If you’re seeing costly inefficiencies and disconnected teams, it’s time to address those organizational silos. Silos lead to delays and missed opportunities. For that purpose, Business Process Management (BPM) breaks down these walls, streamlining workflows to truly boost efficiency and unlock your growth potential.
So this article will delve into the core features and benefits of BPM (Business Process Management), covering its definition, key types, and essential aspects. We’ll also discuss how BPM brings significant advantages to organizations, streamlining operations to boost efficiency and productivity.
- Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic way to model, analyze, and improve an organization’s workflows, map, and automate core business processes.
- Understand the different types of BPM, including human-centric, document-centric, and integration-centric, to determine which approach best fits your specific business needs and challenges.
- Explore the key aspects of BPM, from strategic alignment with business goals to the continuous improvement cycle that ensures long-term operational excellence and adaptability.
- ScaleOcean ERP integrates your business processes seamlessly, offering a comprehensive solution designed to automate and optimize your operations for sustained growth.

What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic way to model, analyze, and improve an organization’s workflows, map, and automate core business processes. It’s more than just software. It’s a continuous effort focused on optimizing workflows, which dramatically reduces inefficiencies and ultimately boosts overall performance.
BPM helps businesses streamline critical tasks, such as managing sales leads or onboarding new staff. By constantly refining these processes, businesses stay agile and responsive to change, ensuring smoother day-to-day operations and achieving better results over time.
Types of BPM
Business Process Management (BPM) isn’t one-size-fits-all. It has different types focusing on specific needs, be it people, information, or systems. Recognizing these differences is key to tailoring BPM to your company’s unique challenges for truly effective operational improvements. Here are the key types of BPM to explore:
1. Human Centric
Human-Centric BPM focuses on processes that critically depend on people for task completion and key decisions. Think of employee onboarding or handling customer complaints, these workflows rely on people’s input, often involving approvals, high collaboration, and careful exception handling.
These BPM systems are designed specifically to support complex human interactions through user-friendly interfaces, timely notifications, and clear task assignments. The technology acts as an assistant, guiding people to ensure key decisions are made by the right person at the right time.
2. Document Centric
If your process revolves entirely around a key document, like a contract, invoice, or legal agreement, that’s document-centric BPM. The workflow is structured by how that document is routed, approved, and stored. The document itself truly drives the process from beginning to end.
Take contract management, for example, drafting, review, signatures, and archiving. This BPM software helps automate the entire document lifecycle, ensuring proper version control, security, and compliance. It’s critical for industries dealing with heavy paperwork and regulatory needs.
3. Integration Centric
Integration-centric BPM focuses intensely on linking various IT systems, such as your ERP, CRM, and HR software, often with minimal human effort. These are usually automated, background processes supported by the Enterprise Development Grant, handling data syncing and system-to-system communication to ensure your platforms work seamlessly together.
A good example is the ERP system automatically updating inventory after an e-commerce sale. This type of BPM heavily uses APIs and connectors to effectively bridge application gaps. It’s ultimately about building a truly cohesive and automated IT ecosystem for the entire business.
Key Aspect of Business Process Management (BPM)
To truly grasp Business Process Management (BPM), we need to focus on its core components. These foundational elements are what transform basic operations into powerful, sustainable business improvements, ensuring long-term growth and efficiency, not just temporary fixes. Here are the key aspects of BPM to explore:
1. Strategic Alignment
Effective BPM must link directly to your company’s big-picture strategic goals. Any process change should always point back to those larger objectives, like boosting market share or customer happiness. Otherwise, you risk optimizing tasks that don’t genuinely contribute to progress.
This kind of strategic alignment ensures your resources are focused right where they matter most for business success. It’s about ensuring every single improved workflow contributes effectively toward the overall goal of organizational growth and maintaining a competitive edge.
2. Continuous Improvement
Think of BPM not as a one-off fix, but as an ongoing commitment to continuous improvement, which is vital in today’s dynamic world. Since things always shift, your processes must adapt through a steady cycle of modeling, implementation, monitoring, and optimizing to ensure agility.
