Amidst Singapore’s rapid digital transformation, Cloud ERP has emerged as a new foundation for modern business management. Originating from traditional on-premise ERP systems in the early 1990s, Cloud ERP has evolved with the advancement of the internet and cloud computing.
It enables companies to manage finances, operations, and supply chains in an integrated manner through a flexible online platform. However, many companies that have not yet made the switch to Cloud ERP still face various obstacles.
Such as high IT infrastructure costs, fragmented systems, limited real-time data access, and difficulties adapting to regulatory changes and the dynamic business scale in Singapore. Cloud ERP offers a solution, offering cost efficiency, scalability, data security, and comprehensive business visibility.
To that end, we’ve outlined a comprehensive article on Cloud ERP as the future of enterprise resource planning software, discussing the benefits, trends, and why companies should choose a Cloud ERP solution to stay competitive in the digital age. Learn more here!
- Cloud ERP is an ERP system delivered as a service over the internet, unifying core business processes like finance and supply chain.
- The importance of using cloud ERP software for business can support your company, including cost efficiency, accessibility and mobility, scalability, automatic updates, and more.
- Top 5 Cloud ERP providers examples, such as ScaleOcean, SAP, NetSuite, Acumatica, and Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Using ScaleOcean’s cloud ERP solutions may help your business optimize procedures, stimulate innovation, and drive long-term success.

What is Cloud ERP?
Cloud ERP is a cloud-based system that centralizes and manages essential business functions, such as finance, human resources, and supply chain, through an internet connection rather than on local servers.
Hosted on a provider’s cloud platform and basically delivered as a service or software as a service (SaaS). It enables companies to benefit from greater flexibility, easy scalability, reduced initial investment through a subscription-based model, and real-time access to data from any location.
By unifying multiple operational processes into a single, web-accessible platform, Cloud ERP serves as a centralized data hub and enterprise software system that supports higher efficiency and more informed business decisions.
Cloud ERP vs. On-Premises ERP
Cloud ERP or SaaS ERP is hosted by the vendor’s cloud storage, allowing easy remote access and quick recovery while eliminating the need for physical hardware. It typically comes with lower initial costs, as companies avoid huge infrastructure or maintenance spending. It offers scalability and flexibility instantly.
On-Premises ERP is hosted and stores data locally, requiring significant upfront investments in hardware, maintenance, and security. Scaling an On-Premises system often demands substantial infrastructure changes. Plus, data security relies heavily on potentially constrained internal IT teams.
When choosing a type of ERP, businesses must look closely at data storage, implementation costs, scalability, and security. As reported by Business Research Insights, the global ERP market is projected to reach $105.4$ billion USD by 2029, fueled by the growing shift towards cloud solutions.
The Importance of Cloud ERP for Medium-to-Large Companies
For mid-to-large-sized businesses, Cloud ERP plays a critical role in sustaining growth while maintaining operational control. It is a transformative solution, offering benefits across sectors. It streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and ensures a competitive edge.
The benefits of Cloud ERP go beyond just tech upgrades. They truly empower businesses to optimize resources and encourage innovation. Here are some key benefits that highlight why Cloud ERP is a vital resource for modern businesses:
- Cost Efficiency. Cloud ERP lowers initial expenses on hardware, installation, and maintenance, avoiding large capital investments. The pay-as-you-go model lets businesses pay for only what they use. Integrated ERP finance modules streamline financial processes, making it a smart choice for SMEs and startups.
- Accessibility and Mobility. It enables businesses to access their systems and data from anywhere, at any time. Employees can collaborate effortlessly, especially with remote teams. SaaS ERP further enhances this flexibility, boosting productivity and ensuring uninterrupted operations across locations. For instance, managers can check financial reports, monitor inventory, or approve transactions while on the move. Such features are essential for businesses in fast-paced environments where quick responses are critical.
- Scalability. Cloud ERP is designed to grow alongside your business. Whether you’re expanding your operations, entering new markets, or adapting to seasonal fluctuations, the system can easily adjust resources as needed. In contrast to on-premises systems, which often require hefty investments for expansion, cloud-based ERP solutions can adapt to your changing needs without additional infrastructure. So, customizing hybrid ERP systems enhances scalability by combining cloud flexibility with on-premise control for tailored growth.
