Singapore’s banking business is renowned for its innovation, stringent regulatory standards, and rapid digital change. Adoption of ERP systems has been an important strategy for banks looking to improve operational efficiency, compliance, and client experiences.
These solutions allow banks to remain competitive in a changing market. ERP systems are crucial for banks, automating finance, customer relations, and risk management to improve efficiency and ensure compliance.
IRAS mandates GST-registered businesses to transmit invoice data via InvoiceNow-Ready Solutions. Neglecting the right ERP can lead to inefficiencies, poor data management, and missed compliance deadlines.
Without proper ERP, banks risk penalties, higher costs, and integration issues. This can harm growth and customer satisfaction. This article can provide a complete guide to an ERP for the banking industry, from features and components to the examples that you can choose to suit your needs. Learn more here!
- ERP for the banking sector provides key functions such as financial management, compliance, risk management, and customer service in one platform.
- The benefits of ERP banking industry are operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, enhanced customer service, and real-time analysis
- Key components and modules of ERP for the banking industry are financial management, risk and compliance, CRM, loan and credit management, treasury management, and HRM
- Examples of ERP for the banking industry are ScaleOcean ERP, Oracle NetSuite, Infor, Microsoft Dynamics 365, SAP, Epicor, and more
- ScaleOcean ERP is a Singapore-based solution designed for the banking industry, offers a flexible design that allows for customization to meet specific banking needs.

What is an ERP System for the Banking Industry?
ERP for the banking sector combines key functions such as financial management, compliance, risk management, and customer service into one platform. This enhances efficiency, lowers costs, and ensures regulatory compliance.
It does so by automating tasks like transaction processing and report generation, while offering real-time data analysis and centralized data management. As a result, banks can optimize operations, improve risk management, and quickly respond to market changes.
ERP systems are also critical in the banking industry because they centralize financial data, streamline operations, and support decision-making. Given the banking industry’s reliance on real-time data and regulatory compliance, implementing ERP solutions enables banks to remain competitive and operationally efficient.
Key Benefits of ERP for Banking Industries
Implementing an ERP system provides considerable benefits to banks by streamlining operations and increasing overall efficiency. These advantages include increased automation, improved regulatory compliance, and better customer service. With ERP, banks can make better judgments and adapt to changing market situations. Here are several significant advantages:
1. Operational Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of ERP in banking is its capacity to automate routine activities, hence decreasing human error. This speeds up operations and enables banks to focus on more important tasks.
Automation improves workflows, making operations more efficient and boosting net sales. Ultimately, this allows banks to better serve their customers and enhance production.
2. Regulatory Compliance
ERP systems guarantee that banks follow local requirements, such as those established by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). These systems aid in the creation of accurate reports as well as the maintenance of audit trails.
They make compliance easier by automatically upgrading systems with regulatory changes. This improves the efficiency and transparency with which rules and regulations are enforced.
3. Enhanced Customer Service
ERP systems that include CRM modules allow banks to provide more tailored client interactions. These systems monitor service requests and preferences, which helps to improve response times.
Banks can enhance client relationships by providing superior customer service, leading to higher client satisfaction and loyalty. Similarly, an ERP system for service companies in Singapore streamlines operations, boosting efficiency and improving client interactions.
4. Real-Time Analytics
ERP systems give real-time data, allowing banks to make informed decisions. This information is critical for strategic planning and anticipating future trends.
Real-time analytics enables banks to optimize operations and identify potential opportunities. It improves the bank’s capacity to respond rapidly and stay ahead of the competition.
Key Components and Modules of ERP for the Banking Industry
ERP systems play an important role in optimizing operations in the banking sector by providing integrated solutions adapted to the industry’s specific requirements. With the complexity of financial services, ERP modules can help manage vital processes and maintain compliance.
The following are some important ERP modules and critical characteristics for the banking industry:
1. Financial Management
ERP systems include crucial functions such as a general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, and financial reporting. These features help banks manage their financial operations effectively, maintain accuracy, and meet regulatory obligations.
Banks can optimize finance ERP modules to ensure that their accounting processes remain precise and efficient.
2. Risk and Compliance Management
ERP systems provide tools to manage and mitigate financial and operational risks, ensuring compliance with local and international regulations. This reduces the risk of non-compliance and streamlines reporting.
