In today’s business world, risks are everywhere, and they seem to be growing. Managing these risks isn’t just about avoiding disaster. It’s about making smarter, more strategic decisions for growth. This is where enterprise risk management (ERM) comes into play, offering a structured way to handle uncertainty.
According to MAS, FHC-N126 requires all DFHCs (Licensed Insurers) to create an enterprise risk management framework and conduct an Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA). This guarantees that insurers are ready for market volatility, promoting resilience and solvency.
This article will provide you with a full introduction to Enterprise Risk Management (ERM), including what it is and how it works. We will look at its primary benefits, step-by-step processes, and real-world examples, providing insights to help you understand its importance in modern corporate strategy.
- Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a comprehensive method that assists firms in identifying, assessing, and planning for risks and opportunities that may impact their objectives.
- The benefits of ERM include improved decision-making, enhanced resilience against disruptions, better resource allocation, and increased confidence from stakeholders.
- How the ERM process works includes A continuous cycle of identifying potential threats, assessing their likelihood and impact, developing response plans, and constantly monitoring the results.
- ScaleOcean’s ERP software provides the integrated data platform needed to automate risk identification, assessment, and monitoring, turning ERM into a strategic advantage.

What Is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a comprehensive method that assists firms in identifying, assessing, and planning for risks and opportunities that may impact their objectives. It is not limited to financial hazards, but encompasses all areas of the business to ensure efficient management.
By offering an integrated perspective of risks and opportunities, ERM enables leaders to coordinate their responses across departments. This unified strategy allows for better decision-making and improves the organization’s ability to expand and manage future difficulties.
Key Characteristics of ERM
Understanding Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) requires a focus on key features such as governance, strategy, performance, and communication. These features set ERM apart from prior, compartmentalized risk management techniques and fuel its success. Let’s explore the core attributes of ERM:
1. Governance and Culture
It all starts at the very top, where governance really sets the overall tone for the whole organization. The board and senior management really need to be the ones championing a fully risk-aware culture, which helps ensure everyone truly understands their role in managing risk.
What we mean by a strong risk culture is basically that people aren’t scared to actually speak up and report issues when they see them. It really fosters open communication and accountability across all levels, making this kind of culture the absolute foundation for any effective ERM program.
2. Strategy Focus and Objective Setting
ERM, as a framework, is pretty much tied right into a company’s overall strategy and its core goals. It’s about giving leaders a clearer picture of the risks connected to various strategic choices, helping them make much more informed decisions.
Typically, the ERM process involves setting your objectives first, and then you go about identifying the risks that might impact those. This way, you’re always making sure that all risk management efforts stay completely aligned with the company’s overall mission.
3. Performance (The Risk Management Cycle)
When we talk about performance in ERM, we’re really looking at the everyday activities of managing risk. This means identifying, assessing, and then actually responding to all sorts of different risks, which is an ongoing, cyclical process. Using performance metrics, organizations can more effectively track and assess their risk management strategies.
It’s not a one-and-done kind of thing; this cycle is definitely a continuous loop, ensuring the company is constantly adapting to threats that are always evolving. This approach really helps make the business more resilient over time.
4. Review and Revision
It’s just a given that any ERM framework really needs regular reviews and revisions. Since the business environment is constantly shifting, so are the risks, which definitely call for a process of continuous improvement.
Doing these regular reviews helps you really see what’s hitting the mark and what isn’t quite working out. It gives the organization the chance to adjust its overall approach as required, making sure the ERM program remains relevant and effective over time.
5. Information, Communication, and Reporting
Frankly, clear communication is just absolutely vital for ERM to function properly, you know. Information concerning risks has to be gathered and then openly shared across the entire company, just so everyone can stay on the same page about potential threats.
Good reporting should deliver useful insights to decision-makers, not just a list of risks, but actual analysis. By understanding business analytics, leaders get the bigger picture and are better equipped to take appropriate action.
