Logistics is critical to Singapore’s economy, serving as an important link in global supply networks. If a company’s logistics processes are not optimal, the impact can be significant, especially in Singapore, a global logistics hub.
This is especially true for companies that frequently experience challenges such as rising operational costs, supply chain disruptions, and declining customer satisfaction. Therefore, every logistics process must be optimized to reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and strengthen the business’s position in the competitive Singapore market.
According to EDB Singapore, which has been named the World Bank’s top global logistics center for 2023, Singapore’s world-class connectivity increases its importance in international trade. The country’s strategic position and efficient infrastructure make it an excellent center for global logistics operations.
This article will discuss logistics in depth, from its definition, functions, and benefits, workflow, to examples, and how to optimize the process. Learn more here.
- Logistics involves overseeing the movement of goods, services, and information from their starting point to their ultimate destination.
- Activities of logistics, including: procurement, inventory management, warehousing and storage, transportation, order fulfillment and processing, packaging, and reverse logistics
- Types of logistics are 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL, inbound logistics, outbound logistics, reverse logistics, e-commerce logistics, and many others
- Best practices in logistics are secure, discontinued shipping rates, optimizing warehouse design, user route optimization rules, and investing in logistics management software
- ScaleOcean’s logistics software is an ideal solution for managing different types of logistics, providing real-time tracking, integration, and efficiency to streamline operations.

What Is Logistics?
Logistics involves overseeing the movement of goods, services, and information from their starting point to their ultimate destination. It is a key role in supply chain management, focusing on planning and carrying out tasks such as transportation, warehouse, and inventory control to ensure timely and efficient product delivery.
Although the term originated in the military, it is now widely used in business to describe the movement and management of resources to satisfy customer demand while minimizing costs.
What is Logistics Management?
Logistics management is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient movement and storage of goods, services, and information throughout the supply chain.
Companies should have effective logistics management to help businesses optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
What is Logistics in Business?
In business, logistics refers to the detailed coordination of the movement of goods, services, and information from suppliers to customers. It also ensures that the right products are delivered to the right place at the right time, while also maintaining efficiency and minimizing costs in businesses.
Logistics in businesses is also a critical component of supply chain management, directly impacting a company’s ability to meet customer demand and maintain a competitive advantage.
Key Aspects of Logistics
Logistics plays a pivotal role in the smooth functioning of the supply chain. By optimizing processes and enhancing efficiency, businesses can achieve greater control over their operations. Here are the key aspects of logistics that contribute to its overall effectiveness in business.
1. Supply Chain Integration
Logistics with supply chain integration ensures seamless coordination across various stages of production, from raw materials to finished goods.
Through logistics to connecting suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, businesses can improve communication, reduce delays, and enhance overall supply chain visibility. This integration allows for real-time tracking, minimizing errors, and ensuring a more synchronized flow of goods and services.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness is the next main aspect in logistics is achieved by optimizing routes, reducing transportation costs, and improving inventory management.
Businesses often focus on streamlining processes, leveraging technology, and consolidating shipments to lower operational expenses. A well-managed logistics system ensures that resources are used efficiently, reducing waste and boosting profitability.
3. Customer Demand
Logistics directly impacts a company’s ability to meet customer demand by ensuring timely deliveries and maintaining product availability.
Understanding demand patterns and forecasting accurately allows businesses to adjust inventory levels and distribution strategies accordingly. A responsive logistics system ensures customers receive the right products at the right time, enhancing satisfaction and loyalty.
Activities in Logistics
Logistics involves a range of activities that ensure the smooth movement and storage of goods, services, and information throughout the supply chain. These activities are critical in optimizing operations, improving efficiency, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
1. Procurement
Procurement in logistics refers to sourcing raw materials, goods, or services from suppliers to meet production or customer needs. This involves supplier selection, negotiating contracts, and ensuring the timely delivery of quality materials.
Effective procurement ensures that the right products are acquired at competitive prices and in the required quantities, forming the foundation of efficient logistics operations.
2. Inventory Management
Inventory management involves tracking and controlling stock levels to meet customer demand without overstocking or understocking. This activity includes monitoring product quantities, organizing inventory, and determining reorder points.
By using strategies in inventory management logistics, such as just-in-time inventory, businesses can reduce holding costs and maintain efficient supply chains.