For accurate compliance and bank reconciliation, ERP systems are designed to track every transaction and generate reports that support internal audits and regulatory requirements.
3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The CRM module enables banks to manage client interactions, track service requests, and personalize offerings. ERP systems allow banks to streamline customer service while improving overall customer retention rates.
This contributes to the best ERP for financial services by supporting personalized banking experiences.
4. Loan and Credit Management
ERP solutions improve loan and credit management by automating loan approval, monitoring, and reporting. These features ensure that loans and credit lines are processed efficiently, lowering associated risks like defaults and compliance concerns.
5. Treasury Management
ERP technologies enable banks to manage their liquidity, investments, and cash flow more effectively. These modules assist banks in optimizing their treasury operations, ensuring that adequate cash is accessible for day-to-day operations while properly managing investments.
6. Human Resources Management
HR elements within ERP systems make payroll processing, recruitment, and employee performance tracking easier. Automating these operations allows banks to reduce administrative load, ensure labor law compliance, and increase overall HR management efficiency.
According to MOM, the HR Industry Transformation Plan provides a 5-year roadmap to strengthen the HR profession and practices in Singapore, further enhancing the role of ERP systems in optimizing HR functions.
Methods for Integrating ERP Systems for the Banking Industry
Integrating an ERP system in the banking industry involves connecting various software and platforms to streamline data flow and enhance operational efficiency. There are several methods for successful integration, each with its benefits and challenges.
Below are key integration methods for ERP systems in the banking sector.
1. File Transmission
File transmission is a method where data is exchanged between the ERP system and other platforms through secure file transfers. This method is commonly used for batch processing, where large volumes of data, such as transaction records or financial reports, are transferred at scheduled intervals.
File transmission is simple and cost-effective, but it may not provide real-time integration or handle complex data exchanges efficiently.
2. APIs
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) enable real-time integration between the ERP system and other software applications used by banks. APIs allow different systems to communicate directly, providing seamless data exchange and faster processing.
This method is highly flexible, allowing banks to integrate various third-party tools, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems or payment platforms, with minimal disruption to operations.
3. Plug-Ins and Adapters
Plug-ins and adapters act as intermediaries, connecting the ERP system to external applications or platforms. These tools are designed to enhance the ERP’s functionality without requiring major changes to the core system.
Plug-ins are ideal for banks that want to add specific capabilities, such as integrating payment gateways or reporting tools, without overhauling their entire IT infrastructure.
4. Upload Portals
Upload portals are web-based interfaces where users can manually upload data from external sources into the ERP system. In the banking industry, this method is often used for integrating external financial data, customer information, or regulatory reports.
While upload portals provide an easy way to bring in external data, they are generally slower and more prone to errors compared to automated integration methods.
5. Middleware Solutions
Middleware solutions act as a bridge between the ERP system and other applications, enabling smooth data transfer and system communication. Middleware software can process and transform data, ensuring that it is compatible across different platforms.
In the banking industry, middleware solutions are often used to connect legacy systems with modern ERP platforms, facilitating a more gradual and controlled transition to newer technologies.
Limitations of ERP in the Banking Industry
While ERP systems offer numerous benefits to the banking industry, they also come with certain limitations that banks need to consider. These challenges can impact system performance, integration, and scalability. Below are the key limitations of implementing ERP in the banking sector.
1. High Implementation Costs
Implementing an ERP system in the banking sector can be costly, especially for large institutions with complex operations. The initial setup, customization, and integration with existing systems require significant investment in both time and money.
Additionally, ongoing maintenance, updates, and training can add to the total cost, making it a heavy financial commitment.
2. Complexity in Customization
Banking institutions often require highly specific features to comply with regulatory standards, manage risks, and serve a diverse customer base. Customizing an ERP system to meet these unique requirements can be a complex and time-consuming process.
Customization may also result in increased system complexity, which can make it difficult for employees to navigate and use effectively.
3. Integration Challenges
ERP systems need to integrate seamlessly with a variety of other banking software, such as core banking systems, payment platforms, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools.
Achieving this integration can be challenging due to differences in software architecture, data formats, and system protocols. Poor integration can lead to data silos and inefficiencies, hindering the bank’s ability to leverage real-time data across departments.
