In today’s business world, you’re probably juggling dozens of different software applications. From CRM to finance tools, they all hold vital data, but they don’t always talk to each other. This is where application integration comes into play, acting as the bridge that connects these disparate systems.
According to the Developer Tech Portal, Singapore’s first Maritime Digital Twin, launched on March 24, 2025, integrates maritime operations. This functions much like application integration in business, by streamlining data flow across systems, significantly boosting efficiency and operational oversight.
This guide explores the concept and function of application integration, highlighting its importance for modern businesses. By streamlining operations and ensuring seamless system communication, integration empowers companies to significantly boost efficiency, cut costs, and enhance strategic decision-making.
- Application integration is the strategic process of linking diverse software, such as ERP or CRM, to ensure smooth data exchange.
- The application integration process works by connecting applications, sharing data, and automating workflows, often through technologies like APIs and middleware to facilitate communication.
- Key benefits of application integration include significantly increased operational efficiency, better data visibility for decision-making, and an improved overall customer experience.
- A unified solution from ScaleOcean’s ERP software provides a centralized platform, simplifying the entire integration process and overcoming common operational hurdles.

What is Application Integration?
Application integration is the strategic process of linking diverse software, such as ERP or CRM, to ensure smooth data exchange. This creates a cohesive, unified IT ecosystem where information flows effortlessly, eliminating data silos and reducing the inefficiencies and errors associated with manual data handling.
The main objective is to streamline operations and automate workflows across all applications. This strategic integration fosters an agile and responsive technology stack, enabling businesses to quickly adapt to market changes while ensuring optimal efficiency and accuracy in managing critical business data.
How Application Integration Works
Application integration functions by creating defined channels and rules for systems to share data effectively. This guarantees that data, especially for ERP systems, is accurately interpreted and utilized across platforms. Now, let’s explore the essential steps in this process:
1. Connecting Applications
So, the very first thing you need to do is establish a direct link between the applications you want to integrate. This connection is essentially the road map for information to travel, and it’s the foundational layer that makes any further data exchange possible, no matter the application integration tools you’re using. Without it, nothing else really happens.
You’ll find these connections can be pretty straightforward, like a simple point-to-point link, or they might be part of a much larger, more complex network. The approach you pick really depends on how many applications you’re trying to link up and the complexity of the workflows you need to manage for your business.
2. Sharing Data
With those connections in place, the applications can then start sharing data, all guided by rules you’ve set beforehand. This often looks like a one-way sync, where one system just pushes updates to another, or sometimes it’s a two-way sync where changes in either application are reflected in the other, keeping everything aligned.
Often, the data being shared gets transformed into a common format, which is a really smart move. This transformation ensures the receiving application can properly understand and process the information, effectively preventing any data compatibility issues that could otherwise pop up.
3. Automating Process
Honestly, one of the biggest reasons for application integration is to automate business processes that touch multiple systems, making things smoother. Imagine adding a new customer to your CRM with integration, and an invoice can automatically pop up in your accounting software, which completely removes manual intervention.
This kind of automation really helps cut down on errors and lets your employees focus on more strategic, valuable tasks instead of repetitive ones. It’s undeniably one of the most significant ways application integration delivers a solid return on investment for businesses, especially those leveraging ERP systems.
4. Using APIs
When it comes to modern integration, APIs, that’s Application Programming Interfaces, are easily the most common and effective tools you’ll encounter. They’re sets of rules that allow software applications to communicate, acting like a messenger to transfer data between systems.
Developers really lean on APIs to get specific functionalities or data from an application without needing to understand its complex internal workings. This approach makes building new connections and integration points so much faster and more standardized across your entire technology stack, which is a huge win.
5. Leveraging Middleware
Middleware is another key player. It’s a type of software that effectively sits right between different applications to help them communicate properly. It’s a translation layer that converts data from one application’s format to another, especially useful for integrating legacy systems with different formats.
Middleware is pretty powerful. It can handle all sorts of complex tasks like message queuing, data transformation, and intelligent routing. By taking on these jobs, it significantly simplifies the entire integration development process, giving you a much more robust and scalable framework for your application integration examples.
