In Singapore, efficiently managing payroll cycles is critical for ensuring timely and correct wage payments, as well as regulatory compliance. Businesses must adhere to severe labor laws in order to avoid penalties and maintain smooth operations. A well-structured payroll cycle fosters employee trust and pleasure. The Employment Act requires companies to pay salaries at least once a month, within 7 days of the compensation period ending, according to the Ministry of Manpower (MOM).
This article delves into important areas of payroll cycle management in Singapore, such as compliance requirements and best practices. It discusses CPF contributions, the Skills Development Levy, tax duties, payroll cycle types, and HR’s role in administering payroll. Understanding these characteristics enables firms to optimize procedures, assure compliance, and increase employee happiness.
- A payroll cycle is the regular timeframe in which employees are paid, and selecting the right cycle is crucial for timely and accurate salary processing.
- Key payroll components, such as employee salaries, deductions, employer contributions, and taxes, are essential for accurate payroll management and compliance with legal standards.
- Payroll cycle types, including weekly, bi-weekly, semi-monthly, and monthly, should be chosen based on business needs and employee preferences to optimize efficiency and satisfaction.
- ScaleOcean HRIS software automates payroll cycle management, reducing administrative errors, ensuring timely and compliant payroll processing, and improving data security.

What is a Payroll Cycle?
A payroll cycle is the regular timeframe during which employees get their salaries. Businesses can select numerous cycles based on their operational requirements and industry standards. In Singapore, selecting the correct cycle is crucial for quick and accurate paycheck processing.
The cycle is also necessary for assuring compliance with local tax regulations. It determines how frequently companies disperse salaries, as well as how they calculate and report payroll taxes. A well-defined cycle helps organizations stay compliant while also ensuring that employees receive their pay consistently and on time.
Key Payroll Components Every Business Should Know
Payroll management entails several critical components that ensure employees are fairly compensated and in accordance with the law. Understanding these components is critical for businesses to ensure smooth payroll processing and error-free results. The following are the key things that every firm should consider when managing payroll:
1. Employee Salaries and Wages
Employee salaries and wages form the foundation of any payroll cycle. This includes base pay, overtime, bonuses, and allowances like transportation or lunch stipends. For employees joining mid-month or working part-time, calculating a prorated salary ensures fair compensation based on actual hours worked. Proper calculation ensures employees are fairly compensated for their time and role.
2. Deductions
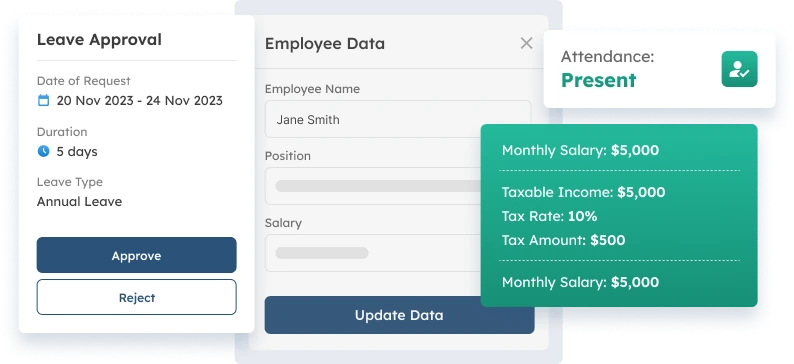
Deductions are an important part of the payroll process, and include tax withholdings, CPF (Central Provident Fund) contributions, and any other deductions such as insurance premiums or retirement fund contributions. Businesses must guarantee that deductions are completed correctly and on schedule in order to avoid penalties and ensure that employees contribute to obligatory savings and benefits.
3. Employer Contributions
Employers in Singapore must contribute to CPF, a mandatory savings plan that helps employees with their retirement, healthcare, and housing needs. In addition to the CPF, employers may need to contribute to other statutory benefits. These contributions support employees’ financial security in the future, and businesses must follow these guidelines to avoid legal complications.
4. Payroll Taxes
Payroll taxes are another important aspect of the payroll cycle. These include income tax withholdings, which businesses must deduct from employee pay and remit to Singapore’s Inland Revenue Authority (IRAS). According to IRAS, AIS employers are required to submit their employees’ employment income information to IRAS electronically by 1 March each year. Proper calculation and submission of these taxes is required to ensure compliance with local tax legislation and prevent costly fines or legal consequences.