This iterative approach, known as the business process management lifecycle, keeps operations sharp and effective for the long haul. It also helps foster a workplace culture where people are always seeking smarter ways to work, which is truly fundamental to sustained success.
3. Broad Scope
What’s quite strong about BPM is just how widely its principles can be used across pretty much any business function you can think of. It’s definitely not just for things like manufacturing or shipping; it actually has a super broad application scope. You’ll find it useful in HR, finance, marketing, and even IT. It’s quite versatile.
This flexibility means BPM can really bring value to every corner of the organization, helping to knock down those pesky departmental silos. Taking a whole-system view lets you fine-tune those end-to-end processes that often span different functions, and that usually results in some pretty noticeable efficiency boosts.
4. Efficiency and Optimization
At its core, BPM is about eliminating waste, clearing bottlenecks, and removing unnecessary workflow steps. The main goal is always to make processes quicker, cheaper, and more reliable. This sharp focus on optimization drives most of the concrete advantages BPM offers.
You typically achieve this by mapping current processes, identifying weak spots, and then creating a much more streamlined workflow. The direct result is usually significant savings on operational costs alongside a solid boost in overall team productivity.
5. Enabling Technologies
Although BPM is fundamentally a management strategy, it relies heavily on technology, especially within the ERP sphere, to effectively deliver results. Software like BPMS or advanced ERP functions helps us model, automate, and monitor processes, acting as the true enablers of necessary change.
These tools essentially give us the platform to run automated workflows, collect all sorts of performance data, and get insights for even more fine-tuning down the road. Honestly, without the right tech, a lot of BPM’s coolest benefits, like automation and watching things happen in real-time, would be just about impossible to pull off.
Benefits of Business Process Management
When BPM is implemented well, it drives meaningful improvements, cutting costs and boosting satisfaction for both customers and staff. Ultimately, BPM helps businesses streamline operations, making them more resilient, competitive, and better prepared for the long run. Here are the key benefits of BPM:
1. Increased efficiency and Productivity
Getting workflows streamlined and letting automation handle the boring, repetitive stuff with BPM really just pushes efficiency way up. Employees then have more time for the truly strategic work, not getting bogged down by manual, low-value tasks, which in turn leads to higher overall productivity across the board for everyone.
When your processes are crystal clear and working optimally, things just move along without a hitch, with fewer delays and errors popping up. This means getting more done in less time, which is certainly a huge win for any business looking to boost its output.
2. Cost Reduction
Inefficient processes are undeniably costly, wasting resources, time, and materials. Business Process Management actively seeks out and eliminates these inefficiencies, leading to significant cost reductions. By optimizing resource use and minimizing manual errors, businesses genuinely lower operational expenses.
Plus, automating those repetitive tasks means you just don’t need as much manual labor for them anymore, freeing people up. This lets you move your team into more valuable roles, giving you a much better ROI on your payroll spend.
3. Enhanced Agility and Flexibility
In today’s fast-moving market, organizational agility is a massive competitive advantage. BPM inherently builds this in by creating well-defined, flexible processes that are easy to adjust. Knowing your processes deeply simplifies changes in response to market shifts, which is absolutely key.
This kind of flexibility really lets companies shift their strategies, roll out new products, or even jump into new markets way faster than those stuck with old, clunky systems. It essentially turns what used to be stiff, rigid processes into truly adaptable business assets for the long haul.
4. Improved Quality and Consistency
Standardizing processes ensures teams complete tasks the same way every time, resulting in consistent and high-quality outcomes. Establishing a clear ‘best practice’ reduces errors and variations, which helps deliver a reliable customer experience.
BPM helps put these standards into practice, often using automation to bake quality checks right into the workflow from the start. This steady focus on consistency helps build real trust with customers and, in the end, strengthens your brand reputation quite a bit.
5. Greater Transparency and Compliance
Because BPM documents and monitors everything, it provides a clear window into how work is being completed. This transparency simplifies performance tracking, makes spotting bottlenecks easier, and ensures compliance with grant management procedures. Managers gain a real-time view of operations.