Application Integration Technologies
Effective application integration depends on key technologies that establish effortless system connections. These diverse tools and platforms are essential for choosing the best strategy for your business. Now, let’s explore the core technologies that drive successful application integration:
1. Application programming interfaces (APIs)
APIs have pretty much become the go-to standard for connecting applications these days, especially with so much moving to the cloud. They define how software components communicate securely, ensuring functions are exposed in a controlled manner, which is crucial for any integration tool.
You’ll definitely run into REST and SOAP, which are probably the two most common types of APIs out there, especially when looking at application integration examples. These really give you a flexible, powerful method to build those real-time integrations that need to be both scalable and maintainable for long-term use.
2. Middleware
Then there’s middleware, which I often think of as that central hub or ‘software glue’ that pulls together various enterprise systems. It steps in to offer services that your operating systems don’t typically handle, making it a key component of an enterprise management system solution, covering data management and application messaging services.
Honestly, this technology becomes absolutely crucial when you’re trying to integrate older, legacy systems with more modern applications. It really helps bridge that gap between the old ways and the new, a challenge that’s quite common for many established enterprises trying to keep up with current ERP system integration trends.
3. Webhooks
Webhooks are a much simpler, more event-driven way to go about integrating applications, which is quite refreshing. A webhook automatically sends data when a specific event occurs, unlike polling, which constantly asks for updates. This makes webhooks more efficient for real-time updates across systems.
Just to give you an example, imagine your inventory system getting a notification the exact second a sale closes on your e-commerce site. That’s a webhook in action. This kind of immediate communication is precisely what makes them so popular for modern apps and various application integration examples we see today.
4. Integration platform as a service (iPaaS)
Moving on, iPaaS, or Integration Platform as a Service, is essentially a cloud-based solution that gives you a whole platform for building and deploying your integrations. These platforms simplify application connections with pre-built connectors and tools, reducing development time significantly.
They really shine for businesses that are juggling a mix of cloud-based and on-premise applications, making hybrid integration much less of a headache. iPaaS solutions provide that much-needed scalability and flexibility that most modern digital businesses require to stay competitive, especially in the ERP landscape.
5. Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Finally, we have Low-Code/No-Code Platforms, which are fantastic because they let people with hardly any coding experience actually build integrations themselves. These tools use visual, drag-and-drop interfaces, allowing business users, or citizen integrators, to create simple integrations, making application integration more accessible.
Now, they might not be the best fit for extremely complex integration scenarios, but they’re absolutely perfect for automating those simple, repetitive tasks we all face. Democratizing integration is a growing trend that helps businesses become more agile, showcasing the clear benefits of application integration.
Application Integration Approaches and Tools
Application integration can be implemented through various methods, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages. Selecting the optimal strategy and tools is vital, as it must align with your current IT environment, specific business needs, and future objectives. Now, let’s examine the common approaches and tools available:
1. Point-to-point integration
This one is the most basic approach you’ll find, where you literally build a custom connection directly between just two applications, one-to-one. It’s a quick fix if you’re only trying to integrate a handful of systems, but it can get out of hand really fast as more applications get added, quickly becoming what people call ‘spaghetti architecture’.
While it seems simple initially, this method truly lacks scalability, because every single new integration needs a brand-new custom build. This makes it very costly and difficult to maintain in the long run, which is a major drawback for businesses.
2. Enterprise application integration (EAI)
EAI steps in using middleware to connect applications through a central hub, standardizing and centralizing all your integration efforts. It’s a much more structured way to manage integrations across a big organization, helping you avoid the chaos of point-to-point connections we just talked about.
This method gives IT teams a single, unified interface for monitoring all integrations, which truly simplifies troubleshooting and system updates. Furthermore, IMDA noted that the 2025 Singapore Conference on AI (SCAI) convened 100+ global experts to define AI safety research priorities, underscoring the need for streamlined, integrated systems.
3. Hub and Spoke Integration
This is actually a specific kind of EAI where you have one central ‘hub’ connecting to all the various ‘spokes,’ which are your applications. All communication flows through this hub, handling things like data transformation and routing, and it simplifies adding new applications because you just link them to the central hub.
The main issue here, though, is that the hub itself can become a single point of failure. If that hub goes down for any reason, all your integrated processes stop, which is a significant operational risk you absolutely need to consider.
4. Enterprise service bus (ESB)
An ESB is really a more advanced kind of middleware, essentially acting as a universal translator and the main communication backbone for an entire organization. It decouples applications, allowing them to communicate without direct ties, making the architecture flexible and scalable for complex integrations.