6. Proactive & Forward-Looking
ERM isn’t merely about reacting once problems have already cropped up. It’s genuinely about looking forward, trying to anticipate future risks and even opportunities. This kind of proactive stance is really a key differentiator for enterprise risk management.
Being forward-looking allows a company to truly prepare for upcoming challenges, and sometimes, you can even pivot potential threats into a competitive advantage. This particular approach definitely helps to secure long-term success.
7. Integrated
An integrated approach basically means ERM isn’t sitting off in its own little silo as a separate function, you know. It’s meant to be woven right into all of the company’s processes and its decisions, making risk management genuinely part of everyone’s job, as demonstrated in an application integration example.
This level of integration really helps to break down those old silos between different departments. It ensures that risks are handled in a much more coordinated way right across the organization, building a more unified defense against threats overall.
8. Addresses Diverse Risks
ERM really takes into account a very wide spectrum of potential risks, which is quite encompassing. This includes everything from strategic, operational, financial, and compliance risks, ultimately giving you a truly holistic view of uncertainty.
By genuinely considering all these various types of risks, a company ends up much better protected. It means avoiding those potential blind spots that could otherwise escalate into significant problems, and this comprehensive coverage is truly a hallmark of a strong ERM program.
Benefits of Enterprise Risk Management
An effective Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework not only prevents losses but also creates value, offering a strong return for the business. It improves decision-making and boosts stakeholder confidence, transforming how a company operates. Let’s explore the key benefits in more detail:
1. Improved Decision-Making
When you think about it, ERM actually gives leaders much better information concerning various risks, and that’s a game-changer. This better understanding truly allows them to make more strategic and informed decisions, which is always a good thing. They can better balance potential rewards and risks for success.
It’s pretty clear that when decisions are based on a truly clear understanding of risk, the chances of actually achieving business objectives tend to increase quite significantly. This is part of the enterprise risk management process, really. Ultimately, this leads to better overall performance, which is the goal for any organization.
2. Enhanced Resilience
You’ll often find that a company with a strong ERM program, like an ERP system, would support, become much more resilient, which is absolutely vital. They are simply better prepared to handle all sorts of unexpected events and disruptions that might come their way. This ability to bounce back makes a strong ERM program essential, don’t you think?
Enhanced resilience basically means the business can just keep operating, which is the main point. Even when faced with really major challenges, a strong enterprise risk management framework helps it adapt and recover, which is something you truly need. It protects the company’s value, reputation, and brand integrity long-term.
3. Better Resource Management
ERM is great because it genuinely helps to prioritize risks, basing that on their potential impact, which is a smart way to go about things. This then allows the company to really focus its valuable resources on the biggest threats, where they matter most. This approach boosts efficiency, saving both time and money.
By allocating resources more effectively, through a clear enterprise risk management process, the company can absolutely get more value out of every dollar. It also avoids wasting precious effort on those low-priority risks, which is a common pitfall without ERM. This approach is key to optimizing business operations.
4. Increased Stakeholder Confidence
It’s quite simple. A really well-managed ERM program significantly increases confidence among all kinds of stakeholders, and that’s a huge plus. This group includes investors, customers, and employees, among others. They just get to see that the company is proactively managing its risks, which builds a lot of trust.
This kind of confidence can actually lead to a higher stock price and certainly foster better relationships across the board, which is a tangible benefit. It clearly shows everyone that the company is well-governed and quite stable, painting a positive picture. It’s a valuable asset for long-term business success.
5. Competitive Advantage
Ultimately, and this is a big one, ERM can absolutely provide a significant competitive advantage in the marketplace, which is something savvy leaders aim for. By managing various risks effectively, a company can actually take on more opportunities, which allows for growth.
This whole setup allows the business to grow faster and, importantly, more sustainably over time, which is the long-term goal. ERM is not just some defensive tool you put in place. It truly can be a powerful engine for growth, pushing things forward. Smart leaders turn risk into opportunity.