- Automatic Updates. With cloud-integrated ERP, businesses can always access the latest features and updates without needing to intervene manually. Providers take care of upgrades and security patches, enabling companies to concentrate on their core operations rather than IT upkeep. This proactive strategy minimizes downtime and helps businesses stay competitive. When considering custom ERP vs off-the-shelf ERP maintenance, automatic updates ensure both systems remain up-to-date and efficient.
- Data Security. Data security is a primary concern for Cloud ERP providers, who utilize advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular backups to protect sensitive information. Additionally, compliance with international data protection regulations provides an extra layer of reassurance. For companies in regulated industries, adopting Cloud ERP ensures they meet necessary standards while maintaining operational integrity.
- Improved Collaboration. Cloud ERP genuinely enhances teamwork by giving teams a centralized platform to share real-time data. Whether it’s reports or inventory details, everyone stays on the same page, making it much easier to collaborate and work efficiently across all departments and locations. Mobile ERP access further enhances this by allowing employees to collaborate on the go, improving communication, decision-making, and reducing errors or misunderstandings.
- Enhanced Data Analytics. Built-in analytics tools within Cloud ERP give businesses valuable, real-time insights into operations. By tracking key metrics, companies can easily analyze performance, spot trends, and identify areas for improvement. These data-driven insights lead directly to smarter business decisions.
- Faster Implementation. Compared to traditional on-premises systems, Cloud ERP is much quicker to implement. Since cloud solutions are pre-configured, they don’t need the same infrastructure setup. This lets businesses get up and running faster, reducing the time it takes to achieve a return on investment (ROI).
Types of Cloud ERP
Cloud ERP is available in several deployment models designed to match different business needs, budgets, and security requirements. Understanding these types helps organizations choose the right balance between cost efficiency, customization, scalability, and data control as they modernize their enterprise systems.
- Multi-tenant SaaS. Allows multiple companies to share the same software instance and infrastructure while keeping data securely separated. It offers lower costs, automatic updates, faster deployment, and standardized best practices, making it ideal for businesses seeking efficiency and scalability.
- Single-tenant SaaS. It provides a dedicated software environment for one organization. While still hosted in the cloud, it allows greater customization, enhanced performance control, and stricter compliance, making it suitable for enterprises with complex processes or regulatory demands.
- Public Cloud. Deployed on shared cloud infrastructure operated by providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. It delivers high scalability, rapid deployment, and cost efficiency, enabling businesses to adjust resources on demand without managing physical hardware.
- Private Cloud. Runs on infrastructure dedicated to a single organization, either hosted internally or by a third party. It offers greater control, security, and customization, making it ideal for businesses with strict data governance, security, or industry-specific compliance requirements.
Key Components of Cloud ERP
Cloud ERP systems provide a variety of modules that enhance business operations and facilitate improved decision-making. These components work together smoothly, allowing organizations to oversee various functions from a single platform. By utilizing these tools, companies can increase efficiency, reduce expenses, and align with their strategic objectives.
According to ERPnews, essential Cloud ERP components consist of HR for handling employee life cycles, CRM for enhancing customer interactions, and Business Intelligence for gaining data-driven insights. These modules help businesses remain agile and competitive in an ever-changing market.
- Financial Management. This module enhances accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting, giving businesses clear insights into their financial status. It ensures compliance and makes tax reporting easier, helping companies maintain financial clarity.
- Human Resource Management (HRM). Cloud ERP consolidates employee records, payroll, and recruitment processes, leading to improved workforce management. Automation reduces administrative tasks and boosts employee engagement.
- Supply Chain Management. Manage inventory, procurement, and logistics effectively with Cloud ERP’s supply chain modules. Integrated supply chain features allow businesses to accurately forecast demand, reducing the risk of stock shortages or surplus inventory. The process of ERP consolidation enhances this by streamlining procurement and distribution, leading to better coordination with suppliers and vendors.