It’s quite capable of routing, transforming, and even enriching messages as they travel between applications. An ESB is definitely a powerful tool for complex environments that have lots of different systems and tricky communication protocols to manage.
5. Event-Driven Architecture (EDA)
In an EDA setup, applications communicate by producing and consuming ‘events’ – when something important happens in one application, it publishes a message. Other interested applications then subscribe to these messages and react accordingly, creating a very decoupled and responsive system, which is pretty neat.
This approach is genuinely excellent for building real-time, highly scalable systems, especially in modern business contexts. You’ll find it commonly used in contemporary applications like e-commerce platforms and many Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, for good reason.
6. API-Ied Connectivity
This more modern approach really puts APIs front and center as the primary way to connect applications, data, and various devices. It involves setting up a network of APIs that are both reusable and well-governed, a strategy that truly promotes agility and lets you rapidly develop new digital experiences with ease.
By treating every application and data source as a manageable API, businesses can honestly innovate much faster than before. It’s a foundational element, really, for any successful digital transformation initiatives, especially when thinking about ERP systems.
7. Message-oriented middleware (MOM)
MOM uses a messaging system to shuttle data between applications. Essentially, applications send messages to queues, and other applications pick them up from those queues. Asynchronous communication allows systems to interact without being connected simultaneously, offering greater flexibility.
This approach significantly improves the reliability of your integrations, which is a major plus. If a receiving application happens to be temporarily unavailable, the message simply waits patiently in the queue until the application is back online, preventing data loss.
8. Microservices integration
When you break down big applications into smaller, independent microservices, as is common with many modern ERP systems, integrating these pieces calls for a different strategy. You often use lightweight mechanisms like APIs or an event bus, with the main goal being to maintain the independence and agility of each service.
This particular style of application integration is absolutely crucial for organizations that have committed to a microservices approach. It directly supports the scalability and resilience that are the core benefits of this architectural pattern, and that’s incredibly important.
9. Data Mapping
Data mapping is, without a doubt, a critical component of any integration approach you choose to take. It’s all about meticulously defining how data fields in one system correspond perfectly to fields in another, ensuring that when data is transferred, it remains accurate and gets placed into the correct destination field, every single time.
Honestly, without proper data mapping, integrations can quickly lead to corrupted or completely misinterpreted data, which can cause huge problems for ERP data. It’s a detailed and often complex process, but it is essential for the success of any integration project, period.
The Evolution of Application Integration
Application integration has evolved significantly. Early methods relied heavily on custom-coded links for specific system connections, such as ERPs. However, these first-generation integrations were typically fragile, expensive, and difficult to maintain, creating numerous operational hurdles for businesses.
Today, the landscape is transformed by cloud computing and SaaS applications. Modern approaches, like API-led strategies and cloud-based iPaaS, prioritize agility, scalability, and innovation. They deliver a more flexible, robust, and cost-effective solution compared to outdated, traditional integration setups.
Benefits of Application Integration
A well-crafted application integration strategy can truly transform your business, elevating overall operations beyond mere technology. The benefits, spanning everything from boosting efficiency to significantly improving customer experiences, touch many parts of the organization. Now, let’s dive into the core advantages of integration:
1. Increased Efficiency
When you automate workflows and get rid of all that manual data entry, which is always a drag, integration truly increases your operational efficiency quite dramatically. This frees up employees from repetitive, often low-value tasks they do, allowing them to focus on much more strategic initiatives that can actually drive business growth.
Processes that used to gobble up hours or even days can now be completed in just minutes, which is quite something. By leveraging performance metrics, this kind of accelerated business process, honestly, gives you a crucial competitive advantage in today’s very fast-paced market.
2. Improved Data Visibility
Integration really helps break down those frustrating data silos, giving you one consolidated, much clearer view of all your business information. When data from sales, marketing, finance, and operations all come together, leaders can make genuinely more informed decisions.
Having access to real-time, really accurate data from every part of the organization truly empowers better business analytics. This then leads to deeper insights into how things are performing and what customers are doing, ultimately helping you make smarter business moves.
3. Better Customer Experience
When all your systems are talking to each other, you can offer customers a much more seamless and, importantly, personalized experience. Think about it: a support agent can quickly see a customer’s whole order history and every past interaction in one go, which means they can provide faster and more effective support.