How Enterprise Risk Management ERM Works
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a dynamic, continuous cycle that responds to change. It entails recognizing, assessing, responding to, and monitoring risks while aligning all aspects of the business with organizational resilience and enterprise management. Let’s begin the key steps for the ERM process:
1. Risk Identification
So, the very first thing you do in this enterprise risk management framework is to identify all those potential risks out there. This really means taking a good look at both what’s happening inside your organization and what external factors could come into play. The goal is to create a comprehensive list of potential business threats.
You can approach this using methods like brainstorming sessions, workshops, or even just by carefully reviewing past incidents to spot patterns. It’s pretty crucial, I think, to get people involved from every corner of the organization at this stage. This collaboration ensures no major risks are overlooked.
2. Risk Assessment
After you’ve identified those risks, the next logical step in the enterprise risk management process is to assess them properly. This part is all about figuring out both how likely a risk is to happen and what kind of impact it could potentially have. This assessment helps prioritize the most significant risks for better focus.
It’s pretty common practice to map these risks out on a “heat map,” which gives you a great visual representation of which ones really demand the most attention. This kind of visual aid really clarifies things, showing you plainly what’s most pressing. This assessment helps focus resources where needed in your ERP system or operations.
3. Risk Response
Once those risks have been properly assessed, the next big hurdle is deciding how the company will actually respond to them. You’ve got a few key options here. You can try to avoid the risk entirely, reduce its impact, share it with another party, or simply accept it. The path must align with the company’s risk appetite, non-negotiable.
To give you an idea, a business might purchase insurance to effectively share a financial risk, or perhaps put in place some new safety procedures to reduce an operational risk. These are practical steps, and it’s not uncommon to see them in an ERP context. The key is having a clear plan for each major threat.
4. Risk Monitoring and Reporting
Now, for what’s really the final, but never-ending, stage in this enterprise risk management framework. monitoring those risks and the response plans you’ve put in place. This step ensures your plans work and helps identify new or changing risks.
Regular reporting is essential here. It keeps leadership fully informed about the current risk landscape, which is vital for an enterprise risk management framework. This kind of insight empowers them to make necessary adjustments quickly, as things evolve. Ongoing monitoring is what makes the ERM process effective, not just theoretical.
Types of enterprise risk
Enterprise risks take many forms, ranging from strategy errors to cybersecurity threats. A solid ERM framework organizes these risks, making them easier to manage and assign ownership. Let’s explore the different types of enterprise risks:
1. Strategic Risk
Strategic risks, well, these are the ones that really mess with a company’s big picture goals, impacting their ability to get where they want to be. They can pop up from making bad business decisions or just not being able to change with the times, which is a common pitfall. These are the most significant risks, shaping a company’s future.
Think about a new competitor suddenly showing up, or customer tastes just shifting completely, making an old product totally irrelevant. These kinds of things are tough, and managing these strategic risks is absolutely critical for a company’s long-term survival and growth, no doubt about it.
2. Operational Risk
Operational risks are the nitty-gritty ones, tied directly to how a company runs its day-to-day activities. They often come from internal processes that don’t quite work, human error, or even system failures, just the everyday stuff. In essence, these are the risks of simply doing business, the things you encounter when the wheels are turning.
We’re talking about things like the supply chain suddenly breaking down, or maybe equipment just failing unexpectedly, or even a simple human error. These kinds of issues, which are quite common, can lead to some pretty significant financial losses and major disruptions to the business.
3. Compliance Risk
Compliance risks are the ones that surface when a company isn’t playing by the rules, whether that’s laws, regulations, or even its own internal policies. The fallout can be serious, ranging from hefty fines and penalties to some pretty bad damage to the company’s good name.
Imagine not meeting environmental standards, or maybe overlooking those critical data privacy laws like GDPR. These are real-world compliance headaches. This is where a robust enterprise risk management process comes in, helping track these ever-changing requirements.
