Manufacturing is the core of a country’s economy, so manufacturing businesses must have the right strategy and optimal processes to manage all aspects of manufacturing. This is especially true in Singapore’s competitive market, where proper manufacturing processes are crucial for businesses to be efficient, meet consumer demand, and achieve profitability.
According to EDB Singapore, the country manufactures 10% of global chips and around 20% of semiconductor manufacturing equipment, making it an important player in the worldwide supply chain. This highlights the need for the right manufacturing processes to support industries like electronics in Singapore’s economy.
This article discusses various aspects of manufacturing, from the primary function of manufacturing in the country’s economy to the methods and techniques commonly used in various manufacturing companies. Learn more here.
- Manufacturing involves converting raw materials or components into finished, tangible products on a large scaleoften using machinery, tools, labor, and chemical or biological processes.
- Methods of manufacturing are casting, forming, machining, joining/assembly, additive manufacturing, advanced manufacturing, and contract manufacturing
- Types of manufacturing are discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, job shop manufacturing, and repetitive manufacturing. mixed mode, batch process, continuous process.
- ScaleOcean’s software manufacturing helps manufacturing companies manage production processes more efficiently, reduce errors, and improve cost control in the entire manufacturing lifecycle, from planning to product delivery

What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing involves converting raw materials or components into finished, tangible products on a large scale, often using machinery, tools, labor, and chemical or biological processes. This value-creation process enables businesses to sell the final products at a price higher than the cost of raw materials, driving economic growth.
In manufacturing, the primary input consists of raw materials or components, such as metals, plastics, or other substances, which serve as the basic building blocks for creating products. These materials undergo various processes, such as machining, assembly, or chemical treatment, where they are transformed into a finished product that has value.
The output of the manufacturing process is the final, tangible product that is ready for sale or use, such as a car, electronics, or clothing. The efficiency of input-to-output conversion plays a significant role in the overall effectiveness and profitability of the manufacturing process.
A Brief History of Manufacturing
Manufacturing has evolved significantly over the centuries, from early handicrafts and simple tools to the sophisticated, automated production lines we see today. The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries marked a pivotal moment, introducing machinery and mass production techniques that drastically increased output and efficiency.
As technology advanced, so did manufacturing processes, with the introduction of electrical power, assembly lines, and computer-aided design (CAD) systems in the 20th century. Today, advanced technologies like robotics, AI, and IoT continue to shape the future of manufacturing, enhancing productivity and customization capabilities.
Manufacturing’s Role in the Economy
Manufacturing plays a crucial role in driving economic growth by producing goods that are essential for both domestic consumption and international trade. It supports job creation, stimulates innovation, and contributes significantly to GDP.
The sector also drives investment in infrastructure, technology, and supply chains, fostering economic development across industries. Manufacturing provides raw materials and finished products for various sectors, such as construction, healthcare, and consumer goods, making it integral to the functioning of the global economy.
By improving productivity and enabling trade, manufacturing companies remain a key pillar of economic stability and growth.
Key Manufacturing Techniques
Manufacturers use various techniques to meet production demands efficiently, each offering unique advantages based on product and market needs. Understanding these methods is key to optimizing production and ensuring cost-effectiveness with manufacturing cost estimating tools in Singapore.
1. Make to Stock (MTS)
Make to Stock (MTS) involves producing goods based on forecasted demand. Products are manufactured in advance and stored as inventory, ready to be sold when customers place orders. This technique is suitable for products with consistent demand, allowing businesses to quickly fulfill orders without delay.
2. Make to Order (MTO)
Make to Order (MTO) is a manufacturing strategy where production begins only after a customer places an order. This approach minimizes inventory costs and reduces the risk of overproduction. It is commonly used for customized or high-value products, ensuring that products meet specific customer requirements.
3. Make to Assemble (MTA)
Make to Assemble (MTA) involves producing components in advance, then assembling them into final products once an order is received. This method, combining the efficiency of MTS with the flexibility of MTO, is one of the key methods of assembly manufacturing, reducing lead times while offering customization.
4. Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing reduces waste while increasing value by eliminating non-value-added processes. Businesses can streamline processes by implementing tactics such as just-in-time inventory, continuous improvement, and remaining current with manufacturing trends.
Implementing lean methods improves operational efficiency, lowers costs, and enables manufacturers to adapt to customer demand rapidly. It contributes to the development of a culture of continuous improvement in which every process is optimized for maximum value while minimizing waste.
5. Mass Customization
Mass customisation combines the cost-effectiveness of mass production with the ability to tailor products. It lets firms produce vast quantities of things while allowing customers to customize specific aspects, resulting in products that are unique to individual desires.
This strategy is extensively employed in industries such as the automobile, textiles, and electronics, where demand for individualized products is increasing. Mass customization increases client happiness while preserving the efficiency of large-scale production systems.
Methods of Manufacturing
Manufacturing methods vary based on product design, materials, and production volume. Each method offers unique benefits, from traditional processes like machining to newer techniques like 3D printing. Understanding these methods is crucial for selecting the best approach for product development.
1. Casting/Molding
Casting and molding involve pouring liquid material into a mold to form a desired shape. It is commonly used for metals, plastics, and glass. This process allows manufacturers to create complex shapes with high precision, making it ideal for producing large quantities of items such as automotive parts and consumer goods.
2. Forming
Forming is a manufacturing process where materials are reshaped without adding or removing material, typically through pressure. This includes techniques such as stamping, bending, or rolling. It is often used for sheet metal or plastics and is widely applied in industries like automotive and construction.
3. Machining
Machining involves removing material from a workpiece using cutting tools like drills, lathes, or mills. It’s ideal for creating precise, detailed parts. Machining can be applied to metals, plastics, and composites, making it essential for industries requiring high-accuracy components such as aerospace and electronics.
4. Joining/Assembly
Joining and assembly processes involve connecting separate parts to create a final product. Methods include welding, riveting, and fastening, as well as more complex assembly techniques for electronics or machinery. This method is crucial in industries where complex products are made from multiple components, like automotive and electronics.
5. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds products layer by layer from digital designs. It allows for complex geometries and customization without the need for molds. This technique is useful for rapid prototyping and small production runs, and it’s becoming increasingly important in industries like healthcare and aerospace.
6. Advanced Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing combines innovative technologies with traditional techniques to improve product quality, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency. This includes automation, robotics, and data analytics. It’s typically used for high-tech industries that require precision, such as electronics, medical devices, and defense.
7. Contract Manufacturing
Contract manufacturing is when a company outsources its production to another company. This method helps businesses focus on design and marketing while leaving manufacturing to specialists.
It’s particularly useful for manufacturing companies looking to scale production or tap into specific expertise, often in electronics, pharmaceuticals, or consumer goods.
Types of Manufacturing

Manufacturing processes can be classified into several types based on product nature, production volume, and customization requirements. Understanding the distinctions among these manufacturing types helps businesses optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
1. Discrete Manufacturing
Discrete manufacturing involves producing distinct, individual items that can be easily counted and separated. This method is used for products like cars, appliances, and electronics. It focuses on assembling parts or components into finished products, often with customized features, using batch or assembly line processes.
2. Process Manufacturing
Process manufacturing is used for products that cannot be broken down into separate pieces after production. It’s commonly applied in industries like chemicals, food, and beverages. In this method, raw materials are transformed through chemical, biological, or thermal processes, producing items like paint, soap, or soft drinks.
3. Job Shop Manufacturing
Job shop manufacturing involves producing small batches of custom-made products based on specific customer orders. This type of manufacturing is highly flexible and often used for specialized, one-of-a-kind products, such as custom machinery, prototypes, or tools, where production runs are typically short and varied.