Getting that unified view of the customer journey really allows you to start anticipating their needs before they even ask. This kind of thoughtful service doesn’t just build loyalty. It can truly be a significant differentiator in a crowded market.
4. Greater Agility
An IT environment that’s properly integrated just makes the whole business much more agile, full stop. It simplifies adopting new technologies, launching fresh products, or even getting into new markets, making the business capable of responding much more quickly to those ever-changing market conditions.
With a truly flexible integration architecture, you can actually add or swap out applications without completely disrupting your entire system, which is a huge plus. This kind of adaptability is, no doubt, essential for long-term survival and sustainable growth, especially with how quickly things evolve.
5. Reduced Costs
Sure, there’s an initial investment, but good integration strategies ultimately lead to some pretty significant cost savings. Automation alone drastically cuts labor costs tied to manual tasks, and it also helps avoid those expensive errors that often pop up from manual data entry.
What’s more, by really optimizing processes and boosting overall efficiency, integration helps you squeeze even more value from your current technology investments. It’s fundamentally about getting your whole IT ecosystem to work smarter, which, as we know, directly and positively impacts the overall bottom line.

Challenges to Application Integration
Despite its benefits, application integration presents significant hurdles. Today’s IT landscapes are complex, mixing legacy systems, on-premise solutions, and various cloud apps, all having unique data standards. Expert planning and precise execution are crucial for navigating these intricate environments successfully.
Security is a primary concern, as connecting systems may introduce new vulnerabilities. Protecting sensitive data throughout the integration process is vital, requiring robust enterprise risk management to mitigate exposure. Furthermore, the long-term maintenance of these integrations often proves both challenging and costly.
Application Integration vs. Data Integration
Application integration is focused on connecting diverse applications to automate core business workflows. It enables systems to collaboratively execute processes in real-time, such as instantly triggering an inventory update right after a sales order is placed, significantly streamlining cross-platform operations.
In contrast, data integration centers on consolidating information from multiple sources into a unified structure, typically residing in a data warehouse. Its primary use is for reporting and deep analysis, establishing a reliable single source of truth for business intelligence, rather than immediate, real-time process automation.
Types of Application Integration
Application integration links different software to ensure shared data and cooperative functionality. The required approach depends on your applications’ hosting and the company’s IT structure. Most businesses favor a flexible hybrid strategy to meet diverse needs. Let’s explore the various types of application integration:
1. On-premise application integration
On-premise application integration is all about linking up systems that live entirely within your company’s own data center. This was the predominant integration method for quite a while, often relying on traditional middleware like an ESB to get those large, monolithic systems, maybe even your core ERP, to talk to each other.
Even though it’s not as common as it once was, this type of integration still holds a lot of relevance, especially for many larger enterprises. These organizations have often poured significant investment into legacy systems, which are absolutely crucial for their day-to-day operations and simply can’t be swapped out easily.
2. SaaS application integration
Now, with so many cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications, this integration type has really surged in importance. We’re talking about connecting various cloud apps like Salesforce or HubSpot, which usually happens through APIs, and it’s a big focus for modern iPaaS platforms and other application integration tools.
The main idea here is to get a smooth, seamless flow of information going between all those different cloud tools a business depends on. This way, data stays consistent across every platform, and your important workflows can comfortably span across multiple SaaS products without a hitch.
3. Application to application integration
Application-to-application integration is a pretty wide-ranging category, essentially meaning any direct connection between two specific applications, no matter if they’re in the cloud or on-premise. This is common in hybrid integration, like linking a cloud CRM to an on-premise ERP system.
It’s becoming more and more common for businesses to take a ‘best-of-breed’ approach with their software choices, picking the top application for each specific function. This means they then need solid application integration tools to make sure all those different systems can actually work together seamlessly, which is crucial for overall efficiency.
Example Use Application Integration Cases in Business
To truly grasp application integration, examining real-world scenarios is very helpful. These use cases show how connecting various systems with the right tools resolves business challenges and unlocks significant value across different industries. Now, let’s explore some practical examples of application integration in business:
1. E-Commerce
For an e-commerce business, it’s a big win when they integrate their online shop right with their inventory system and their shipping provider. This means that when someone places an order, the inventory updates itself, and a shipping label gets printed without anyone lifting a finger, making sure stock levels are accurate.