- Manufacturing and Production. Cloud ERP covers every aspect of manufacturing, from planning to quality control. By tracking production metrics in real-time, businesses can boost productivity and reduce waste.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM). CRM modules assist businesses in fostering stronger customer relationships by managing interactions and analyzing behaviors. It also ensures a smooth customer experience by integrating with support and service systems.
From these components, you can use integrated cloud ERP software to comprehensively manage all processes within a single platform. You can use ScaleOcean’s comprehensive cloud ERP software solution, which can unify core business functions such as finance, sales, inventory, and human resources into a single, secure digital ecosystem.
By leveraging a cloud-based architecture, ScaleOcean ensures that these key components are not just siloed tools but are deeply interconnected, allowing for real-time data synchronization across departments. Request a free demo to get this comprehensive solution for your business.

Is Saas ERP Secure?
Cloud-based ERP systems or Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) are generally very secure, often more secure than traditional on-premises systems. However, security in the cloud is a shared responsibility, and it depends on how you manage it. While vendors secure servers and software, companies are responsible for who they allow to access users and data.
Why It’s Often More Secure:
- Expert Management: Vendors employ elite security teams to monitor threats 24/7. This is especially true for large companies with critical data that should be stored in on-premises systems.
- Automatic Patching: Security updates are applied automatically. With on-premises systems, companies often lag in applying patches, leaving the door open to hackers.
- Physical Security: Data is stored in highly protected data centers with biometric access, backup power, and disaster recovery.
- Compliance: Leading vendors maintain rigorous certifications such as SOC 1/2, ISO 27001, and GDPR compliance by default.
Why Companies Should Choose the Cloud ERP?
Why choose Cloud ERP? It offers remarkable cost savings by removing the need for expensive hardware and ongoing IT maintenance. With its subscription model, businesses can better predict costs and free up vital resources for key growth initiatives, like market expansion.
Cloud ERP truly boosts mobility by allowing teams to access data and apps from anywhere, improving collaboration and productivity. It simplifies updates, ensuring your business always uses the latest technology easily. An ERP software demo can show how it streamlines operations and supports growth.
When Should You Move Your Business to Cloud ERP?
Knowing when to migrate to Cloud ERP is vital for a seamless and effective implementation. Delaying the transition can impede growth, while jumping in too soon may overextend resources.
Identifying key indicators is essential for businesses to determine the right moment for the switch. Timing the migration correctly allows for better resource management and reduces the risk of disruptions during the process. Here are some typical situations that signal the need to transition to Cloud ERP:
- Rapid Business Growth. The adaptability of Cloud ERP allows businesses to add new users, incorporate features, and manage larger data volumes. Two-tier ERP scalability enhances this by offering flexible, tiered solutions for both local and global needs. This scalability guarantees smooth operations without the need for substantial infrastructure investments.
- Outdated Systems. When traditional enterprise systems fail to meet current business requirements, migrating to a cloud-based solution becomes a strategic choice. SaaS platforms offer expanded features, like automation, real-time information, and enhanced integrations, all in line with modern operational requirements.
- Real-Time Data Needs. Real-time analytics enable managers to monitor important performance metrics and respond quickly to market changes. These platforms provide consolidated data access, which minimizes the need for manual data collection and processing. This feature improves cross-departmental collaboration and enables informed decision-making. Companies that use real-time analytics may improve workflows, increase customer satisfaction, and grasp opportunities faster than their competition.
- Compliance Requirements. It provides advanced reporting capabilities and secure data management in accordance with legal norms. Built-in compliance tools reduce the risk of penalties while increasing transparency with stakeholders. Companies that implement these solutions may demonstrate accountability while protecting sensitive data, resulting in increased trust from investors and clients.
Top 5 Cloud ERP Provider Examples
Choosing the right Cloud ERP provider is essential for the success of your business operations. Each provider has its own unique features, strengths, and specializations that cater to different industries and business sizes.
By understanding these options, businesses can better align their ERP selection with their specific operational and strategic goals.