4. Repetitive Manufacturing
Repetitive manufacturing is a continuous production process where the same product is made in large volumes. It typically involves automated equipment to produce high quantities of identical products, such as in the production of consumer goods, electronics, or automotive components, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
5. Mixed Mode Manufacturing
Mixed mode manufacturing combines elements of both make-to-order and make-to-stock methods. It allows manufacturers to produce high-volume standard products while accommodating customized orders. This approach offers flexibility, enabling manufacturers to adjust production plans based on demand or customer specifications.
6. Batch Process Manufacturing
Batch process manufacturing involves producing products in specified quantities or batches. These products are often similar but may require different processing steps, such as in pharmaceuticals or food processing. It’s suitable for industries that need to handle variations in product specifications while maintaining efficiency.
7. Continuous Process Manufacturing
Continuous process manufacturing involves the production of goods without interruption, often for high-volume, standardized products like chemicals, oil, or paper. Raw materials are continuously fed into the production system, allowing for uninterrupted manufacturing, which maximizes efficiency and reduces the risk of production delays.
Challenges and Risks in Manufacturing
Manufacturing is a complex and dynamic industry, subject to various challenges and risks. From supply chain disruptions to fluctuating market demands, businesses must navigate several obstacles to ensure efficiency, quality, and profitability. Understanding these risks is crucial for long-term success.
1. Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions are one of the most common risks in manufacturing, often caused by natural disasters, geopolitical issues, or transportation delays. These disruptions can lead to inventory shortages, production delays, and increased costs, affecting the overall efficiency and profitability of manufacturers.
2. Equipment Failure
Unplanned equipment failure is a significant challenge in manufacturing, leading to downtime and delayed production. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent breakdowns, but even with the best preventive measures, unexpected failures can occur, resulting in costly repairs, lost production time, and potential safety hazards.
3. Quality Control Issues
Maintaining consistent product quality is critical in manufacturing. Defects or poor materials during the product lifecycle phases can lead to high rejection rates and increased costs. Implementing strong quality control and worker training is essential to mitigate this risk.
4. Labor Shortages and Workforce Management
Labor shortages, skill gaps, and high turnover rates can impact manufacturing operations. Finding qualified workers, especially in specialized fields, can be challenging. In addition, managing a diverse workforce and maintaining high productivity levels requires effective labor strategies and ongoing employee engagement.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Manufacturers must comply with various local and international regulations regarding safety, environmental impact, and product standards. Non-compliance can lead to fines, legal issues, and reputational damage. Staying updated on regulatory changes and implementing robust compliance systems is essential for manufacturers.
6. Rising Costs
Manufacturers are constantly facing rising costs for raw materials, labor, energy, and transportation. These increased costs can squeeze margins, especially if manufacturers are unable to pass them on to customers. Effective cost management strategies, such as lean manufacturing or automation, can help mitigate these challenges.
7. Technological Changes
The rapid pace of technological advancements presents both opportunities and risks in manufacturing. While new technologies like automation, AI, and IoT can improve efficiency, they also require significant investment and can disrupt existing workflows. Manufacturers must balance adopting new technologies with managing implementation risks.
Scale and Technology in Manufacturing
Manufacturing can vary from small-scale handicraft work to large-scale automated production in factories utilizing advanced technology and assembly lines. The integration of advanced technologies is reshaping the manufacturing industry, enabling businesses to scale their operations more efficiently and cost-effectively.
As manufacturers seek to expand and innovate, embracing scalable technologies has become essential for staying competitive in an increasingly fast-paced global market. Here are the scales and technologies in manufacturing that you can use, including:
1. Software ERP for Manufacturing
ERP software for manufacturing in Singapore integrates various business functions, including production, inventory management, and procurement, into a unified system. It streamlines processes, enhances data accuracy, and enables real-time monitoring of operations. This helps manufacturers scale operations efficiently while maintaining consistency.
2. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and 3D Printing
CAD and 3D printing technologies revolutionize product design and prototyping. CAD software allows for precise design creation, while 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and small-scale production of complex parts. These tools reduce lead times, enhance customization, and lower production costs, fostering innovation and scalability.
3. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
MES are systems that track and monitor production processes on the shop floor. They provide real-time data on machine performance, inventory levels, and production efficiency. By integrating one of Singapore’s manufacturing execution systems (MES) into manufacturing operations, businesses can optimize production, improve scheduling, and reduce downtime, helping them scale quickly and effectively.
4. AI and Flexible Robotics
AI and flexible robotics are transforming manufacturing by enabling smart automation. AI algorithms optimize production workflows, predict maintenance needs, and improve quality control.
Flexible robotics adapts to different tasks, enhancing efficiency and scalability by automating complex, repetitive processes across various production stages.
You can use scaleocean manufacturing ERP software, which can be integrated with any renewable manufacturing technology, such as CAD and 3D automation, MES, also AI and robotics.
With automated AI integration, ScaleOcean can predict demand and plan production with accurate, real-time analysis.
ScaleOcean’s AI for manufacturing can also analyze production schedules and raw material requirements, monitor the entire supply chain, predict condition-based machine maintenance, and monitor machine performance in real time.
ScaleOcean’s comprehensive and seamless integration optimizes the manufacturing process from start to finish, enabling companies to be more intelligent and predictive in optimizing the entire manufacturing lifecycle from planning to product delivery. Do a free demo now to get the best solution for your manufacturing processes.

How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Process for Your Singapore Business
The optimal manufacturing process is determined by a variety of criteria, including product complexity, market needs, and operational considerations. These aspects will assist your company in implementing a process that is in line with its goals and resources.
1. Product Factors
Product complexity and customisation are critical factors in selecting the best manufacturing method. Products with detailed designs or specific features are better suited to job shop manufacturing, which allows for small batch production and customization.
Products with high standardization and low customization are suited for repetitive manufacturing, boosting productivity in industries like electronics. According to JTC, Singapore’s manufacturing sector employs 450,000 workers and contributes 21% to GDP. Here are key characteristics of product complexity and personalization:
- Complexity: Products with intricate designs and specifications may require job shop manufacturing.
- Customization: If your product needs to be tailored to individual customer orders, job shop or mass customization processes may be ideal.
2. Market Factors
Market demand and lead time are important considerations in determining the manufacturing process. High demand for standardized items usually necessitates repetitive or continuous manufacturing, as these procedures are intended for high-volume production and rapid turnaround times.
Industries that require customized or low-volume products may profit from batch or job shop manufacturing. These processes provide flexibility for specialized production, but with longer lead times and greater prices than high-volume production. The following are significant elements affecting demand and lead time:
- Demand Volume: High volume products benefit from repetitive manufacturing, while smaller, custom orders are suited for job shop or batch processes.
- Lead Time: For industries with rapid production needs, continuous or repetitive manufacturing is advantageous.
3. Operational Factors
When deciding on a manufacturing method, cost is an important consideration. Some methods, such as repeated manufacturing, are excellent for low-cost production on a large scale. These techniques are extremely efficient and ideal for high-volume manufacture of standardized products with little customization.
Scalability and worker skills are also important considerations. Processes such as job shop production may necessitate the use of expert labor for precision jobs, boosting prices while providing flexibility for unique or complex items. Choosing the proper method requires balancing these operational factors:
- Cost: Consider the capital and operational costs involved with each manufacturing process.
- Scalability: Repetitive and continuous processes are often more scalable, while job shops and batch processes may require more manual labor.
- Workforce Skills: Job shop processes demand highly skilled workers, whereas repetitive manufacturing often requires less specialized labor.
Examples of Manufacturing Companies in Singapore’s Industrial Landscape
Singapore’s manufacturing scene is dynamic, with diverse businesses using different procedures to remain competitive. Here’s how businesses are using manufacturing methods like job shop and batch production to innovate:
1. Job Shop and 3D Printing in MedTech Startup
A Singapore-based MedTech startup manufactures personalized medical equipment using job shop manufacturing and 3D printing technology. Job shop manufacturing provides flexibility, allowing the organization to create one-of-a-kind products tailored to specific patient needs. It’s perfect for elaborate or customized products.