Plus, this kind of application integration typically involves syncing all that valuable customer data straight into the CRM. This allows for super-targeted marketing efforts that are based on what people have bought before, ultimately giving customers a more personalized shopping experience, which tends to keep them coming back.
2. Finance
In finance, a firm might integrate its trading platform directly with its risk management and compliance systems, and this is crucial because every single trade then gets automatically checked against strict compliance rules in real-time. This setup is a key to ensuring compliance and preventing questionable activity.
On top of that, having transaction data automatically pushed into the accounting system really simplifies the whole financial reporting process. It also gives management a pretty clear, real-time look at the company’s actual financial position, which is incredibly valuable for quick decision-making.
3. Human Resources
An HR department often finds itself integrating its recruitment platform with the main HR information system, or HRIS, which makes a lot of sense. So, when a new hire comes on board, all their data just flows right into the HRIS to create their employee profile and kick off the entire onboarding process without a hitch.
This kind of automation truly saves the HR team a huge chunk of time that they’d otherwise spend on manual data entry, which is a common pain point. More importantly, it helps ensure that all employee data stays consistent and accurate right from day one, which is vital for an effective ERP system in HR.
4. Healthcare
In healthcare, a hospital will typically integrate its Electronic Health Record (EHR) system with its billing system and the patient portal, which is a smart move. When a doctor updates a patient’s record, for instance, the billing information is automatically generated and sent, really streamlining the whole revenue cycle management process.
And it’s not just about internal processes. Patients themselves can easily view their medical records and lab results through that same portal. This really empowers patients to be more involved in their own health journey, ultimately improving the overall quality of care they receive, which is the main goal.
5. Retail
For a retail chain, integrating all its point-of-sale (POS) systems with a central ERP system is practically non-negotiable these days. Sales data from all stores syncs in real-time, giving the head office an up-to-date view of sales and inventory nationwide, essential for managing operations across locations.
This consolidated data is then used to really optimize stock replenishment, making sure popular items are always on the shelves while also cutting down on the risk of overstocking. This is a massive benefit for effective supply chain management, helping businesses save money and keep customers happy.
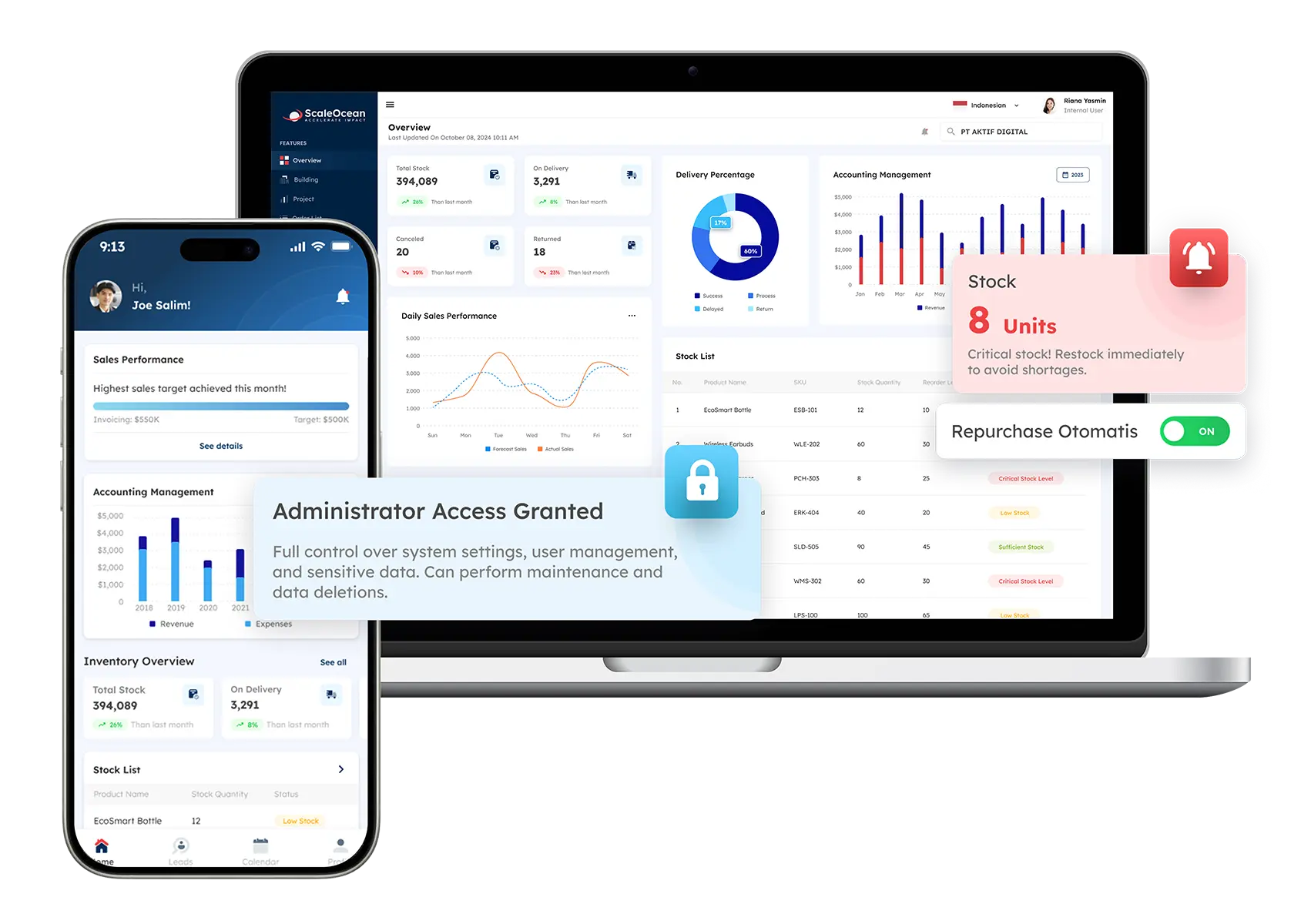
Centralized and Seamless Application Integration with Scaleocean ERP Software
ScaleOcean’s ERP software delivers a unified platform, seamlessly integrating finance, HR, and supply chain management. It offers unlimited users and transparent pricing, eliminating hidden costs. The system’s flexibility, scalability, and industry-specific setup ensure streamlined operations, faster ROI, and reliable after-sales support.
