, payments, and bank fees, preventing overdrafts and aiding in future planning. According to IRAS, businesses must keep records for at least five years to ensure that income and expenses can be easily verified. This practice also supports better investment decisions and ensures compliance with tax regulations.
4. Compliance and Tax Purposes
Accurate financial records are essential for organizations to comply with regulatory and tax requirements. According to Singapore Statutes Online, bank accounts for the funds of a Town Council must be maintained, with preference given to banks incorporated in Singapore. By reconciling bank statements with internal records on a regular basis, companies ensure that their financial data is up to date and compliant with local rules and regulations. This reduces the risk of penalties and ensures that audits run smoothly.
How to Do Bank Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation is a critical activity that helps firms ensure that their financial records match the bank’s statements. By analyzing transactions and spotting inconsistencies, it provides precise cash flow management, eliminates errors, and promotes wise financial decisions. The following are the steps to efficiently do a bank reconciliation:
1. Gather Necessary Documents
The first step in bank reconciliation is collecting all pertinent financial papers. This contains the company’s bank statement, which reveals the bank’s transaction history, as well as internal accounting records such as cash receipts, cheques issued, and any other financial papers associated with the transactions. Having all of the relevant documents on hand ahead of time helps to streamline the process and prevents any important data from being overlooked.
2. Compare Bank and Business Records
Next, compare the company’s internal records to the bank’s statement. Carefully match each transaction indicated on the bank statement to the corresponding entries in the company’s accounting records. Pay particular attention to any variations in transaction amounts, dates, or descriptions. This comparison will identify any discrepancies that require additional study.
3. Identify Discrepancies
Common differences that may develop during reconciliation include bank fees, deposits in transit, and unpaid checks. Other difficulties could include transactions that the bank has not yet completed or mistakes in transaction descriptions. Identifying these differences is critical because it allows firms to pinpoint the causes and implement corrective measures.
4. Make Adjustments
Once discrepancies have been detected, make the necessary revisions to the accounting records. For example, update internal records to account for any missed bank fees or add transactions that the bank recorded but are not yet on the company’s books. If an issue cannot be fixed quickly, flag it for future study.
5. Finalize the Reconciliation
Finalize the reconciliation once all inconsistencies have been resolved and adjustments made. This entails amending the accounting records to reflect the true financial situation. Check that the bank statement and internal records match exactly.
Once the reconciliation is completed, the records should be accurate, with any unresolved errors documented for future reference. Performing a financial audit periodically can help ensure that the reconciliation process remains thorough and that any discrepancies are properly addressed before they affect the overall financial statements.
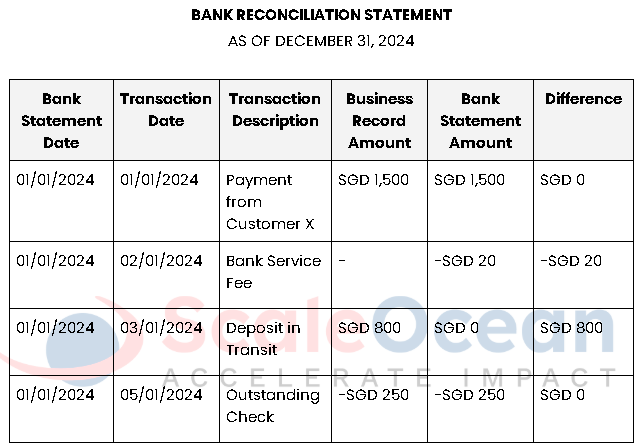
Example Template for Bank Reconciliation
This template helps organizations match each entry with their records, providing a clear overview of the reconciliation process. It enables easy identification of discrepancies between internal financial records and the bank statement.
By ensuring accuracy and efficiency, it reduces errors and fraud, supporting reliable financial management data for better decision-making and management. Below is an example of how companies can track the reconciliation process:
Challenges That Arise When Businesses Don’t Perform Bank Reconciliation
Neglecting bank reconciliation exposes firms to financial risks that might disrupt operations. Without this approach, errors might jeopardize financial integrity and result in costly blunders. If issues such as erroneous reporting and inadequate cash flow management are not addressed, they might worsen. It is critical to recognize the hazards associated with failing to reconcile bank statements on a regular basis. The following are the primary challenges businesses may face:
1. Inaccurate Financial Reporting
Without bank reconciliation, firms risk mistakes in their financial statements, resulting in incorrect data. This can lead to poor decision-making because managers may act on inaccurate financial information.