This is also incredibly crucial for staying on the right side of regulatory compliance, as it basically creates an audit trail for every single process. You can easily show that you’re sticking to industry standards and regulations, which in turn helps to really mitigate legal and financial risks down the line.
6. Better Customer and Employee Experience
When processes run smoothly, it really does make a positive splash for both your customers and your own team, which is a win-win situation. Customers get faster service, fewer screw-ups, and just an all-around smoother experience, and this absolutely builds loyalty and satisfaction over time. It’s a practical outcome everyone appreciates.
Clear, streamlined processes reduce frustration and make tasks easier for employees. Providing the right tools boosts morale, leading to more engagement and retention of top talent. The Randstad 2025 Workmonitor survey found 62% in Singapore would leave if they felt no sense of belonging.
7. More Scalable Processes
When a business grows fast, unruly processes can easily collapse under the pressure. BPM is key here. It helps you build scalable processes that can handle increased demand without breaking. Designing workflows with scalability in mind ensures smooth, sustainable expansion.
This capability means you can bring in more customers, hire more staff, and process way more transactions without needing to completely rebuild your systems every time you hit a new benchmark. It really sets a strong foundation for sustainable, long-term growth, which is what every business is after.
8. Less Dependency on Development Teams
A key feature of modern BPM is the low- or no-code interface, allowing business users to build and adjust workflows without writing any code. This capability significantly reduces reliance on busy IT teams and puts the power to improve processes directly into the hands of those who use them.
This self-service feature speeds up process improvement and empowers teams to adjust workflows independently. With ScaleOcean, businesses can configure dashboards, approve tasks, and track KPIs in real time, driving agility and innovation across the BPM lifecycle.

Steps Lifecycle and Methodology of BPM
Business Process Management (BPM) follows a structured, cyclical approach focused on continuous, not one-time, improvement. Each stage builds on the last, helping businesses efficiently optimize and adapt processes, ensuring consistent operational growth and agility. Here are the key steps in the BPM lifecycle:
1. Discovery/Analyze
The initial discovery phase is dedicated to truly understanding your current, real-world processes. This means carefully gathering information, mapping workflows, and identifying every pain point, bottleneck, or inefficiency. The goal is a clear, honest picture of your operations, the ‘as-is’ state.
In this stage, you’ll typically find yourself chatting with employees, pulling together relevant data, and really digging into performance metrics. This analysis really gives you that solid baseline, which is what all future improvements will be measured against, helping you decide which processes to tackle first for the biggest impact.
2. Design/modeling
After understanding the current process, the next step is designing the ‘to-be’ process. This involves reimagining the workflow to make it far more efficient and truly effective. You’ll be building a new model, automating tasks, and optimizing the flow of work by removing unnecessary steps.
This design phase relies on collaboration, often involving heavy brainstorming with the team members who will actually use the new process. The main goal is to craft a solid blueprint for a better way of working, one that is both practical and aligned with broader business and ERP goals.
3. Execution/Implementation
Once the new process design is complete, it’s time for execution. This phase involves bringing the workflow to life, setting up necessary software, training employees, and officially rolling out the fresh procedures. It’s the exciting moment when the theoretical blueprint becomes a practical reality.
Often, implementation is best done in phases, which really helps keep disruption to the business at a minimum. Strong communication and good change management are super critical here to ensure a smooth transition and user adoption, making sure everyone is on board.
4. Monitor
Once the new process is live, close performance tracking is essential. The monitoring phase involves collecting data on key metrics, like cycle time, cost per transaction, or error rates, to truly see how the new process compares to the old one. This visibility helps you quickly spot any immediate issues.
Modern BPM software, especially when integrated with ERP systems, includes dashboards and reporting tools. These tools make monitoring much easier. Real-time visibility is essential for understanding the impact of changes. It helps you make data-driven decisions for the future.
5. Manage
Now, process management itself is really about overseeing the day-to-day operations of that new workflow. This means you’re handling any exceptions or issues that come up, making sure employees are sticking to the new procedures, and providing consistent support. Ultimately, it’s about maintaining the stability and health of the process over time.