3. Warehousing and Storage
Warehousing and storage play a crucial role in logistics by providing space for storing goods before they are distributed. Efficient warehouse management ensures products are stored properly, easily accessible, and ready for dispatch.
Warehouse operations in logistics also include inventory tracking, order picking, and maintaining proper conditions for goods, particularly for perishable or fragile items.
4. Transportation
Transportation is the movement of goods from one location to another, whether by road, air, rail, or sea. It is a vital logistics activity that directly impacts delivery times and costs. Optimizing transportation routes, managing fleets, and selecting the right transport mode are all key factors in ensuring timely, cost-effective deliveries.
5. Order Fulfillment and Processing
Order fulfillment involves receiving, processing, and delivering customer orders. This activity includes picking, packing, and shipping goods, as well as managing returns. Efficient order fulfillment ensures customer satisfaction by ensuring that products are delivered on time, in the correct quantities, and with minimal errors.
6. Packaging
Packaging is crucial in logistics for protecting products during storage and transportation. Proper packaging prevents damage and ensures that goods reach their destination intact.
It also includes labeling, which helps with inventory management and ensures compliance with regulations. Packaging plays a significant role in reducing returns and improving customer satisfaction.
7. Reverse
Reverse logistics refers to the process of managing returns, recycling, or disposal of products. This can include returning damaged goods, recycling packaging, or handling product recalls.
Efficient reverse logistics reduces waste, recovers value from returned items, and supports sustainability initiatives, while also enhancing the customer experience by streamlining the return process.
The Importance of Effective Logistics
Effective logistics are crucial for ensuring businesses meet customer expectations while maintaining smooth operations. By optimizing processes and improving coordination, logistics directly influence overall business performance and competitive advantage. Here’s why effective logistics is essential for success.
1. Enhances Customer Satisfaction
Effective logistics ensures the timely and accurate delivery of products, which is key to customer satisfaction.
By maintaining optimal inventory levels, tracking shipments in real time, and reducing delays, logistics can significantly improve the customer experience. When businesses can consistently meet or exceed delivery expectations, customer loyalty and retention improve, driving long-term success.
2. Boosts Operational Efficiency
A streamlined logistics operation enables companies to optimize their supply chain, reducing bottlenecks and improving the flow of goods. This leads to smoother operations and enhanced productivity across departments.
By automating processes such as inventory management and order fulfillment, logistics can reduce manual labor, minimize errors, and ensure faster decision-making.
3. Reduces Costs
Effective logistics can reduce operational costs by optimizing routes, improving inventory turnover, and minimizing waste. Lower costs result in higher profitability and a better competitive position in the market.
By focusing on efficient transportation management, warehousing, and procurement strategies, businesses can cut unnecessary expenses.
4. Mitigates Risk
Logistics processes can also help mitigate various risks in companies, such as delays, stockouts, or damaged goods, by implementing effective supply chain strategies.
It involves monitoring suppliers, managing potential disruptions, and ensuring proper handling and packaging of goods. Effective risk management in logistics ensures that businesses can respond quickly to unforeseen events, maintaining continuity and customer trust.
5. Drives Business Growth
Efficient logistics directly contribute to business growth by improving supply chain responsiveness and scalability.
With optimized logistics processes, businesses can handle increasing demand, expand their reach to new markets, and grow their customer base. It also provides the flexibility needed to innovate and adapt to changing market conditions, fostering sustainable growth.
Types of Logistics
Logistics encompasses various types, each serving distinct functions within the supply chain. From the movement of raw materials to the final delivery of finished goods, each type of logistics plays a crucial role in ensuring products reach their destination efficiently and cost-effectively.
Understanding the different types of logistics helps businesses optimize their operations and meet customer demands effectively. Here are the key types of logistics that drive supply chain success.
1. First-Party Logistics (1PL)
First-Party Logistics (1PL) refers to a company managing its own logistics operations without outsourcing. In this model, a business directly handles transportation, warehousing, and inventory management.
This is typical for small-scale businesses that prefer to maintain full control over their supply chain, though it can be resource-intensive.
2. Second-Party Logistics (2PL)
Second-Party Logistics (2PL) involves the outsourcing of specific logistics functions to a third-party service provider. These companies offer transportation and storage services but do not manage the entire supply chain.
Businesses using 2PL retain responsibility for the management of their supply chain, while the provider handles specific logistics functions, often at a more cost-effective rate than 1PL.
3. Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) outsourcing involves engaging external companies to handle logistics services like shipping, warehousing, and inventory management. It provides organizations with experience and infrastructure without significant investment.
Logistics software optimizes 3PL operations, improving efficiency and management. By leveraging the benefits of 3PL, businesses can streamline their logistics, cut costs, and gain access to specialized logistics expertise, enhancing overall operational performance.
4. Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL)
Fourth-party logistics (4PL) is a more advanced kind of logistics outsourcing in which a single service provider oversees the complete supply chain operation. 4PL providers provide strategic control over logistics operations by overseeing and integrating the whole supply chain.
A 4PL has the advantage of providing full integration throughout the supply chain. Businesses that use a 4PL supplier to manage all areas of logistics can improve visibility, lower costs, and overall supply chain effectiveness.
5. Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics manages the transportation and storage of raw materials required for production. Businesses that manage vendor relationships and transportation operations provide a consistent supply of critical items, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency in the manufacturing process.
Inbound logistics is critical for ensuring the movement of raw materials to production lines. Optimizing vendor management and transportation helps reduce lead times and ensure that businesses receive the goods they require on time. Efficient incoming logistics reduces production delays and storage expenses.
6. Outbound Logistics
The goal of outbound logistics is to get finished items from manufacturers to buyers. This procedure entails handling order processing, packaging, and shipping to ensure timely delivery.
Efficient outbound logistics increases customer satisfaction by reducing shipping errors and ensuring that the correct products arrive at the correct destinations. Outbound logistics ensures that products reach clients quickly, hence boosting service standards.
Businesses can save money and time by improving their distribution systems. Managing this function successfully is critical to customer satisfaction and retaining a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
7. Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics refers to the return of items from customers to manufacturers for repair, recycling, or repackaging. This job oversees product returns, warranty claims, and recycling procedures.
An effective reverse logistics system improves sustainability and customer happiness by efficiently managing returns. Reverse logistics enables organizations to handle product returns and repair operations while minimizing waste.
Companies that design a streamlined return process can improve customer experiences, increase loyalty, and cut expenses. Sustainable reverse logistics strategies also aid environmental efforts to reduce waste.
Inbound, outbound, and reverse logistics are types of logistics that can be used to optimize the shipping process. Inbound focuses on delivering goods to the company, outbound manages the distribution of goods to customers, and reverse logistics handles the return of goods from customers to the company.
These three types are essential for ensuring the smooth flow of goods, improving operational efficiency, and maintaining customer satisfaction through proper management.
8. Production Logistics
Production logistics is the process of controlling the flow of materials and goods within industrial facilities. This guarantees that raw materials reach production lines, inventory is correctly handled, and completed products are ready for distribution. Efficient production logistics reduces downtime and increases production speed.
Businesses that maintain an effective system can match production schedules with material delivery. This lowers production delays, improves manufacturing efficiency, and assures that items are ready for timely distribution. Effective manufacturing logistics enables smooth operations.
9. Warehouse & Fulfillment Logistics
Warehouse logistics entails coordinating storage, inventory, and order fulfillment. Due to limited space, automated, multi-story warehouses are common in Singapore. These warehouses optimize space and efficiency by automating commodities retrieval and storage.
Automated warehouses are becoming increasingly common in Singapore, particularly in the Jurong Innovation District. These solutions lower operational costs, increase storage capacity, and improve retrieval time, making warehouses more efficient at handling enormous amounts of commodities.
10. Transportation & Freight Logistics
Transportation logistics ensures that products flow smoothly between sites, and Singapore’s integrated maritime, air, and road networks increase cost-effectiveness and speed. Using freight forwarder software improves the process by speeding shipments and managing documentation more efficiently.
Singapore’s logistics system allows for cost-effective multi-modal transport by combining several modes of transportation. Sea, air, and road transportation are all closely linked, resulting in faster deliveries and more flexible shipping alternatives that cater to the different demands of enterprises.
11. Green Logistics
Green logistics aims to reduce the environmental impact of logistical activities. In Singapore, this is consistent with the Green Plan 2030, which advocates for more sustainable logistical techniques. This includes adopting environmentally friendly transportation and decreasing waste during packaging and distribution.
Singapore’s Green Plan 2030 encourages enterprises to embrace sustainable logistics methods. These efforts include lowering carbon emissions, increasing fuel economy, and optimizing delivery routes. Businesses that use green logistics can help to promote sustainability while also improving their public image.