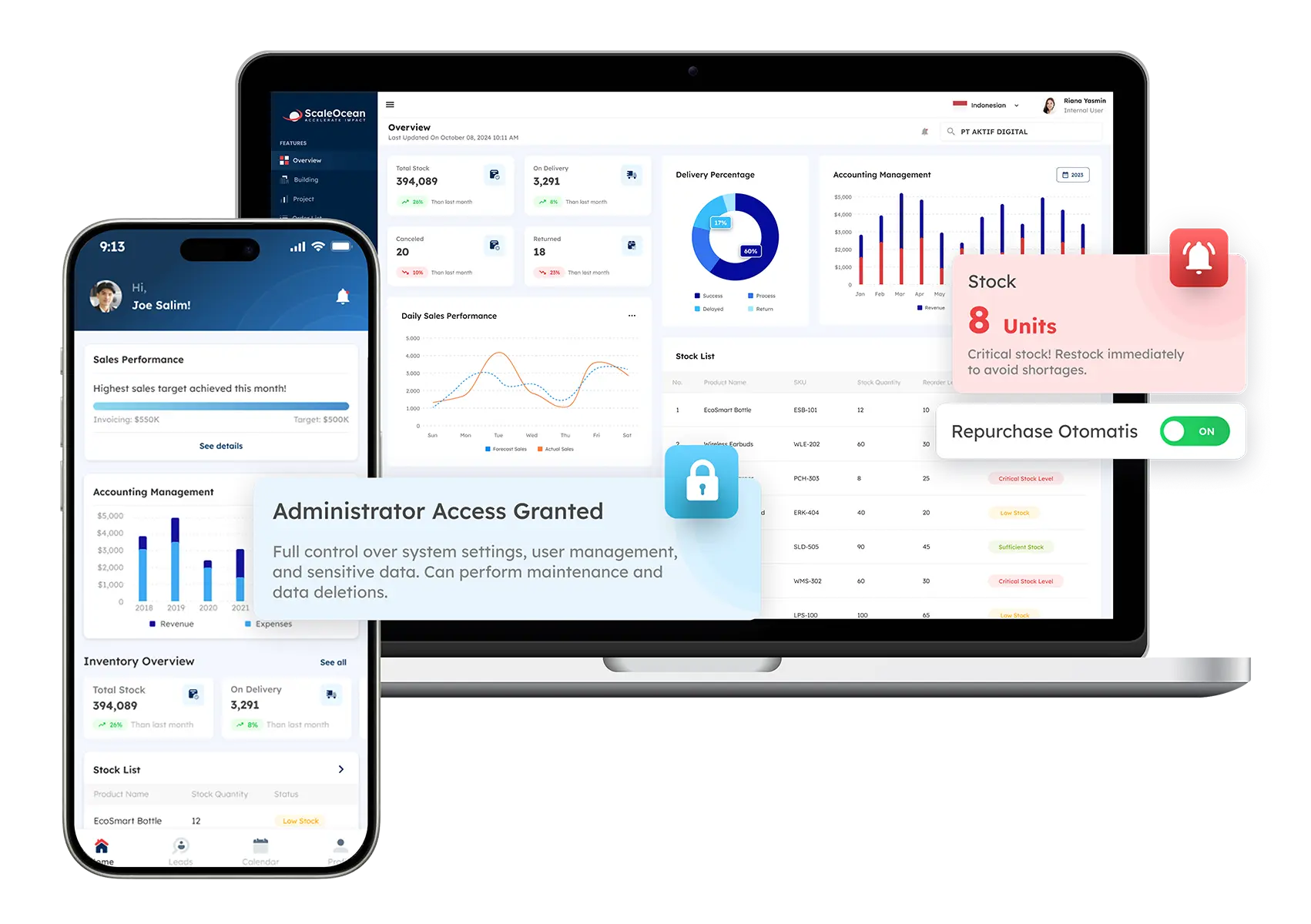
1. ScaleOcean’s Cloud ERP
ScaleOcean’s cloud ERP is a major supplier in Singapore, helping businesses streamline and consolidate their essential processes. Its flexible platform meets the needs of our dynamic market, ensuring efficiency and long-term success. They empower enterprises with personalized solutions.