4. Data Security Concerns
Given the sensitivity of banking data, ERP systems must have robust security measures in place. However, ensuring data protection across multiple platforms, especially when integrating with third-party tools, can be challenging.
Vulnerabilities in the system could expose customer financial information to cyber threats, making it crucial for banks to prioritize security throughout the ERP implementation process.
5. User Resistance and Training
Implementing a new ERP system in a banking institution often meets with resistance from employees who are accustomed to existing processes. Adapting to the new system requires substantial training and time, which can disrupt daily operations.
Inadequate training or reluctance to change can result in inefficient use of the ERP system and diminish its benefits.
6. Scalability Issues
As the banking industry continues to evolve and expand, an ERP system needs to scale accordingly. However, some ERP solutions may not be easily scalable, particularly if they were designed for smaller institutions or lack the flexibility needed to accommodate rapid growth.
Banks that face significant expansion might struggle to modify the system to support new services, locations, or customer demands.
How to Build a Banking ERP System
Building an ERP system for the banking industry requires a strategic approach to ensure it meets regulatory requirements, enhances efficiency, and supports seamless integration with various financial services. Below are key steps to successfully develop a robust ERP system tailored to the banking sector.
1. Identify Business Requirements
The first step in building a banking ERP system is to clearly define the business needs. Banks must evaluate their operational requirements, such as financial management, customer relationship management, risk management, and compliance.
A thorough understanding of these needs helps in selecting the right features and ensuring the ERP system aligns with the bank’s goals and industry regulations.
2. Select the Right Technology Stack
Choosing the appropriate technology stack is critical for the development of a banking ERP system. This involves selecting the right programming languages, database management systems, and cloud platforms that can support scalability, security, and integration.
The technology stack should be future-proof, allowing the ERP system to evolve alongside emerging technologies in the financial sector.
3. Ensure Regulatory Compliance
Banking ERP systems must adhere to industry-specific regulations, such as data privacy laws, anti-money laundering (AML) standards, and financial reporting requirements.
Compliance should be integrated into the system’s design, ensuring that the software automatically generates reports that meet regulatory standards. Regular audits and updates are essential to keep the system compliant with changing laws and regulations.
4. Design for Scalability and Flexibility
The banking industry is constantly evolving, and the ERP system must be able to scale as the bank grows. The system should be flexible enough to accommodate changes in business processes, such as new product offerings, geographic expansion, or shifts in customer needs.
Scalable systems can handle increased data loads, user traffic, and new services without performance degradation.
5. Focus on Integration Capabilities
A successful banking ERP system should seamlessly integrate with other banking software, such as core banking systems, customer relationship management (CRM) tools, and payment gateways.
Integration ensures smooth data flow across all platforms, providing a unified view of operations and enabling real-time data sharing. APIs, middleware, and cloud services can help in achieving these integrations.
6. Prioritize Security
Security is paramount in the banking industry, and an ERP system must be designed with robust security features. This includes data encryption, multi-factor authentication, access controls, and secure APIs.
The system should also comply with cybersecurity standards and ensure that sensitive customer and financial data is protected from breaches or unauthorized access.
Custom ERP Solution vs. Off-the-Shelf Platform ERP for Banking Industries
When choosing an ERP for the banking industry, organizations must decide between a custom-built solution and an off-the-shelf platform. Both options have distinct advantages and trade-offs.
1. Custom ERP Banking Industry
A custom ERP is tailored specifically to the bank’s needs, ensuring full alignment with unique processes, regulations, and business models. It offers flexibility, scalability, and the ability to integrate seamlessly with legacy systems.
However, it can be costly and time-consuming to develop, and may require continuous updates and maintenance.
2. Off-the-Shelf ERP Banking Industry
An off-the-shelf ERP is a ready-made solution that offers fast implementation at a lower cost. These platforms are built to serve a wide range of industries, including banking, with standard features for financial management, compliance, and reporting.
While they may lack customization options, they offer quick deployment and come with ongoing vendor support and updates.
Which Option Fits Best?
- A custom ERP is ideal if the bank has complex, unique workflows; rigorous compliance and risk‑management requirements; plans for rapid growth; or depends on deep integration with legacy or specialized banking systems.