12. Demand-Planning Logistics
Demand-planning logistics entails matching logistics with anticipated consumer demand. Businesses that effectively estimate demand can optimize inventory levels, avoid overstocking, and improve fulfillment efficiency.
These types of logistics reduce stockouts while improving client satisfaction. Businesses may improve their demand planning logistics by utilizing data analytics and forecasting algorithms.
This enables businesses to coordinate production plans with actual demand, minimizing extra inventory and saving expenses. Demand-planning logistics improves overall efficiency while lowering the risk of supply chain disruptions.
13. International Logistics
International logistics oversees the movement of commodities across borders, including customs compliance and regulatory administration. Singapore excels at international logistics, with efficient customs and digital tools such as the Networked Trade Platform (NTP) that make trade seamless and rapid.
Singapore’s advanced customs systems and Free Trade Zones (FTZs) contribute to its international logistical efficiency. The usage of digital platforms such as NTP streamlines the logistics process, minimizing paperwork and delays while increasing global supply chain efficiency.
14. E-Commerce Logistics
E-commerce logistics manages the movement of goods for online retailers, from order fulfillment to delivery. In Singapore, the growth of last-mile delivery options and automated parcel lockers, such as the Pick Network, ensures that consumers receive faster and more efficient deliveries.
E-commerce logistics in Singapore benefits from developments like the automated Pick Network. This worldwide network of parcel lockers enables consumers to pick up their items at convenient places, providing a more flexible and efficient delivery method.
15. Humanitarian Logistics
Humanitarian logistics is concerned with delivering supplies during times of emergency. During disasters or humanitarian emergencies, this logistics type transports crucial supplies such as food, medical equipment, and shelter materials, ensuring that help arrives on time.
In humanitarian logistics, speed and flexibility are essential. Efficient logistical systems guarantee that relief arrives rapidly in affected areas, giving critical resources to individuals in need. This reduces the effect of calamities and ensures that impacted populations receive timely assistance.
16. Military Logistics
Military logistics refers to the transportation and management of supplies for military operations. This includes transporting personnel, equipment, and supplies to other areas, often in difficult situations that necessitate meticulous coordination and preparation.
Military logistics necessitate careful planning and execution to ensure that armed forces have adequate supplies for operations. This specialist logistics industry entails managing complicated supply chains and resolving logistical obstacles in remote or hostile locations.
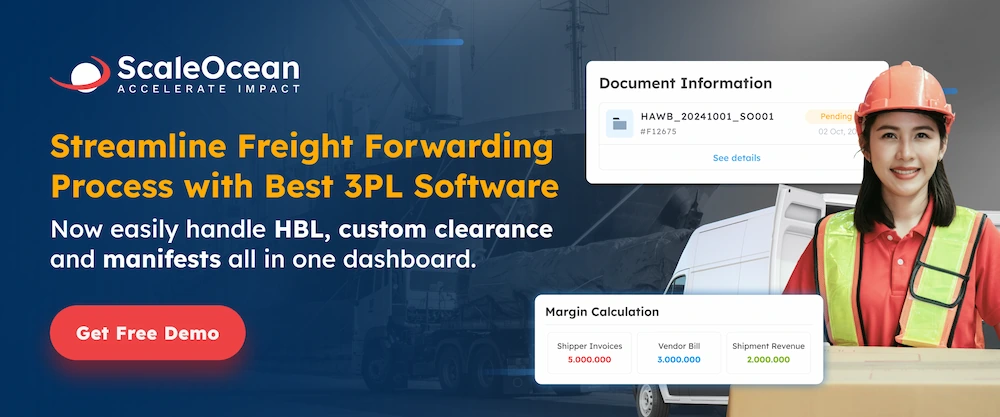
Best Practices for Optimizing Logistics Operations
Optimizing logistics operations is essential for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Implementing the right practices can streamline processes and ensure seamless product movement from suppliers to customers. Below are some key best practices for optimizing logistics operations.
1. Secure Discounted Shipping Rates
Negotiating discounted shipping rates with carriers is a crucial cost-saving measure for logistics operations. By establishing long-term relationships with trusted shipping providers, businesses can secure lower rates, which significantly reduce transportation costs.
Additionally, businesses can consolidate shipments or leverage volume discounts to negotiate better deals, optimizing their shipping budget while maintaining reliable service.