4. Financial Risk
Financial risks, as you’d guess, are all about how a company manages its money, encompassing things like credit, liquidity, and market exposures. These aren’t abstract; they can, and often do, have a direct impact on the company’s bottom line, affecting profits pretty immediately. It’s a core area where careful oversight is always needed.
Picture interest rates suddenly jumping up, making borrowing way more expensive, or a big customer just not paying their bills, creating a real cash flow crunch. These are tangible financial risks that can hit hard, and dealing with these financial exposures is a core part of ERM, something you can’t really ignore.
5. Reputational Risk
Reputational risk is essentially the threat of something damaging a company’s brand or how the public sees it, which is something every business watches carefully. This can stem from all sorts of things, like a product recall gone wrong or maybe a big ethics scandal surfacing. A good reputation is, without a doubt, a valuable but fragile asset, easily lost.
When negative publicity hits, it can quickly translate into lost customers and a noticeable drop in sales, which nobody wants. Especially in today’s social media-driven world, news, good or bad, can spread incredibly fast, often before you can even react. So, protecting a company’s reputation is a critical priority in ERM.
6. Technology and Cybersecurity Risk
Technology risks range from system failures to serious data breaches, and with our increasingly digital world, they are becoming more significant. According to MFA, Singapore has chaired the Open-Ended Working Group on ICT security from 2021-2025, addressing these global challenges.
Cybersecurity threats, specifically, are a huge concern that pretty much all companies are grappling with these days, and rightly so. A single successful cyberattack can honestly lead to massive financial losses and equally damaging hits to reputation, which is a scary thought. IT risk management, supported by ERP systems, is crucial for data security.
7. Environmental and External Risk
These risks are the ones that really come at you from the outside, stemming from the broader external environment. We’re talking about things like natural disasters, sure, floods or earthquakes, but also those much larger economic or political events that can shake things up significantly. You often have very little control over these.
While a company might have very little direct control over these external risks, that doesn’t mean you’re powerless. A well-designed enterprise risk management program, for example, can certainly help a business prepare for them, which is a practical choice. This involves contingency plans or diversifying operations to minimize damage.
8. Human Capital Risk
Human capital risks are all about the people within a company, specifically the workforce and its various challenges. We’re talking about difficulties attracting or keeping hold of key talent, which is a big one, but also more sensitive issues like employee fraud or simply a lack of skilled workers. It’s a broader category than many initially think.
Your employees, let’s be honest, they’re truly one of a company’s most important assets, invaluable really. So, managing the risks directly associated with them is absolutely crucial for any kind of sustained success. Focus on succession planning and fostering a positive, inclusive work environment.

Examples of ERM Frameworks
Organizations apply ERM using recognized frameworks that provide structure and best practices for effective risk management. Choosing the correct framework is critical because it establishes the foundation for success. Let’s look at several common ERM frameworks:
1. The Casualty Actuarial Society (CAS) ERM Framework
The CAS framework is something you’ll often see in the insurance industry, focusing heavily on identifying and managing risks that could really impact a company’s financial health. It’s particularly known for its strong quantitative focus, which makes sense given the nature of insurance.
This framework proves incredibly useful for companies dealing with complex financial risks, offering detailed guidance on how to properly model and measure them. The goal here, ultimately, is to ensure the company remains financially solvent and stable, which is critical in that sector.
2. The COSO ERM Integrated Framework
The COSO framework is definitely one of the most widely used around the globe, providing a principles-based approach that’s pretty adaptable to just about any industry you can think of. What’s neat about it is how it ties risk management directly into strategy and performance, making it more than just a compliance exercise.
It’s famous for its five interconnected components: governance and culture, strategy and objective-setting, performance, review and revision, and information and communication. This whole comprehensive structure makes it a very popular choice for businesses looking for an integrated view of risk.
3. The ISO 31000 ERM Framework
ISO 31000 stands as an international standard for risk management, offering a universal set of principles and guidelines that any organization can apply. It really pushes the idea that risk management shouldn’t be separate, but instead an integral part of all activities within the business.