- An off‑the-shelf ERP makes sense if the bank’s operations are relatively standard, the budget is constrained, and the priority is to deploy quickly and cost-effectively.
8 Examples of ERP Software for the Banking Industry in Singapore
Singapore’s banking sector is rapidly evolving, with financial institutions seeking solutions to streamline operations, boost compliance, and improve customer experience. ERP systems offer a centralized platform for all essential banking processes, assuring efficiency and scalability.
The following are the best ERP solutions customized for the banking industry in Singapore:
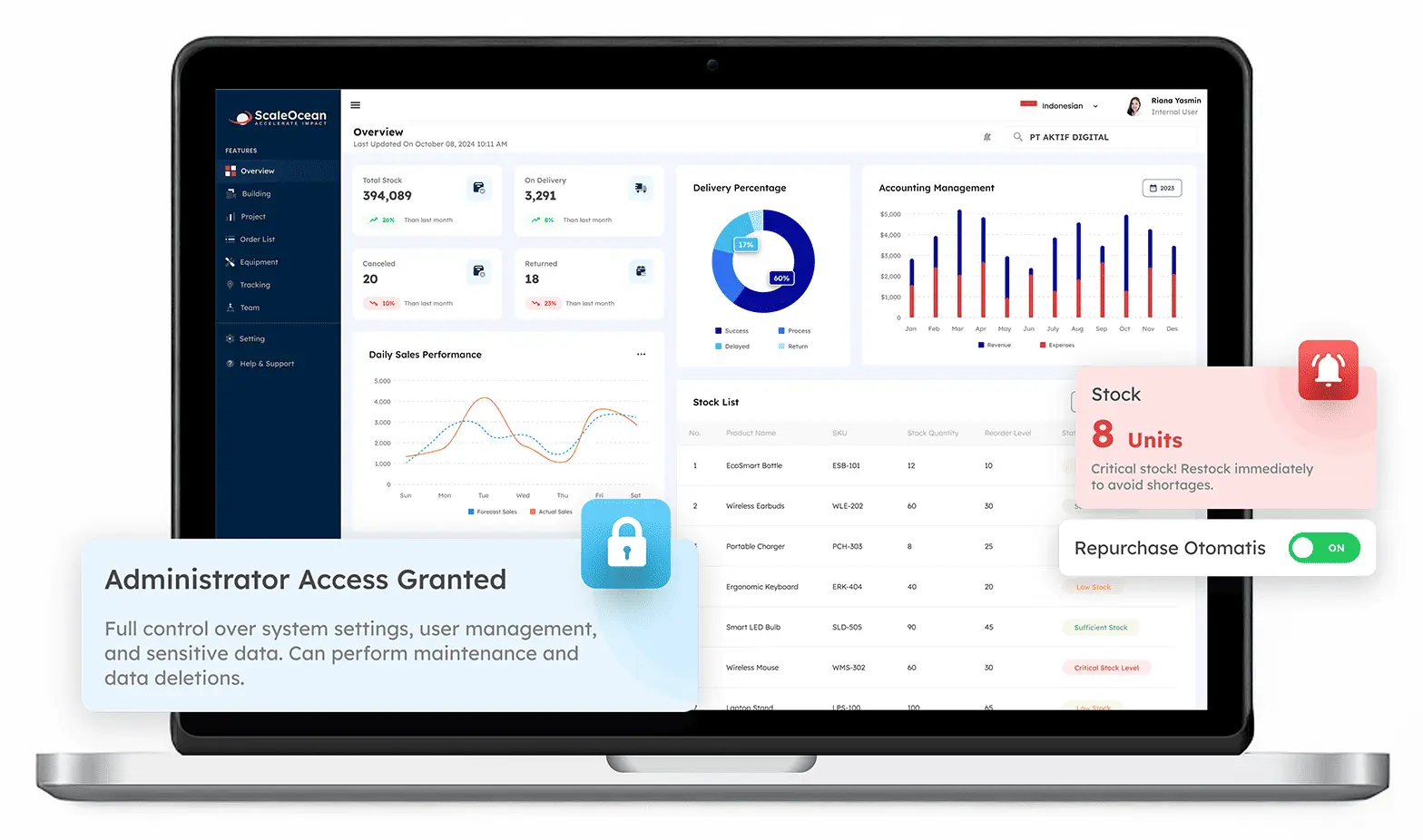
1. ScaleOcean ERP
ScaleOcean’s professional service ERP is a Singapore-based solution tailored for various industries. Its modular design offers flexibility, allowing customization to meet specific banking needs, making it an ideal choice for the banking sector.