Regular reconciliation ensures that financial reports represent the company’s true financial condition, enabling smarter business decisions. ERP for Banking industry solutions can help automate the reconciliation process, reducing the chance of errors and ensuring accurate financial reporting for banks and financial institutions.
2. Missed Opportunities for Cost Control
Neglecting regular reconciliation might lead to organizations overlooking overpayments or unneeded expenses. For example, duplicate charges or concealed costs may go unreported, reducing profitability. Businesses that reconcile their accounts regularly can identify anomalies early on, allowing for better cost control and increased savings.
3. Increased Risk of Errors and Fraud
Failure to reconcile bank statements raises the danger of unreported errors and fraud. Unrecorded transactions or fraudulent activity can go undetected, inflicting considerable financial damage. Regular reconciliation assists in identifying such difficulties, ensuring that financial records are accurate, and safeguarding the company from financial fraud.
4. Difficult Cash Flow Management
Without effective reconciliation, businesses struggle to accurately track cash flow, which can result in overdrafts or missed payments. If available finances are overstated, businesses may encounter unanticipated financial difficulties. Regular bank reconciliation provides a comprehensive picture of cash flow, allowing businesses to prevent cash shortages and better manage their finances.
Examples of Bank Reconciliation in Business
Bank reconciliation is a practical method that businesses employ to ensure that their financial records are correct and in line with their bank statements. The procedure aids in error detection, discrepancy identification, and effective cash flow management. Regular bank reconciliation can benefit a variety of firms, including small and medium-sized corporations and e-commerce companies. Here are some instances of how different organizations use bank reconciliation in their operations:
1. Small Business Example
A local retailer reconciles their bank statement on a regular basis to reflect sales, payments, and deposits. By doing so, the store verifies that its financial records match the bank’s reported transactions. This method is critical since it identifies inconsistencies fast, such as missed payments or unreported bank fees. By addressing these issues early on, the retailer may ensure proper financial reporting and minimize possible cash flow challenges.
2. Medium Enterprise Example
A manufacturing company with worldwide transactions uses bank reconciliation to match bank payments to internal accounting records. This method facilitates foreign exchange, currency changes, and overseas payments.
Regular reconciliations help the organization prevent accounting errors and ensure correct reporting of international transactions, lowering the risk of overpayment or underreporting.
3. E-commerce Example
Bank reconciliation is critical for online businesses since it allows them to trace payments and ensure accurate order processing. By comparing payments to bank data, the company prevents missed orders and payment mistakes.
This helps to avoid shipment delays and assures smooth customer transactions, resulting in increased confidence, managing inventory accounting process, and efficient order fulfillment.
Common Problems Faced in Bank Reconciliation
When performing bank reconciliation, businesses often face common issues that can cause discrepancies between their financial records and the bank’s statement. These problems can arise from a variety of factors, such as unexpected fees or timing issues. If not addressed promptly, these discrepancies can lead to inaccuracies in financial reporting and mismanagement of cash flow. Below are some common problems encountered during bank reconciliation:
1. Bank Fees and Charges
Unexpected bank fees are a regular occurrence during reconciliation. These payments, such as service charges or transaction fees, are frequently not recognized promptly in the company’s accounting records. As a result, anomalies occur when these fees appear on a bank statement but not on the company’s books. Regularly reviewing bank statements helps ensure that these fees are accounted for in a timely and accurate manner.
2. Timing Differences
Timing disparities occur when the company records transactions, such as checks issued or payments made, but the bank has not yet processed them. These delayed transactions may cause problems in the reconciliation process. To address this issue, businesses should monitor the status of all transactions and ensure that any outstanding transactions are modified when the bank processes them.
3. Human Error
Human error, such as inaccurate data entry or transaction classification, can cause disparities throughout the reconciliation process. These problems may arise when transactions are recorded manually. Businesses can reduce errors and verify that their records match the bank statement by automating the process and conducting regular assessments.
4. Uncleared Checks or Pending Transactions
Uncleared checks or pending transactions that the bank has not yet processed can cause discrepancies in the records. This happens when the firm issues payments or checks that remain in transit or the bank has not yet cleared. Businesses should frequently monitor the progress of these checks and pending transactions and modify their records whenever the bank processes them.