This framework is quite flexible and, interestingly, isn’t something you get certified for. Instead, it acts as a valuable guide to help companies build out their own specific ERM programs, with its emphasis on integration being one of its key strengths for sure.
4. The NIST ERM Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) framework is widely adopted by the US government, and it’s also gained a lot of traction in the private sector, especially when it comes to cybersecurity risk. It offers a structured way to tackle IT-related threats, which are a big deal these days.
This framework helps organizations move through a practical cycle of identifying, protecting, detecting, responding, and recovering from incidents. This five-function approach to managing cybersecurity risks is super practical and really forms a cornerstone of many IT security programs out there.
5. The COBIT ERM Framework
COBIT, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a framework specifically geared towards IT governance. It helps organizations get a handle on managing and governing their information and technology, playing a truly key role in handling technology-related risks.
COBIT provides a solid set of tools and best practices, all designed to ensure that IT efforts are truly aligned with overarching business goals. This alignment is absolutely crucial for successfully navigating the risks that come with digital transformation in today’s landscape.
6. The RIMS Risk Maturity Model ERM framework
The Risk and Insurance Management Society (RIMS) developed this particular model, which is quite helpful for organizations wanting to assess just how mature their ERM programs actually are. It effectively lays out a roadmap for continuous improvement, which is something every business aims for.
This model examines seven core attributes of what makes an ERM program successful, letting a company clearly see its strong points and areas needing improvement. It’s a very useful tool, then, for both benchmarking and development as you work to strengthen your risk posture.
7. The OECG GRC Capability Model
The Open Compliance and Ethics Group (OCEG) brought this model to life, integrating governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) into one single, cohesive framework. You’ll often hear it referred to simply as the “Red Book”, which is a nice, memorable nickname.
This model is designed to help organizations reliably achieve their objectives, all while skillfully addressing uncertainty and acting with integrity. That integrated approach, combining GRC functions, is really its main advantage and why many find it so valuable.
8. The Basel II/III Framework
The Basel frameworks are international standards, specifically tailored for the banking industry, which lay out requirements for how much capital banks need to hold as a buffer against risks. They’re primarily focused on ensuring the overall stability of the financial system, which is a massive undertaking.
These frameworks delve into credit risk, operational risk, and market risk, being quite technical and highly specific to the banking sector. They definitely represent a key part of the regulatory landscape for financial institutions worldwide, guiding how banks manage their exposures.
9. Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies (COBIT)
COBIT is a framework specifically for the governance and management of enterprise IT, created by ISACA to help businesses really get the most value from their technology investments. It does this by carefully balancing benefit realization, risk optimization, and resource optimization, which is a tricky balance to strike.
It’s particularly handy for managing IT-related risks and making sure compliance requirements are met. Many organizations use COBIT to ensure their IT strategy aligns well with broader business goals, making this framework essential for any company that heavily relies on information technology today.
Examples of ERM Implementation in Business Practice
It’s really quite useful to look at actual enterprise risk management examples, seeing how various industries put these ideas into action makes the whole theory of ERM feel much more tangible and clear. This practical view shows us what enterprise risk management truly means when applied in the real world.
Companies, from the biggest tech firms to food producers, are certainly using ERM right now. They use it to handle their specific challenges and also find new opportunities, which really underscores how adaptable the ERM approach is across different sectors.
1. Technology Firms
You know, tech companies are always in such a fast-moving, changing environment, so they really lean on ERM to manage things like cybersecurity threats and the quick shifts in technology. It’s also quite important for them to assess the risks tied to new product development efforts.
One big risk area, for sure, is intellectual property theft, and ERM helps these firms set up really solid controls to protect their valuable assets. Doing this is absolutely vital if they want to keep their competitive advantage in the market.
2. Food Producers
Food producers definitely have big worries about supply chain risks and, naturally, food safety. They use ERM to meticulously map out their supply chains, pinpointing any weak spots that could cause trouble, and this really helps them prevent disruptions and keep the quality of their products high.