Whether it’s for compliance management or cloud accounting, ScaleOcean delivers real-time data insights to help banks stay ahead of competitors and meet their financial goals. ScaleOcean provides a free demo of its ERP solution to assist you in understanding its capabilities.
Furthermore, ScaleOcean is qualified for the CTC (Capability Transfer and Cooperation) Grant, which provides financial assistance to organizations aiming to achieve digital transformation. If you’d like to learn more, these are the main features of ScaleOcean’s software:
a. Key Features
Each ERP solution offers distinct capabilities that set it apart from the rest. Below are some of the standout features that enhance the value and functionality of ScaleOcean ERP for the banking industry:
- AI-driven Analytics for Real-time Insights: ScaleOcean uses AI to provide real-time financial data insights, helping banks make informed decisions.
- Integrated Compliance with Local Regulations: Built-in compliance tools ensure banks adhere to Singapore’s financial regulations with ease.
- Modular Design for Customization: The flexible, modular system allows banks to tailor the ERP to their specific needs.
- Operational Efficiency through Automation: Automation of routine tasks reduces errors and boosts efficiency across various banking functions.
- Scalable for Growth and Digital Transformation: ScaleOcean grows with the bank, offering scalable solutions to support digital transformation without disruption.
b. Why It Stands Out
ScaleOcean ERP distinguishes itself by providing a specialized solution tailored exclusively for Singapore’s banking sector. It enables scalability and full compliance with local legislation, giving financial institutions the freedom to adapt.
Its modular form enables customization, making it extremely adaptable to the banking industry’s numerous requirements.
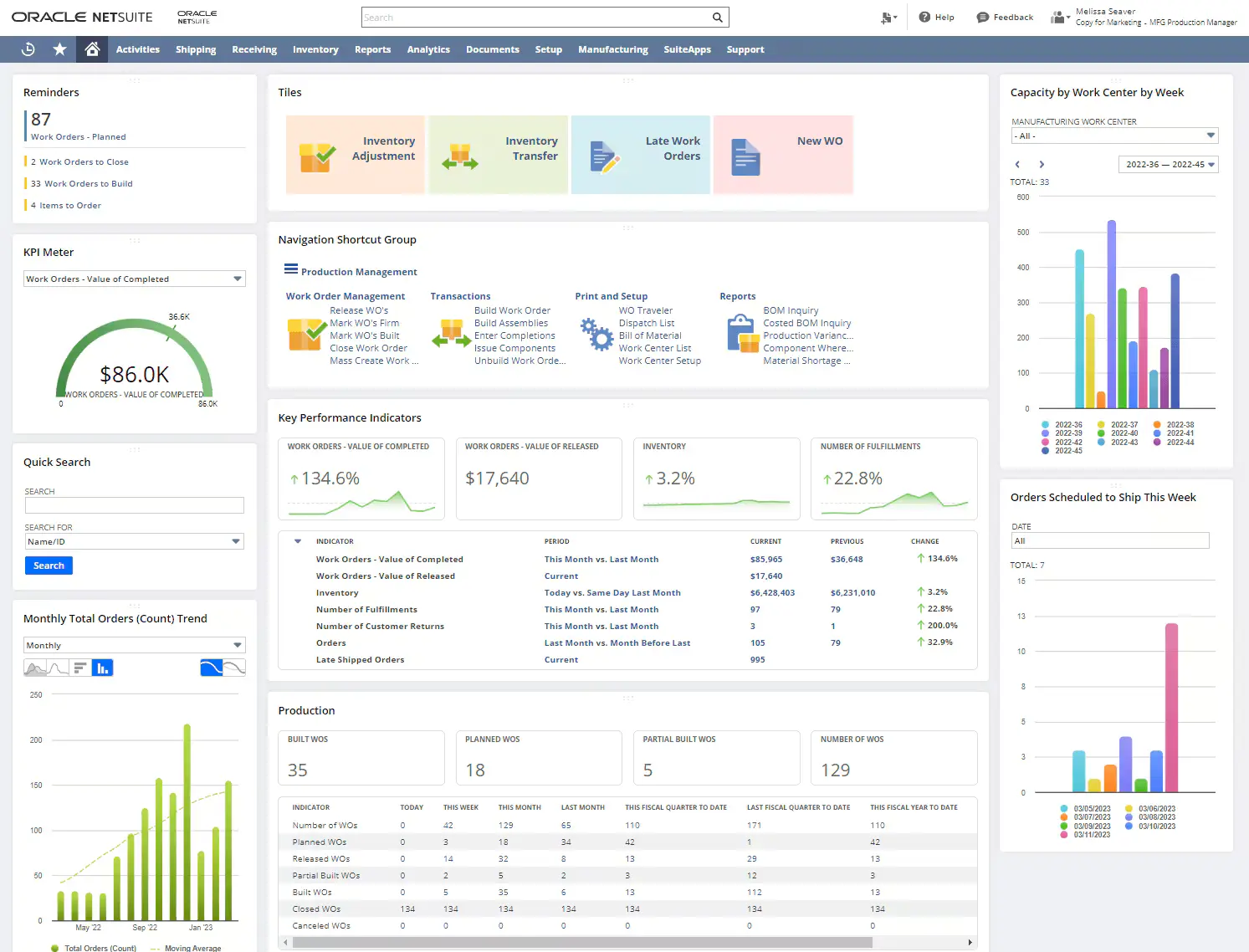
2. Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite is a cloud-based ERP solution commonly used by financial organizations worldwide. It is intended to manage all areas of banking operations, such as financial management, risk assessment, and customer relationship management.