Learn how ScaleOcean’s unique ERP solutions may help your business optimize procedures, stimulate innovation, and drive long-term success. ScaleOcean also offers a free demo today, so you can see ScaleOcean’s full potential for your company.
Key Features:
- Data Integration Across Modules: Integrates business functions like finance, sales, and inventory for real-time data sharing and decision-making.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Scalable and adaptable, ScaleOcean’s Cloud ERP grows with your business without major disruptions.
- Real-time Reporting and Analytics: Provides real-time analytics for informed decision-making and performance tracking.
- Security and Data Backup: Ensures data security with encrypted cloud storage and automated backups to protect against data loss.
- Customizability and Automation: Customizable workflows and dashboards, with automation to increase efficiency and reduce manual tasks.
Many companies have successfully optimized their business processes using ScaleOcean Cloud ERP software. One such company is PT. Bukaka Inti Aircon is an HVAC specialist. ScaleOcean has successfully transformed manual and fragmented operations into an efficient, data-driven business.
By centralizing accounting, sales, work orders, and job costing, the company eliminates data silos and gains the real-time visibility needed to effectively manage field operations.
Ultimately, integration with ScaleOcean Cloud ERP can improve operational efficiency while providing the financial accuracy needed to protect profit margins and support sustainable growth. To see the full story, watch the following video.

| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Best For: ScaleOcean is ideal for medium-to-large businesses across manufacturing, retail, and services. It offers a highly customizable cloud ERP with strong financial and supply chain integrations, providing real-time data visibility and excellent process efficiency.
2. SAP Cloud ERP System
SAP offers cloud ERP systems that support a wide range of company tasks, including financial management, supply chain management, and analytics. Its products are tailored to various industries, providing tools for streamlining company operations and data analysis across departments.
SAP’s cloud ERP solutions include automated workflows and real-time data sharing, which help businesses run operations more efficiently. Its modular design allows organizations to select certain tools based on their needs, providing better flexibility to firms of all sizes.
Key Features:
- Cloud-based ERP platform for enhanced flexibility.
- Comprehensive financial management tools.
- Real-time data sharing across departments.
- Process automation for increased efficiency.
- Analytics capabilities for better decision-making.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Best For: SAP’s cloud ERP solutions are suitable for medium to large-sized businesses across various sectors, including manufacturing, retail, and services, that require a flexible, scalable solution to manage multiple business functions.
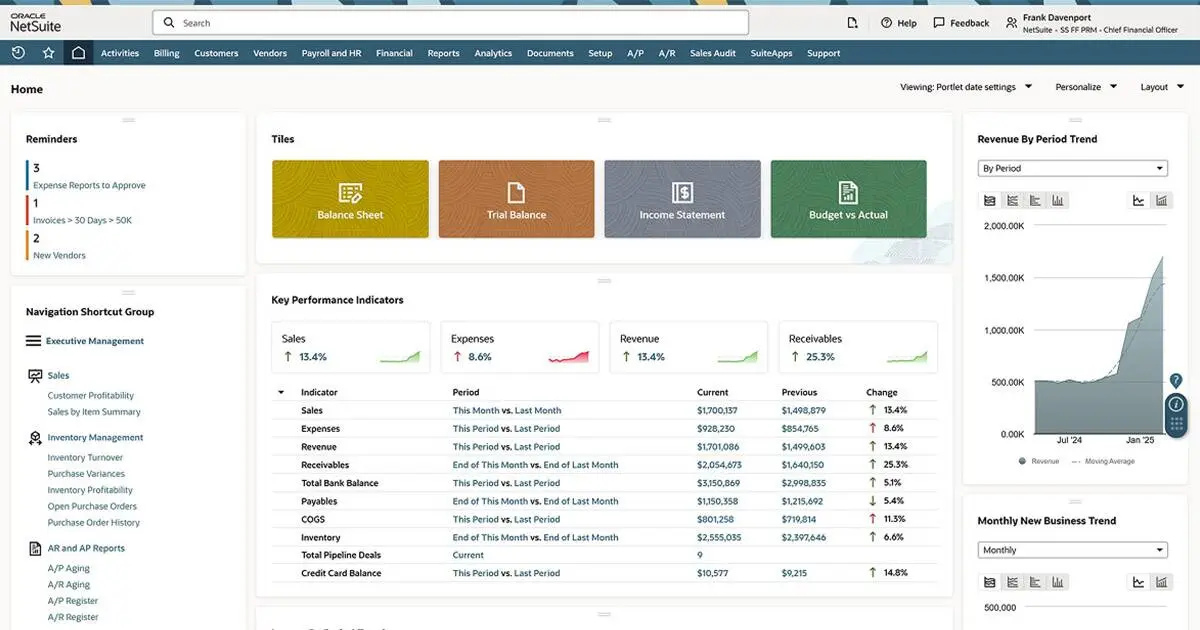
3. NetSuite Cloud-Based ERP Solution
NetSuite is a cloud-based ERP solution that combines financial, customer management, and inventory control. Its platform provides seamless data exchange and cooperation across departments, guaranteeing that firms can make decisions based on real-time, reliable information.