Then there are those risks from shifting consumer tastes and ever-evolving regulations, which ERM helps them anticipate and stay on top of. This way, they can adjust their products and how they operate to meet these emerging market needs.
3. Banks and Financial Services
Now, the financial services sector is just incredibly regulated, facing all sorts of intricate financial risks, so banks deploy really sophisticated ERM programs. These programs are designed to handle credit risk, market risk, and operational risk, often built on established frameworks such as Basel III.
It’s also crucial that they use ERM to manage compliance across a huge number of regulations, which is absolutely vital for sidestepping hefty fines and simply keeping their operating license. Honestly, a strong ERM function is nothing less than a must-have for any financial institution operating today.
4. Energy Companies
Energy companies they’ve got their own distinct set of risks to deal with, from volatile commodity prices and geopolitical tensions to all those environmental regulations. ERM really steps in here to help them navigate this quite challenging and complex landscape.
They often employ methods like scenario planning, which lets them get ready for various potential futures, like a sudden drop in oil prices or the introduction of new carbon taxes. This kind of forward-thinking strategy really helps them stay strong and profitable, no matter what comes their way.
5. Healthcare Providers
In healthcare, providers really rely on ERM to handle risks concerning patient safety, alongside managing data privacy and making sure they comply with all the regulations. The stakes in this industry are always incredibly high, so effective risk management is essential.
For instance, they put specific processes in place to significantly reduce the chance of medical errors, and they also implement robust controls to safeguard sensitive patient data. This all works together to ensure they can deliver top-notch care while also protecting their good name and financial health.
Minimize and Mitigate Any Enterprise Risk with ScaleOcean’s ERP Software
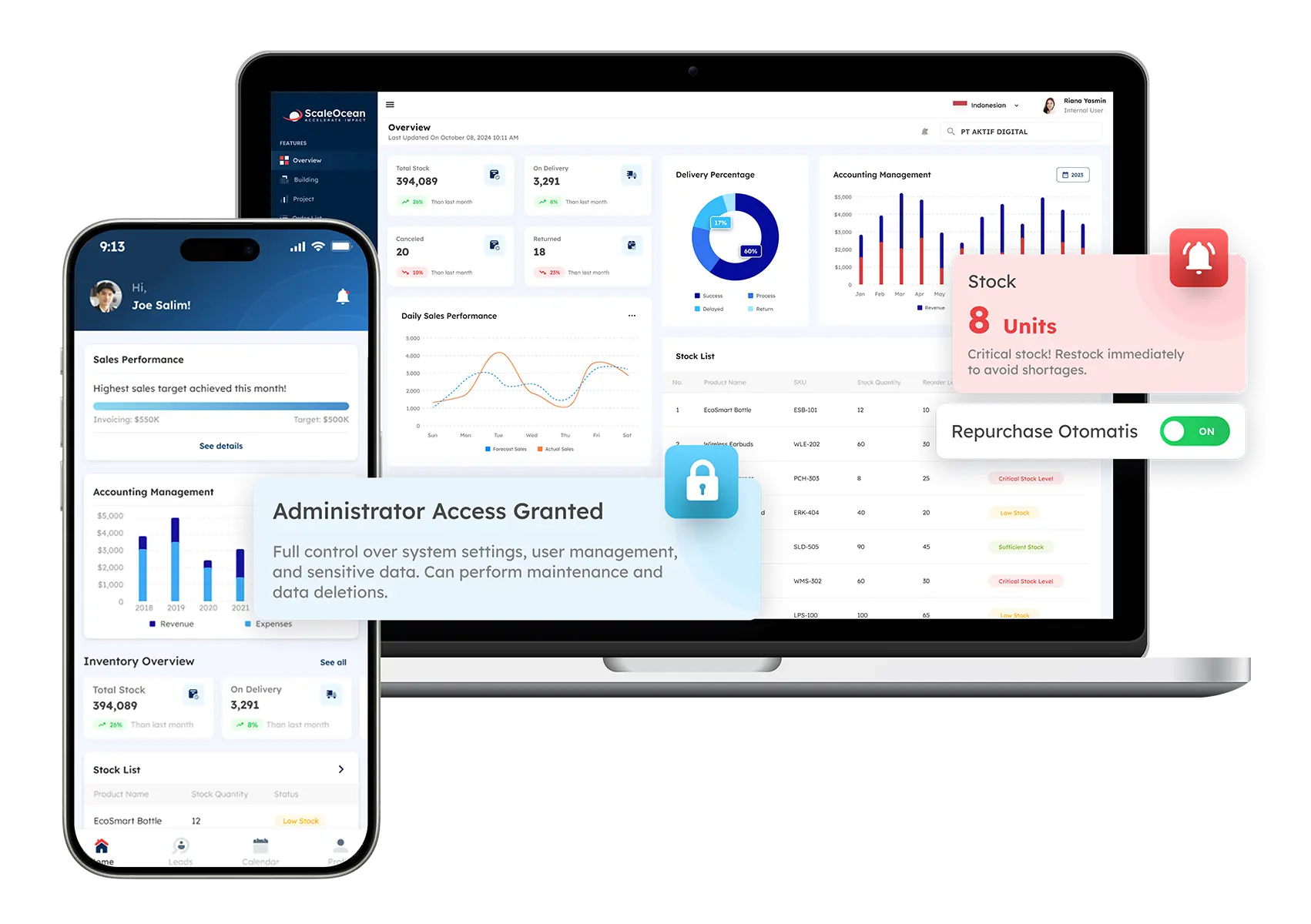
ScaleOcean’s AI technology analyzes millions of data points to detect emerging hazards and evaluate reputational consequences. It is supported by Singapore’s CTC grant and assists firms in managing risks proactively and making educated decisions. The following are the primary features of ScaleOcean’s software:
- GRC Compliance Support: Ensures compliance with Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) standards and integrates seamlessly with Singapore’s guidelines, including ISO 31000 and COSO ERM.
- AI-Powered Data Analysis: Utilizes AI technology to analyze millions of data points, enabling businesses to identify emerging risks and assess reputational impacts.
- Risk Identification and Prediction: AI-driven insights help forecast trends and emerging risks, allowing businesses to take proactive measures.
- Seamless Integration with Standards: ScaleOcean ERP easily integrates with international and local risk management frameworks, ensuring your organization meets all necessary regulatory requirements.
- Real-Time Risk Monitoring: Offers continuous monitoring of risks and provides up-to-date information for better decision-making, ensuring the business remains agile in managing potential threats.
Conclusion
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is an important corporate strategy that provides a structured method for managing uncertainty. It’s more than simply compliance. It’s a crucial capacity that enables organizations to make informed decisions and build resilience, transforming risks into opportunities.
Businesses may integrate risk management into their operations by implementing appropriate ERM frameworks and technologies. ScaleOcean, for example, offers ERP solutions that simplify risk management, as well as a free demo to help you see the benefits for yourself and support long-term sustainable growth.
FAQ:
1. What is meant by Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) refers to a coordinated and comprehensive approach for identifying, evaluating, and managing risks that could hinder an organization’s success. The primary aim is to safeguard assets while adding value to the organization.
2. What are the 5 components of ERM?
The five components of ERM, as defined by COSO, are:
1. Internal environment.
2. Goal setting.
3. Identifying potential events.
4. Evaluating risks.
5. Responding to risks.
3. What are the 4 pillars of ERM?
ERM’s four key pillars include:
1. Identifying and assessing risks.
2. Responding to risks.
3. Control and monitoring activities.
4. Reporting and communicating risk information.
4. What is an example of an ERM?
A practical example of ERM is Johnson & Johnson’s strategy to diversify its suppliers, thereby reducing the risk of supply chain disruptions. This method ensures smooth operations and protects the company’s assets, highlighting the role of ERM in effective risk management.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