Payroll Compliance and Legal Requirements in 2025
Maintaining compliance with local payroll rules and regulations is crucial for firms operating in Singapore. To prevent legal complications in 2025, firms must guarantee that all payroll responsibilities are met. Businesses should be aware of the following major compliance requirements:
1. CPF Contributions
CPF is a mandated savings scheme in Singapore. Employees and employers each contribute a percentage of their salaries to the CPF for retirement, healthcare, and housing. Employers must guarantee that CPF contributions are made accurately and timely. This allows employees to save while yet satisfying their legal commitments.
2. Skills Development Levy (SDL)
The SDL is a mandatory charge that all Singapore enterprises must pay for employees who work in Singapore. It is used to fund employee training and development. Businesses must pay SDL on a monthly basis for each employee earning more above a specified amount. This helps to upskill the workforce and promote industry growth.
3. Tax Filing and Employer Obligations
Employers are liable for withholding income tax from their employees’ salaries. The corporation must also file tax returns with the IRAS and furnish annual tax information to employees, such as Form IR8A.
Additionally, a payslip should be used to ensure that all required information, including tax deductions, is clearly presented to employees. This guarantees that both the company and its employees fulfill their tax obligations while avoiding penalties.
Payroll Cycle Types
Different payroll cycle types meet the needs of varied sectors and worker arrangements. Selecting the appropriate type can boost payroll efficiency and employee satisfaction. The following are the common types of payroll cycles:
1. Weekly Pay Cycle
In this cycle, employees are paid weekly. This cycle is frequently employed in industries with hourly employees or those with flexible work schedules. A weekly payroll cycle allows for faster payouts but may necessitate additional administrative labor. It is advantageous to firms that demand regular cash flow updates.
2. Bi-weekly Pay Cycle
A bi-weekly pay cycle means that employees are paid every two weeks. It is a standard payroll cycle across many countries and enterprises. This cycle usually results in 26 pay periods per year, which is easier for employers to administer than a weekly payroll cycle. It creates a compromise between regular payment and manageable management.
3. Semi-monthly Pay Cycle
Employees on a semi-monthly pay cycle are paid twice a month, usually on the 15th and 30th. This cycle is ideal for salaried personnel, making it simple to compute monthly earnings. It provides a consistent rhythm while maintaining compliance with monthly budget planning.
4. Monthly Pay Cycle
Employees are paid monthly. The majority of full-time employees in Singapore follow this pattern. It makes payroll processing easier, but employees must manage their finances until the next pay period. It also fits well into many company and financial reporting timetables.
What is the Most Common Payroll Cycle?
Singapore’s most prevalent payroll cycle is the monthly pay cycle. Many organizations choose this cycle since it is simple and consistent. It is consistent with tax and CPF dates, ensuring that both employees and companies satisfy their statutory duties without confusion. Furthermore, it follows several financial and employment standards, making it a dependable choice.
This cycle also benefits businesses by allowing them to better manage cash flow. Because payments are made once a month, businesses may organize their finances more effectively. The monthly pay cycle reduces administrative work, making payroll processing more efficient and less time-consuming than more frequent cycles.
How to Choose a Payroll Cycle?
Choosing the correct payroll cycle is critical for organizations to maintain smooth financial operations and employee happiness. The cycle you choose will have an influence on everything from payment processing to tax filing and compliance. It is critical to consider various criteria to guarantee that the cycle meets the needs of both the company and the personnel. Here are several important considerations:
1. Industry Type
Certain industries, particularly those with hourly employees, may benefit from a weekly or biweekly payroll cycle. This enables for faster and more frequent payments, which can be useful in industries such as retail and hospitality. However, businesses employing salaried staff, such as banking or technology, may choose a semi-monthly or monthly cycle to coincide with standard payment systems.
2. Business Size
Larger firms with a large number of employees frequently use a monthly payroll cycle to streamline administrative responsibilities. A monthly cycle enables the HR and payroll teams to focus on fewer pay runs, reducing the possibility of errors. Furthermore, it provides adequate time to ensure the payroll process, including tax calculations and deductions, is done correctly.
3. Cash Flow
When deciding on a payroll cycle, take into account your company’s financial flow. A monthly payroll cycle is helpful for firms looking to better manage their cash flow. It enables businesses to better allocate resources and forecast expenses since they know when payroll needs to be done and can align it with revenue cycles.