NetSuite is built for growth, with a modular structure that enterprises can customize to meet particular operational requirements. The technology enables efficient workflows and promotes team communication, resulting in greater departmental cooperation.
Key Features:
- Integrated finance and customer management.
- Real-time data sharing across departments.
- Inventory control and supply chain management.
- Customizable for different business processes.
- Cloud-based platform for flexibility and accessibility.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Best For: NetSuite is suitable for mid-sized to large businesses across various sectors, including retail, manufacturing, and distribution. It provides an integrated solution for managing finance, CRM, and inventory, making it a good fit for companies looking to streamline operations.
4. Acumatica Cloud ERP Platform
Acumatica is a cloud ERP platform designed for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMBs). It provides solutions to streamline a variety of operational tasks, including accounting and financial management, project management, and inventory management, all inside a customizable, cloud-based system.
Its modular design enables firms to implement the features they require, resulting in a personalized approach to business administration. Acumatica assists SMBs in lowering operational expenses and increasing productivity by automating critical business operations and ensuring data accessibility.
Key Features:
- Cloud-based platform for SMBs.
- Accounting and financial management tools.
- Inventory and project management features.
- Customizable to fit different business needs.
- Real-time data access for better decision-making.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Best For: Acumatica is designed for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) in industries like retail, distribution, and manufacturing. Its cloud-based ERP system is particularly beneficial for businesses that need flexibility, scalability, and efficient management of accounting, inventory, and projects.
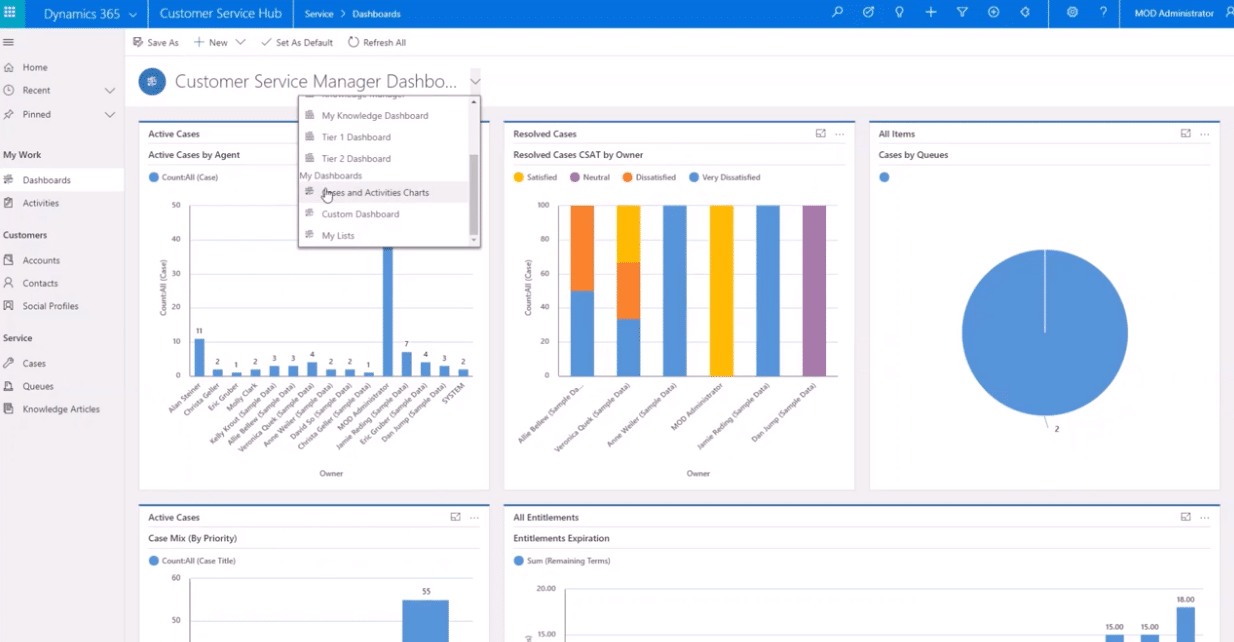
5. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Cloud-Based ERP
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a cloud-based ERP and CRM system. It combines important business processes such as finance, operations, sales, and customer support onto a single platform, helping organizations to manage their operations more effectively.