How to Overcome Bank Reconciliation Challenges With ScaleOcean’s Accounting Software
Bank reconciliation can be difficult for organizations because of human errors, discrepancies, and time-consuming manual operations. Financial ERP software in Singapore, like ScaleOcean, automates this procedure by comparing internal financial data to bank statements, ensuring accuracy and timeliness while saving time and minimizing errors. ScaleOcean also interacts with Bank Reconciliation Software, which streamlines and automates the entire reconciliation process, hence enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
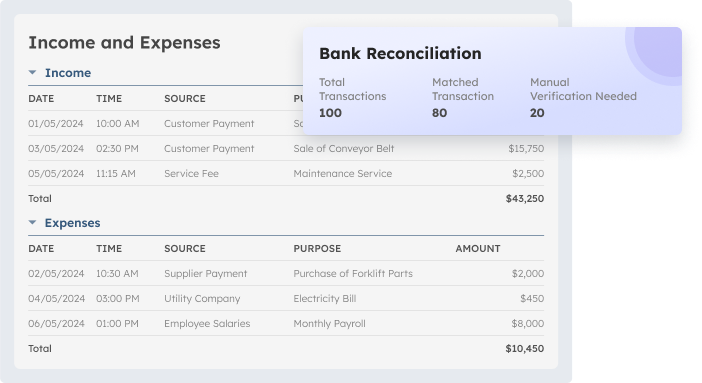
Businesses that use real-time financial insights can make better decisions and stay on track with their budgets. ScaleOcean offers a free demo to individuals interested in exploring its features, and it is qualified for the CTC grant to help decrease installation expenses. Here are the main aspects that improve the bank reconciliation process:
- Automated Bank Reconciliation, ScaleOcean automates the reconciliation process, matching internal records with bank statements, ensuring accuracy, timeliness, and reducing manual errors.
- Real-Time Financial Insights, ScaleOcean provides up-to-date financial tracking, helping managers monitor cash flow, accounts, and transactions for quicker, informed decision-making.
- Comprehensive Integration with Other Modules, The integration of ScaleOcean’s accounting, inventory, and sales modules ensures seamless, accurate financial data across the system, reducing discrepancies.
- Efficient Error Detection and Adjustment, ScaleOcean’s ERP system quickly identifies and resolves discrepancies between bank statements and internal records, streamlining error correction.
- Time and Cost Savings through Automation, By automating transaction matching and payment processing, ScaleOcean reduces manual effort, freeing up resources for more strategic tasks.
Conclusion
Regular bank reconciliation is critical for keeping correct financial records, preventing fraud, and meeting regulatory obligations. Businesses that reconcile bank statements with internal financial data can better track their cash flow, spot inconsistencies, and handle concerns quickly. This method improves decision-making while reducing the chance of errors that could harm the company’s financial health.
ScaleOcean plays an important part in automating the bank reconciliation process, making it more efficient and error free. ScaleOcean’s solution automates the matching of bank statements with internal records, resulting in rapid and accurate reconciliation while saving businesses time and resources. This streamlined procedure enables firms to focus on strategic initiatives while preserving financial accuracy and compliance.
FAQ:
1. What are the 4 steps in the bank reconciliation?
Bank reconciliation involves four key steps:
1. Compare Statements: Review the company’s cash book and bank statement for discrepancies.
2. Identify Unprocessed Deposits: Spot any deposits not yet processed by the bank.
3. Account for Unprocessed Checks: Record checks issued but not cleared by the bank.
4. Correct Mistakes: Adjust discrepancies in the bank statement or company records.
2. What is the journal entry for bank reconciliation?
Journal entries during bank reconciliation depend on the discrepancies found. Typical entries include:
– Deposits in Transit: No entry is required for these, as they’ve already been recorded in the company’s books.
– Unprocessed Checks: No journal entry is needed unless changes are necessary to the financial records.
– Bank Errors: If a mistake was made by the bank, an entry may be required to correct it.
– Company Errors: If there’s an error in the company’s records, a journal entry is needed to fix the discrepancy.
3. How to reconcile a bank account?
To reconcile a bank account, follow these steps:
1. Collect Documents: Get both the bank statement and the company’s cash book for the same period.
2. Match Transactions: Compare each deposit and withdrawal in the company’s records with those on the bank statement.
3. Spot Differences: Identify any deposits or checks that haven’t been processed or any errors in either record.
4. Make Adjustments: Adjust the company’s ledger to account for any errors, such as bank charges or interest.
5. Calculate Final Balances: Ensure that the final, adjusted balances in both the bank statement and the company’s records match.
4. What is the formula for bank reconciliation?
The bank reconciliation formula is:
Adjusted Bank Balance = Bank Statement Balance + Deposits Not Yet Processed – Unprocessed Checks
For the company’s records:
Adjusted Book Balance = Company’s Cash Book Balance + Bank Mistakes – Company Mistakes
Once all differences are resolved and adjustments made, both the adjusted balances should be the same.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