4. Employee Preferences
It is also critical to consider the preferences of your employees. Some employees may want to receive their compensation on a more regular basis, such as weekly or biweekly. Offering flexibility in the payment cycle can boost employee happiness and retention, particularly for individuals who rely on constant, predictable revenue.
Additionally, employers should ensure that any mandatory deductions, such as the foreign worker levy, are accounted for to maintain compliance and avoid payment delays.
What Are the Steps of Running Payroll?
Payroll involves a set of actions that ensure employees are paid correctly and on schedule. Meeting both employee and legal standards necessitates meticulous planning and attention to detail. Understanding the necessary processes can help to streamline the process, resulting in efficient payroll management. The steps involved are as follows:
1. Collect Employee Time Records
It is critical to keep accurate records of all employees’ working hours, overtime, and leave. This involves tracking shifts, absence, and any special accommodations for overtime labor. Using a timesheet helps organize and record this data, ensuring that payroll computations are based on reliable information, reducing payment errors. Keeping accurate records also aids in complying with labor laws and regulations.
2. Calculate Employee Wages and Deductions
Use the payroll cycle calendar to calculate employee earnings based on hours worked or salary. This includes calculating any bonuses, commissions, or incentives that employees may be eligible for. Deductions for taxes, insurance, and CPF must also be considered. Proper calculations assist to avoid inconsistencies and guarantee that employees receive the appropriate amount.
3. Make Statutory Contributions
Employers must deduct CPF (Central Provident Fund) and other obligatory contributions from their employees’ wages. They must submit these contributions on time and in the exact quantities, as required by Singaporean law. If the company fails to make the necessary contributions, it may face fines. Ensuring compliance with these statutory responsibilities is critical for smooth operations.
4. Process Payments
Following the calculation of final salaries and deductions, businesses should pay employees in accordance with the payroll cycle set. They can use bank transfers, checks, or any other agreed-upon payment mechanism. Paying employees on time is critical to maintaining their pleasure and trust. Companies must complete this phase efficiently to avoid delays or errors.
5. File Taxes and Report to Authorities
Employers must file tax returns and make contributions to statutory entities such as the IRAS and the CPF Board. This involves completing the relevant paperwork and paying taxes on behalf of the employees. you avoid penalties and comply with Singapore’s tax requirements, make sure you file your taxes on time and accurately. Proper reporting also aids in keeping accurate financial records.
Off-cycle Payroll vs. Regular Payroll Cycle
Off-cycle payroll refers to any payroll processing that occurs outside of the normal payroll cycle. This often happens when a manager identifies a computation error, a special payment needs processing, or when an employee leaves the organization mid-cycle. It ensures that employers pay employees on time, even when there are anomalies in the standard payroll schedule.
This sort of payroll allows firms to remain flexible and responsive to unforeseen circumstances. Off-cycle payroll lets businesses manage pay anomalies, bonuses, severance, or commission payments that occur outside of the normal cycle. It ensures that businesses pay employees appropriately and on schedule, avoiding any payroll-related complications.
Other Types of Payroll Cycles
Some businesses may choose alternate payment cycles, such as quarterly or customized pay periods. Enterprises that require greater flexibility in their payroll processes often adopt these cycles. However, they remain less widespread in Singapore and typically fit specific business models or industries.
Seasonal enterprises or those with unpredictable work schedules, for example, may use these cycles to better align their cash flow and operational requirements. While businesses don’t generally use them, custom pay periods provide flexibility and efficiency by ensuring that employers properly compensate employees for work completed during non-standard periods.
The Role of HR in Managing Payroll Cycles
HR ensures the payroll cycles run successfully by accurately recording employee work hours, tracking overtime, and checking leave records. HR also completes all calculations, such as wages and deductions, correctly to avoid conflicts. Their cooperation ensures efficient and timely payroll processing.
In addition to payment processing, HR is responsible for ensuring statutory compliance. This includes setting up the payroll cycle calendar to match legal dates, making timely CPF contributions, and following tax requirements. HR also manages any payroll difficulties or anomalies that arise, ensuring employees receive accurate payments in line with business policies.
What Can HR Leaders Do to Maintain a Functioning Payroll Cycle?