Its cloud features make it an excellent solution for organizations seeking scalability and flexibility in their ERP systems.
a. Key Features
Each ERP solution offers unique features that meet the specific needs of financial institutions. Here are some of the key features of Oracle NetSuite:
- Advanced financial management tools.
- Scalable for banks of all sizes.
- Cloud-based integration for real-time updates.
b. Why It Stands Out
Oracle NetSuite’s scalability and strong financial management features make it an ideal solution for both large and growing financial institutions. Its cloud-based nature ensures flexibility, enabling banks to easily adjust to evolving needs.
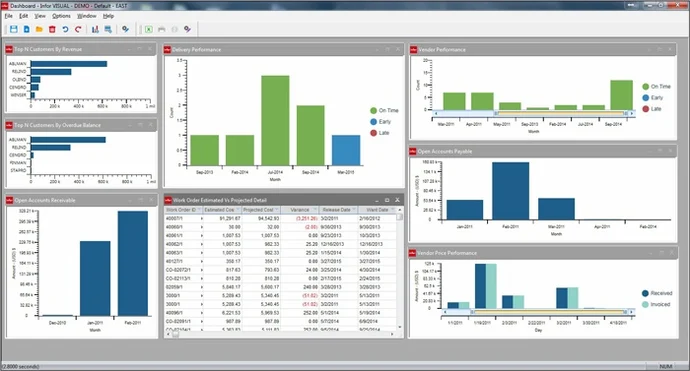
3. Infor ERP
Financial organizations benefit from Infor ERP’s versatile and resilient ERP solutions. It is designed for both large and small banks and integrates financial and operational management, allowing for more efficient banking processes.
Its robust financial tools, together with real-time reporting capabilities, make it a dependable choice for the banking industry.
a. Key Features
Infor ERP offers several key features that make it a robust solution for financial institutions. These features include:
- Robust financial and asset management.
- Scalable cloud-based solutions.
- Customizable to meet unique banking needs.
b. Why It Stands Out
Infor ERP is highly customizable and flexible, providing banking institutions with the tools they need to manage their operations efficiently. Its cloud capabilities and strong financial tools make it a top choice for banks seeking scalability.
4. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a CRM-centric ERP system intended to improve client connections in the banking industry. By combining financial management with customer relations, financial institutions can expedite operations and deliver individualized services to clients, increasing overall customer satisfaction.
a. Key Features
Microsoft Dynamics 365 provides several key features that support banks in improving customer relations and financial management. Below are some standout features:
- Comprehensive CRM integration.