3D printing enhances this procedure by allowing for the rapid fabrication of prototypes and sophisticated pieces. This technology helps to minimize production time and costs while retaining precision, making it an important tool in the MedTech business, where patient care is highly customized.
2. Batch Process and Lean Principles in F&B
To maximize production, a top Singaporean food and beverage business employs batch processing and lean concepts. By focusing on waste reduction and constant development, the organization improves productivity. This strategy reduces downtime and simplifies ingredient management.
Lean principles are essential for lowering operating expenses while maintaining high-quality standards. The company’s drive to waste reduction and process optimization not only improves product quality but also increases profitability, positioning it as a competitive competitor in the F&B industry.
Automatically Monitor the Manufacturing Process From Start To Finish with Scaleocean
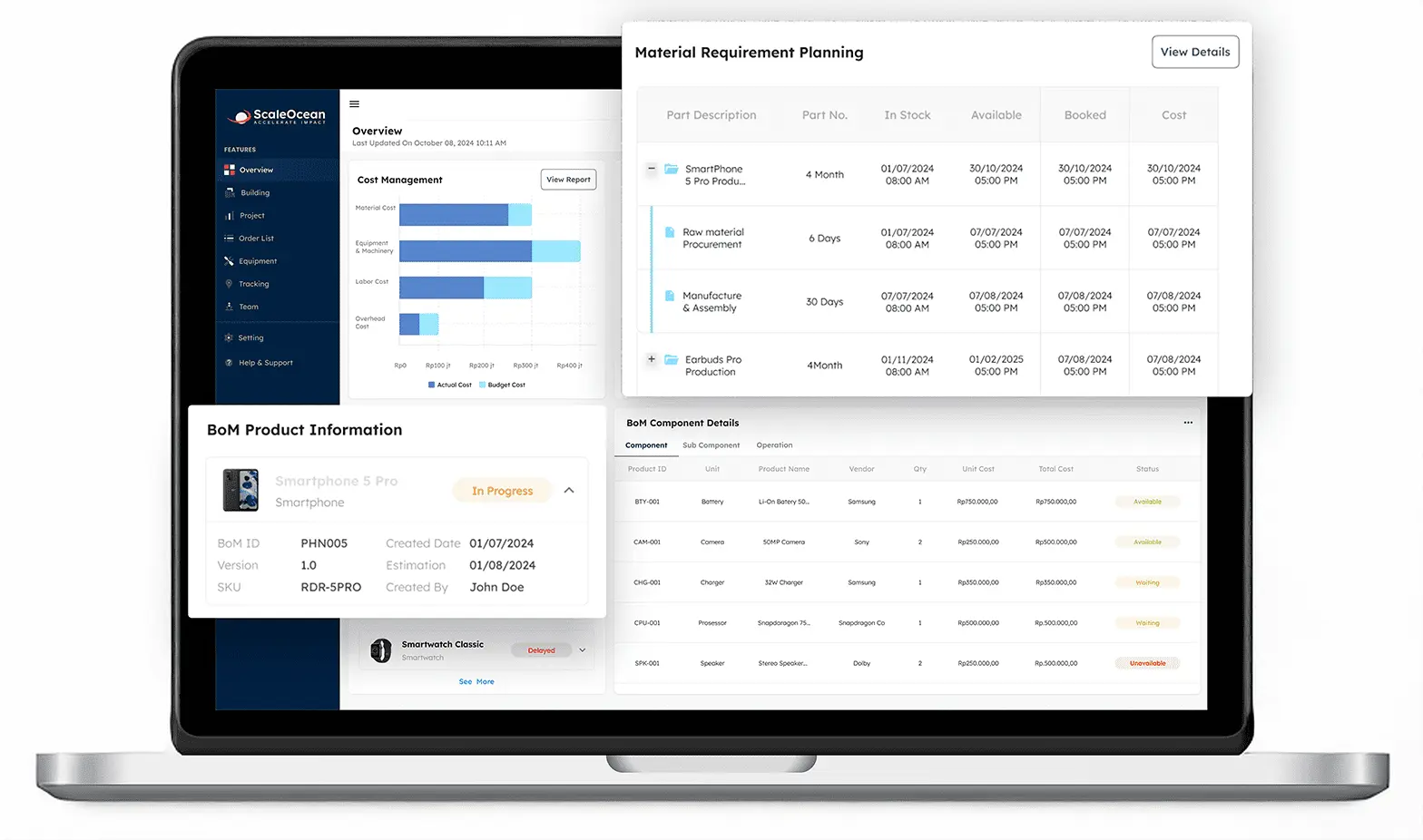
ScaleOcean ERP for manufacturing offers a comprehensive solution that optimizes the entire production process from start to finish. With a variety of integrated automation features, ScaleOcean enables manufacturing companies to plan, manage, and monitor production more efficiently.