The system is very compatible with other Microsoft technologies, allowing firms to leverage existing software to increase productivity. Dynamics 365 also offers real-time data insights and automation capabilities, which improve company decision-making processes.
Key Features:
- Integrates ERP and CRM functions into one system.
- Real-time data access for improved decision-making.
- Automation capabilities to streamline workflows.
- Compatibility with other Microsoft tools.
- Cloud-based for flexibility and accessibility.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Best For: Microsoft Dynamics 365 is best for medium to large businesses looking for a comprehensive, cloud-based ERP and CRM solution that integrates seamlessly with Microsoft tools for better data management and operational efficiency.
How to Choose The Right Cloud ERP for Your Company?
Choosing the right Cloud ERP solution is crucial for achieving business growth. This guide covers key factors like evaluating your specific needs, scalability, integration, support, security, and cost to help you make the best decision for your company:
Evaluate Business Needs and Internal Processes
Understanding your current operational challenges and business processes is crucial when selecting the right Cloud ERP. Assess which areas need improvement and how an ERP system can streamline daily operations. Preventing ERP system failures in cloud-based solutions ensures smooth implementation and better productivity.
By carefully mapping out your specific business requirements, you can easily determine which ERP features are necessary. Identifying key pain points and strategic goals ensures the chosen ERP aligns perfectly with your business objectives and delivers maximum long-term value
Functional Fit with Industry & Business Scale
It’s essential to choose an ERP that supports both your industry-specific needs and your business scale. Every industry has unique demands, so your ERP must offer features like finance, supply chain, and HR that are perfectly tailored to these requirements.
For businesses of any size, ERP scalability is truly key. Smaller companies might not need all the features larger ones do, so opting for an ERP that can easily grow as your business expands ensures efficiency without unnecessary complexity.
Scalability & Integration Capabilities
A Cloud ERP solution must be able to truly grow with your business. Scalability ensures that as your operations expand, the system can handle increased data volumes and users without any performance issues, giving you long-term flexibility and peace of mind.
Additionally, make sure the ERP can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems. Whether it’s CRM, HR software, or accounting, smooth integration allows for easier transitions and minimal disruption during the implementation process.
Vendor Support & Implementation Planning
Evaluating your ERP vendor’s reputation and support services is absolutely crucial for successful implementation. A reliable vendor should provide excellent training, assistance, and proactive support to ensure a smooth onboarding and seamless system integration for your team.
An effective implementation plan is vital to minimizing downtime during the transition. The vendor must offer clear timelines, support structures, and resources to ensure your team can truly and fully utilize the ERP system post-deployment.
Data Security, Compliance & Cloud Infrastructure
Data security and compliance are truly critical when you’re choosing a Cloud ERP system. You need to ensure the vendor follows strict security protocols and offers robust data protection, including features like encryption and essential multi-factor authentication.