- Real-time analytics and reporting.
- Seamless integration with Microsoft tools.
b. Why It Stands Out
Its seamless integration with Microsoft tools, combined with its CRM capabilities, makes it a powerful solution for banks looking to improve customer engagement and operational efficiency.
5. SAP ERP
SAP ERP is a high-performance system that processes data in real time, making it suitable for large institutions. SAP’s ERP system is well-known for its resilience, integrating diverse banking activities while maintaining data quality and compliance across all financial departments.
a. Key Features
SAP ERP is recognized for its strong capabilities. Some of its notable features include:
- Advanced analytics and reporting.
- Real-time data integration.
- High scalability for large banks.
b. Why It Stands Out
SAP ERP’s real-time processing and scalability make it ideal for large financial institutions that require high performance and robust integration. It’s known for handling complex banking operations with ease, making it a trusted choice for large banks.
6. Epicor ERP Banking System
Epicor ERP is intended for financial institutions seeking robust process automation and effective management of banking operations. Epicor’s integration of fundamental banking functions such as financial management and customer interactions provides a comprehensive solution for modern institutions.
a. Key Features
Epicor ERP offers several key features that support banking operations. These features include:
- Workflow automation for increased efficiency.
- Financial and customer process integration.
- Customizable banking features.
b. Why It Stands Out
Epicor ERP stands out for its focus on automation and efficiency, reducing manual tasks and enhancing productivity in financial operations. Its customization options also make it adaptable for a variety of banking functions.
7. Sage X3 ERP for Banking Industry
Sage X3 is a powerful ERP system designed for banks seeking an integrated platform to manage financial and operational tasks. Known for its flexibility, it offers tailored solutions that help banking institutions improve financial management and enhance customer relationships.
a. Key Features
Sage X3 offers a variety of features that enhance its functionality for the banking sector. These include:
- Efficient financial and operational management.
- Real-time reporting and analytics.
- Flexible, modular design for customization.
b. Why It Stands Out
Sage X3 stands out due to its flexibility and powerful integration capabilities, making it an ideal solution for banks looking to optimize both financial management and customer relationship processes.
8. IFS ERP Financial Services
IFS ERP offers full financial and operational management for banks by combining diverse banking operations into a single unified system. With a focus on real-time data and advanced reporting, IFS assists financial institutions in streamlining operations and remaining compliant with industry rules.
a. Key Features
IFS ERP provides a comprehensive set of features tailored to the banking sector. Some of the key features are:
- Real-time financial and operational insights.
- Seamless integration with banking systems.
- Comprehensive data management tools.
b. Why It Stands Out
IFS ERP stands out with its comprehensive integration capabilities, providing banks with the tools they need for better financial and operational management. Its real-time data processing helps ensure that banks make well-informed decisions.
Implementing ERP Systems in Banking Business Operations: Case Studies
ERP systems are being used in the banking industry to streamline processes and increase productivity. From loan processing to customer relationship management, banks are using ERP technologies to improve their services and stay compliant with regulations.
The case studies below show how several banks have effectively deployed ERP systems to handle distinct difficulties.
1. Case Study 1
A major bank in Singapore used ScaleOcean ERP to optimize its loan processing system. This resulted in a 30% reduction in processing time, allowing the bank to manage a larger number of loans.
Additionally, the technology improved compliance with the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) regulatory standards, resulting in smoother operations. Furthermore, ScaleOcean is also a vendor ERP for the Bank of China.
Scaleocean ERP provides an integrated and automated solution to help Bank of China track, organize, and monitor every detail of the contract more easily, and the process becomes faster.
2. Case Study 2
A regional bank implemented SAP S/4HANA to integrate its treasury processes. This led to considerable advances in cash flow management, allowing the bank to track and manage its financial resources more efficiently.
Real-time financial reporting became a crucial advantage, providing decision-makers with up-to-date information on the bank’s financial status.
3. Case Study 3
A multinational bank used Microsoft Dynamics 365 to improve its CRM capabilities, with an emphasis on increasing customer happiness.
With this technology in place, the bank was able to track client contacts, resolve service requests more quickly, and provide personalized experiences, resulting in increased customer retention and loyalty.