This particular stage is key to making sure the benefits of the new process actually stick around and are sustained for the long haul. It definitely calls for active oversight, largely to keep people from sliding back into old habits and to ensure the process runs as designed, which is a common challenge.
6. Optimization
All the valuable data and insights from monitoring are used to pinpoint further improvement opportunities. The optimization stage is where you fine-tune and enhance the process, effectively restarting the cycle. This element is what truly makes BPM a continuous, ongoing journey.
This deep commitment to ongoing optimization ensures that your processes never really get stale or fall behind. It helps build a culture of innovation, where the business is constantly looking for better, smarter ways to operate, and that’s truly the ultimate goal of BPM for any organization.
Business Process Management Use Cases
Business Process Management (BPM) is widely applied across industries to simplify operations and improve consistency. It standardizes workflows like employee onboarding, helping companies automate document handling and equipment setup for a smoother, faster process.
BPM transforms functions like invoice processing and customer service by automating approvals, payments, and ticket resolutions, enhancing satisfaction. According to HRD Asia, in Singapore, the most common AI tools in workplaces are chatbots and virtual assistants (27%), AI for writing (23%), and RPA (19%).
Role of Technology in Business Process Management
Technology is absolutely crucial in BPM for turning process ideas into practical, automated solutions. BPM software, often within ERPs, offers tools like visual modelers, automation engines, and real-time dashboards to effectively streamline complex workflows.
These tools enable seamless integration across different systems, like CRM and HR software, eliminating data silos. With the right tech, businesses get a holistic view of operations and can make informed decisions, often supported by business grants to help with costs.
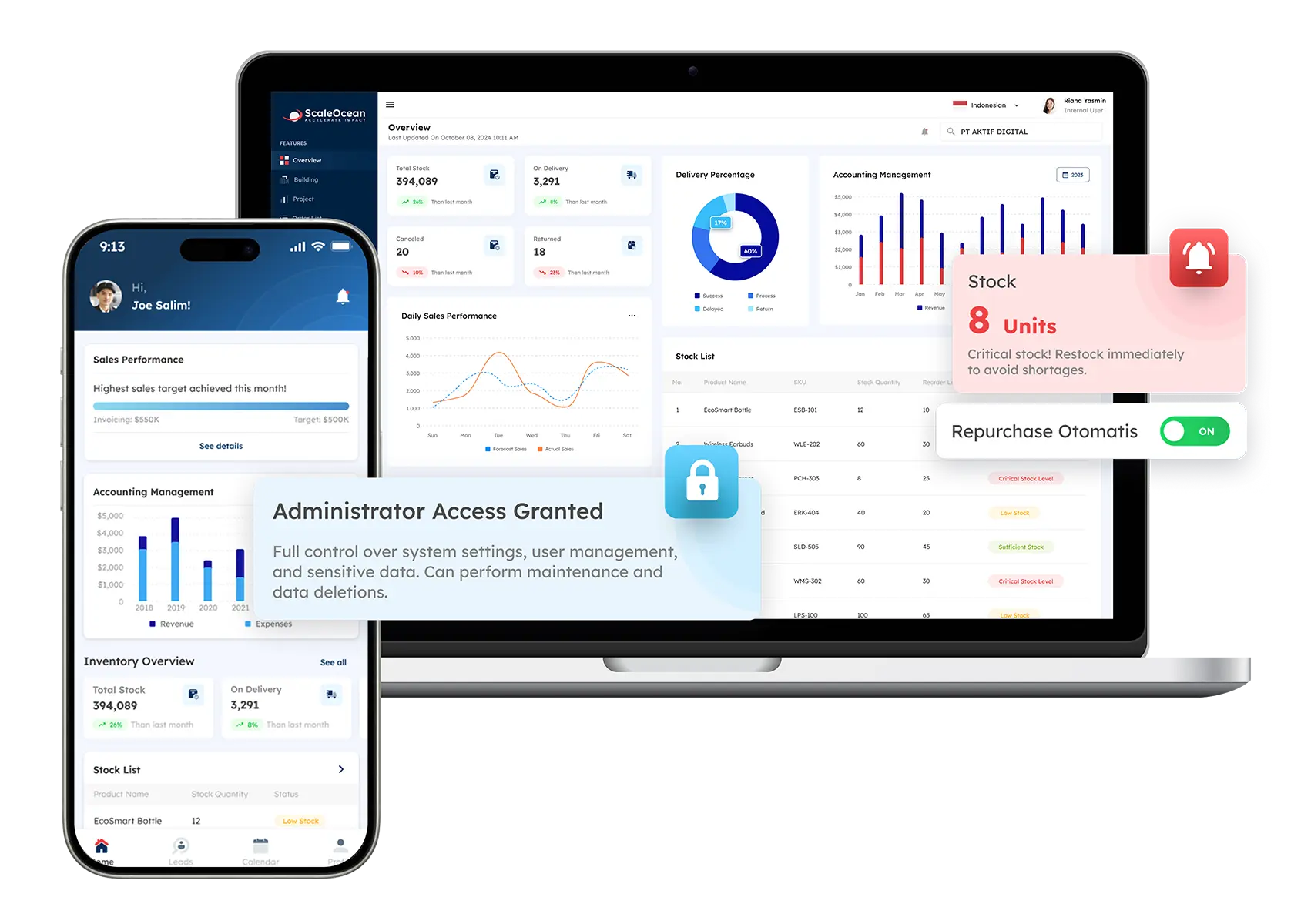
Integrate Business Process Management Comprehensively with Scaleocean ERP
ScaleOcean’s ERP software is a unified platform built to integrate and automate your core business processes. By streamlining operations, it eliminates messy, disparate tools and connects functions like sales, finance, and inventory, boosting efficiency with real-time data and analytics.