Your chosen cloud infrastructure must meet industry standards and fully comply with local regulations. This becomes especially vital for businesses handling sensitive information or operating in heavily regulated fields like healthcare or finance.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Return on Investment (ROI)
When evaluating Cloud ERP, it’s vital to look beyond just the initial license fees and calculate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). This TCO includes everything, such as implementation, training, maintenance, and any potential upgrade costs over the system’s lifetime.
Calculating the potential Return on Investment (ROI) is crucial to gauging the ERP’s long-term benefits. Consider how the system will cut inefficiencies, lower operational costs, and actively drive revenue growth through better decision-making and streamlined processes.
The Future of Cloud ERP in Singapore
Singapore is recognized as a leading global business hub, at the forefront of adopting innovative technologies like Cloud ERP. Thanks to initiatives such as Singapore business grants, companies are encouraged to implement advanced solutions that boost efficiency and flexibility. Cloud ERP is constantly evolving, providing enhanced functionalities and capabilities.
The future of Cloud ERP in Singapore will be shaped by technological advancements, new features, and the nation’s ongoing digital transformation journey. Let’s explore how these factors will influence the next phase of Cloud ERP adoption.
Technological Trends
The rise of AI and IoT promises to transform the capabilities of business resource planning tools. AI-powered automation will improve decision-making by giving predicted insights and streamlining routine processes. Meanwhile, IoT integration will enable real-time data capture from connected devices, hence improving supply chain performance and asset tracking.
These developments will allow businesses to respond more quickly to market shifts and improve their workflows. As these advances progress, ERP platforms will become smarter and more adaptable to shifting business landscapes.
Innovative Features
Next-generation ERP software will prioritize technologies such as predictive analytics and machine learning to improve usability. Predictive analytics will allow businesses to better anticipate market trends and make data-driven decisions with greater confidence.
Machine learning will do complex operations with minimum human intervention, decreasing errors and speeding procedures. The user interfaces will be enhanced for simplicity and straightforward navigation, making ERP tools more accessible. These improvements will enable organizations to get the most out of their systems while remaining competitive.
Digital Transformation
ERP platforms play an important role in Singapore’s efforts for industry-wide digital transformation. As firms progressively digitize their activities, these solutions provide an integrated solution for successful operations management. This synergy reinforces Singapore’s objective of a strong digital economy and promotes innovation.
Businesses that implement modern ERP solutions may remain nimble, meet regulatory standards, and leverage cutting-edge technologies. All of the best ERP platforms will continue to play an important role in Singapore’s march to complete digital integration.
Conclusion
Cloud ERP is essential for boosting business efficiency and competitiveness, particularly in a fast-changing market like Singapore. By bringing together various functions into a single platform, it allows for real-time data access, better decision-making, and more streamlined operations.
Companies that implement Cloud ERP enjoy the flexibility and scalability necessary to succeed in today’s rapid digital landscape. For businesses considering Cloud ERP, choosing a dependable and adaptable solution is vital.
ScaleOcean provides a customized Cloud ERP platform that caters to a wide range of business requirements while ensuring smooth scalability. Start optimizing your operations and gaining a competitive edge by trying ScaleOcean’s free demo today to see how it can enhance your business processes.
FAQ:
1. Is cloud ERP safe?
Yes, cloud ERP is safe. Leading providers use advanced security measures such as data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security patches to protect sensitive business data. Additionally, cloud ERP platforms comply with global security standards, ensuring data protection.
2. How big is the cloud ERP market?
The global Cloud ERP market is growing rapidly, with a projected value of $105.4 billion USD by 2029. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of cloud solutions, as businesses seek scalable, flexible, and cost-effective ERP systems to streamline operations.
3. Can I create my own ERP system?
While it’s possible to create your own ERP system, it requires significant expertise in software development, as well as ongoing maintenance and updates. Most businesses prefer to use established ERP solutions, as they offer reliable, customizable options without the complexity and costs.
4. How much does cloud ERP cost?
Cloud ERP pricing varies based on factors like the size of your business, the modules you choose, and the provider. Generally, subscription costs range from $50 to $300 per user per month, with additional costs for customization, implementation, and support services.












 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