How to Choose the Best ERP for the Banking Industry
Selecting the right ERP for a bank demands more requires a solution that aligns with the institution’s regulatory obligations, operational complexity, and long‑term strategy. A thoughtful selection process assesses compliance readiness, integration capabilities, scalability, security, total cost of ownership, and user adoption.
Here are some tips for choosing the best ERP software for the banking industry in Singapore, including:
1. Evaluate Compliance and Regulatory Fit
Choose an ERP that inherently supports banking regulations, reporting standards, and audit trails. It should offer modules for anti‑money laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), and accurate financial reporting.
Ensuring regulatory compliance out of the box reduces risk, speeds up audits, and avoids costly customizations or non‑compliance penalties.
2. Prioritize Integration and Interoperability
The ideal ERP must integrate seamlessly with core banking systems, payment gateways, CRM, and legacy databases. APIs, middleware support, or built‑in connectors ensure smooth data exchange.
Without strong interoperability, banks risk data silos, manual reconciliation, and inefficiencies, which also undermines the very purpose of an integrated ERP.
3. Assess Scalability and Performance Capacity
As your bank grows, such as increasing customers, transactions, or branches, the ERP must handle the rising load without performance degradation.
A scalable architecture, capable of supporting concurrent users, large datasets, and real‑time processing, ensures longevity. Investing in a scalable ERP prevents frequent replacements or performance bottlenecks down the line.
4. Ensure Robust Security and Data Protection
Security is paramount in banking. The ERP must offer data encryption, role-based access control, secure APIs, and compliance with data privacy regulations.
For example, support for secure authentication and audit logs helps prevent unauthorized access or fraud. A security‑first ERP protects customer data and institutional integrity.
5. Evaluate Vendor Support, Maintenance, and Total Cost
Consider not only license costs, but also maintenance, updates, training, and support. Reliable vendor support, including regular updates for regulation changes and technical assistance, to ensure stability. A full cost‑of‑ownership analysis, including hidden costs, helps determine actual ROI and long‑term feasibility before committing.
6. Test Usability and Adaptability for Staff
The best ERP must offer intuitive interfaces, user‑friendly workflows, and minimal disruption during onboarding. Staff should be able to adopt it quickly for core tasks like transaction processing, reporting, and compliance checks. High usability reduces training time, lowers error rates, and increases overall productivity across departments.
Conclusion
Implementing ERP systems for the banking industry is critical for boosting operating efficiency, guaranteeing regulatory compliance, and providing better customer service in the banking business.
Banks may improve their operations by centralizing data and automating essential processes, reducing manual errors, and making more informed decisions. This results in increased productivity, better risk management, and more customer satisfaction.
For banks wishing to install an effective ERP system, ScaleOcean ERP provides a comprehensive solution. ScaleOcean is designed for the specific demands of Singapore’s banking industry, with AI-driven analytics, integrated compliance tools, and a modular design that ensures both scalability and regulatory conformity.
Request a free demo to customize the system according to your business needs.
FAQ:
1. What is ERP in banking?
ERP in banking refers to software systems that unify and manage essential banking functions like finance, customer service, and risk management. By automating tasks and centralizing data, ERP enhances operational efficiency, reduces errors, and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
2. What is the difference between core banking and ERP?
Core banking systems handle basic banking services such as account management and transaction processing. In contrast, ERP systems go beyond by integrating multiple business processes, including finance, human resources, and risk management, offering a more holistic solution for bank operations.
3. Which ERP do banks use?
Banks utilize ERP systems such as ScaleOcean, Oracle NetSuite, SAP S/4HANA, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and Infor ERP. These platforms automate workflows, ensure compliance, and improve customer interactions. However, ScaleOcean ERP offers a solution specifically tailored for Singapore’s banking sector, featuring strong compliance tools, real-time AI-driven analytics, and flexible customization, making it a highly suitable option for banks aiming for efficiency and growth.
4. What does ERP stand for in finance?
In finance, ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, referring to integrated software systems designed to automate and manage financial processes, such as accounting, reporting, and compliance. ERP helps organizations optimize operations and improve financial decision-making.












 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