Choosing ScaleOcean means implementing a total system designed for future growth. Your business becomes more agile and scalable with ScaleOcean ERP, and the CTC grant can significantly help offset those initial investment costs. Below are its key features:
- Centralized Integration of Core Functions: Integrates accounting, sales, purchasing, production, and inventory for seamless, real-time data flow.
- AI and BI-powered Dashboards: AI and BI analyze data and provide real-time dashboards for optimized business process management.
- Automated Workflow: Automates daily tasks across departments, reducing manual work and enhancing efficiency.
- Industry Flexibility and Customization: Customizable for any industry, ensuring it fits your unique business processes.
- Seamless Integration with External Applications: Easily integrates with existing systems, streamlining operations without disruption.
Conclusion
Business Process Management (BPM) is a crucial discipline for any organization seeking growth and competitiveness. It promotes a culture of continuous improvement, turning every workflow into an optimization opportunity and ultimately boosting operational agility and efficiency.
ScaleOcean’s ERP software lets businesses integrate BPM seamlessly, improving operations and sharpening customer focus. With its comprehensive features, ScaleOcean offers a free demo so you can personally experience its benefits and optimize your processes before committing.
FAQ:
1. What is BPM with an example?
Business Process Management (BPM) involves a strategic approach to optimizing and refining business operations. For instance, in a retail setting, BPM could automate the tracking of inventory, reducing manual errors and ensuring better stock control and operational efficiency.
2. What are the 5 levels of BPM?
1. Defining the process flow
2. Evaluating process efficiency
3. Executing process changes
4. Tracking process performance
5. Continuous process optimization
3. Why are KPIs important in BPM?
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are essential in BPM as they allow organizations to track and assess the effectiveness of their processes. Monitoring these metrics helps identify areas for improvement, supports informed decision-making, and aligns efforts with business objectives.
4. Which is better, BPM or BPO?
BPM (Business Process Management) focuses on improving and refining internal business operations, while BPO (Business Process Outsourcing) shifts certain tasks to external specialists. BPM is ideal for optimizing internal workflows, whereas BPO offers cost savings by outsourcing non-core functions.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