ScaleOcean also provides seamless integration with various business functions, such as finance, sales, and procurement, allowing companies to manage workflows more efficiently and transparently. Furthermore, with unlimited users at no additional cost, this system can also monitor your various warehouses within a single platform.
This provides real-time visibility of inventory spread across multiple warehouses, optimizing distribution of goods and ensuring timely deliveries without shortages or excess stock. You can also customize the system and features to best suit your business needs.
To learn more about this solution, you can request a free demo and consult with ScaleOcean’s professional team. Here are some of the specific features ScaleOcean offers for comprehensive manufacturing process management:
- Smart MRP (Material Requirement Planning): This system automates the calculation of raw materials needed for production based on schedules and delivery times, ensuring they are available on time and in accurate quantities.
- Bill of Materials Management: This feature simplifies the creation of lists of raw materials and components needed for production, thereby increasing efficiency in material management.
- Integrated Supply Chain Management: Manages the entire manufacturing process, from production scheduling to order processing, in a single, centralized platform. This ensures better coordination between all involved parties.
- Cost Management: This system automates the calculation of the cost of goods manufactured, covering all costs involved in manufacturing, to ensure cost transparency and avoid waste.
- Order Management: Automates the entire process of receiving, fulfilling, and processing orders, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in managing customer orders.
- Warehouse Management: Monitors inventory in real time, speeds up the process of selecting goods for shipment, and optimizes warehouse storage.
Through the integration and automation of these modules, ScaleOcean helps manufacturing companies manage production processes more efficiently, reduce errors, and improve cost control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, manufacturing is a dynamic and complex process that requires effective management and advanced technology to optimize efficiency and reduce costs.
As the industry continues to evolve, leveraging integrated solutions like ScaleOcean’s ERP for manufacturing can provide businesses with the tools they need to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and scale effectively.
With real-time insights, seamless integration, and robust support, ScaleOcean ERP manufacturing is the ideal solution for manufacturers looking to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced market. Do a free demo immediately by contacting our team to get this solution!
FAQ:
1. What is production vs manufacturing?
The purchasing management process typically begins halfway through the procurement process. Key elements of purchasing include submitting a purchase request, which is often initiated through a purchase requisition. It’s a formal internal request for approval to purchase on behalf of the company.
2. What is the basic manufacturing process?
There are four fundamental manufacturing processes used to shape a product. These include Casting, Forming (metal deformation), Joining (such as welding, brazing, soldering, and fastening), and Metal Removal (machining) processes. In casting, the material solidifies within a mold to achieve the desired shape.
3. What is in a manufacturing industry?
The manufacturing sector consists of businesses involved in the mechanical, physical, or chemical transformation of materials, substances, or components into finished products.
4. What is the future of manufacturing?
The future of manufacturing will see factories that can self-optimize, self-correct, and self-learn, enabling smooth coordination across supply chains, production networks, and customer demands. By 2040, manufacturers won’t be debating automation, AI, or digitalization; these will be the standard.







 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