To ensure an efficient payroll cycle, HR directors must take a proactive approach to managing payroll operations. This includes maintaining current on industry developments, legislative updates, and ensuring that mechanisms are in place for effective payroll implementation. By focusing on important areas, HR may help to prevent errors and maintain regulatory compliance. Here are three critical steps HR leaders should take to ensure the payroll cycle runs smoothly:
1. Regular Training
HR should stay up to date on payroll changes and legal requirements to avoid compliance concerns. Regular training ensures that the HR team is up to date on the latest payroll requirements, decreasing the risk of errors and penalties. This allows HR to properly manage complex payroll responsibilities. Continuous education also enables HR to identify future difficulties and remain ahead of regulatory changes.
2. Use Payroll Software
Payroll management software, such as ScaleOcean’s HR solutions, can improve payroll efficiency and eliminate errors. Payroll software Singapore automates calculations, ensures on-time payments, and reduces human error. The integration of various HR and finance systems improves data accuracy and operational efficiency. Using software also delivers valuable insights via detailed reports, which aids decision-making.
3. Communication with Finance
HR should work with the finance team to better coordinate payroll and financial planning. Close coordination ensures that the finance team reports payroll expenses appropriately in financial statements. It also helps coordinate budgeting, ensuring that the finance team covers payroll disbursements. Regular discussions between HR and finance help detect and handle possible cash flow issues quickly.
4. Audit Payroll
Conduct regular payroll cycle audits to ensure that all calculations are correct and compliant. Payroll audits ensure compliance with legal and financial requirements. Regular audits can detect problems early on, allowing for appropriate corrective steps. This also helps to avoid any financial or legal fines related to payroll errors.
Optimizing Payroll Cycle Management with HRIS Software ScaleOcean
ScaleOcean is an all-in-one HRIS software solution for optimizing payroll cycle management. Automating payroll tasks saves errors and administrative workload, streamlining the entire process. The program provides benefits such as precise payroll calculations, easy system integration, and improved data security, ensuring that the team processes payroll on time, in compliance, and efficiently.
Our Software provides a free demo to enable organizations to see the benefits of ScaleOcean for themselves. ScaleOcean is also eligible for the CTC (Care and Training) grant, which provides financial assistance to organizations looking to improve their human resources operations. ScaleOcean’s software includes the following major features:
- Automated Payroll Processing, Automates payroll calculations, reducing errors and improving accuracy.
- Seamless Integration, Integrates with other business functions, ensuring real-time data synchronization.
- Employee Self-Service Portal, Provides employees access to payroll info and personal updates, reducing HR workload.
- Real-Time Attendance and Overtime Management, Syncs attendance and overtime directly with payroll for accurate calculations.
- Compliance with Labor Regulations, Ensures payroll processes meet legal requirements, minimizing compliance risks.
Conclusion
Effective payroll cycle management is critical to guaranteeing accurate payments, regulatory compliance, and overall operational efficiency. A well-managed payroll cycle allows organizations to avoid costly mistakes and retain employee happiness. Businesses can eliminate errors, streamline operations, and comply with local legislation by selecting the appropriate payroll cycle and technologies.
ScaleOcean provides comprehensive solutions to help businesses achieve smooth payroll management, including HRIS software designed to optimize payroll cycles. ScaleOcean’s software automates payroll tasks, interacts with other corporate systems, and maintains regulatory compliance, making it an invaluable resource for any corporation seeking to improve payroll management.
FAQ:
1. What is a payroll cycle?
A payroll cycle is the interval at which businesses process and distribute employee salaries. Common cycles include weekly, bi-weekly, semi-monthly, or monthly. Selecting the appropriate payroll cycle is crucial for ensuring timely payments and staying compliant with tax obligations and labor laws.
2. What is the pay period cycle?
The pay period cycle defines the time span for which employees are paid during each payroll cycle. Typical pay periods include weekly, bi-weekly, semi-monthly, or monthly intervals. It helps businesses schedule payments and aligns with legal and regulatory tax filing requirements.
3. What is the HR and payroll cycle?
The HR and payroll cycle is the process where HR departments manage employee records and payroll operations. It includes calculating salaries, tracking hours worked, handling deductions, and ensuring tax compliance. Efficient management of this cycle ensures accurate and timely payments to employees.
4. What is the off-cycle payroll date?
An off-cycle payroll date refers to an additional payroll run outside the regular payroll schedule. It is used for processing special payments, such as bonuses, adjustments, or corrections. This ensures that employees receive their pay promptly despite anomalies in the standard payroll cycle.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