For external connectivity, ScaleOcean provides modern APIs and pre-built connectors, simplifying the integration of third-party applications. Furthermore, ScaleOcean’s ERP software is an approved solution for the CTC grant, ensuring valuable business support. Below, we outline the essential features of our software:
- Seamless Integration Across Business Functions: ScaleOcean connects finance, HR, and supply chain into one customizable, easy-to-use platform.
- AI-Powered System for Streamlined Integration: AI-based ERP automates tasks like data entry and report generation, reducing errors and saving time.
- Data-Driven Insights and Predictions: ScaleOcean’s AI system analyzes data, offering insights and predictions for informed business decisions.
- Easy Integration with External Applications: Modern APIs and pre-built connectors simplify third-party app integration for greater system flexibility.
- Customizable and Scalable: The platform is flexible and scalable, allowing businesses to tailor and expand the system as they grow.
Conclusion
Application integration is a core business strategy, not just a technical requirement. By dissolving data silos and enabling seamless information exchange, organizations gain unmatched efficiency, agility, and deeper customer insights. These are vital advantages for any company aiming to succeed in the fast-paced digital era.
Vendor solutions like the ScaleOcean ERP system can simplify and optimize the integration process for your business. With flexible modules and native integration capabilities, ScaleOcean’s ERP ensures remarkably smooth operations. You can experience its powerful features firsthand by signing up for a free demo.
FAQ:
1. What is the difference between API and application integration?
APIs are mechanisms that allow different software to communicate by specifying how data is transferred. Application integration, however, is the overall process of linking multiple systems to ensure smooth and unified data exchange across various platforms.
2. What is the application of integration?
Integration is used to connect and synchronize different business applications like ERP, CRM, and supply chain systems. It enables real-time data sharing and automates workflows, reducing errors and manual effort, and improving overall operational efficiency.
3. What is the future of application integration?
The future of application integration is expected to be shaped by AI and cloud-based solutions. As businesses focus on API-led strategies, the goal will be to enhance scalability, improve flexibility, and speed up the integration of diverse systems to foster innovation.
4. What is the purpose of application integration?
Application integration aims to connect various software systems to facilitate smooth data transfer and automate processes. It helps streamline business operations, eliminate data silos, and supports better decision-making by ensuring that systems collaborate effectively.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