2. Optimize Warehouse Design
An efficient warehouse design is vital for improving operational flow and reducing handling time. An effective layout minimizes unnecessary movements and boosts productivity, leading to faster order fulfillment and cost savings.
Organizing storage systems, optimizing inventory locations, and using technology like barcode scanners or RFID can improve accuracy and speed in picking and packing.
3. Use Route Optimization Rules
Route optimization is key to improving transportation efficiency. By using advanced software to calculate the most efficient delivery routes, businesses can reduce fuel consumption, minimize delivery times, and improve customer satisfaction.
Factors such as traffic patterns, delivery windows, and load sizes should be considered to ensure that routes are optimized for both cost and time.
4. Invest in Logistics Management Software
Investing in automation technologies for logistics management, such as warehouse robots or inventory management systems, can greatly enhance logistics efficiency.
Automated logistics processes reduce human error, increase order accuracy, and speed up processes like order picking, packing, and inventory tracking. It also improves overall efficiency, lowers labor costs, and enables businesses to scale operations without compromising quality or service.
You can use Scaleocean’s logistics software, which provides integrated solutions to optimize the logistics process from start to finish. You can monitor and manage the entire logistics process in one platform that you can customize to suit your business needs. Take a free demo with ScaleOcean to get this solution.
Logistics vs. Supply Chain Management: Key Differences
Logistics and supply chain management are closely related but distinct concepts that play crucial roles in ensuring products move efficiently from suppliers to customers. While logistics focuses on specific aspects of the process, supply chain management encompasses the entire flow. Here’s how they differ:
1. Logistics
Logistics is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the movement and storage of goods and services. It focuses on the efficient management of transportation, warehousing, and inventory within the supply chain.
Logistics aims to ensure that products reach their destination on time and in optimal condition while minimizing costs. It’s an essential function within the broader supply chain that helps businesses meet customer demands effectively.
2. Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) involves the coordination and management of all activities involved in the production and delivery of goods, from raw material sourcing to final customer delivery.
SCM includes logistics but also focuses on procurement, production, and distribution. It aims to optimize the entire supply chain process to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
SCM also involves collaboration with suppliers, manufacturers, and other stakeholders to create value throughout the entire network.
Manage Your Logistics Operations with ScaleOcean’s Logistics Software
ScaleOcean’s logistics system is a comprehensive solution that optimizes and streamlines logistics processes. It provides businesses with real-time tracking, seamless inventory management, and integration across numerous supply chain processes, resulting in increased efficiency and significant cost savings.
ScaleOcean offers organizations the opportunity to explore its platform, helping them gain firsthand experience and insights into its capabilities. Additionally, firms may be eligible for the CTC grant to help them use ScaleOcean’s software.
You can do a free demo with Scaleocean’s professional team to get a solution to optimize the logistics process from start to finish in an integrated manner. ScaleOcean’s software also includes the following major features:
- Unified Platform: ScaleOcean integrates all logistics processes, including inbound, outbound, and reverse logistics, into one platform, simplifying management and improving efficiency.
- Warehouse Management (WMS): Optimize warehouse operations with real-time inventory tracking, order management, and automated picking/packing workflows for smoother operations.
- Transportation Management (TMS): Enhance transportation logistics through route planning, real-time tracking, and carrier management, reducing costs and improving delivery times.
- Support for Specializations: ScaleOcean caters to international logistics (customs, multi-currency) and e-commerce (last-mile delivery, high-volume orders) for diverse needs.
- Future-Ready Features: With advanced analytics and sustainability tracking, ScaleOcean helps businesses plan demand, optimize operations, and meet environmental goals.
Conclusion
Optimizing logistics operations is essential for businesses to stay competitive, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. From streamlining transportation to managing inventory and warehousing, effective logistics is at the heart of a smooth supply chain.
ScaleOcean’s logistics software offers a comprehensive solution to streamline these processes. With real-time tracking, route optimization, and seamless integration with other supply chain functions, ScaleOcean helps businesses reduce costs, enhance operational efficiency, and deliver exceptional service to customers.
Take a free demo now to get an integrated solution tailored to your needs.
FAQ:
1. What is the work in logistics?
Logistics involves managing the acquisition, storage, and transportation of resources, including raw materials, semi-finished goods, and finished products, from their point of origin to their final destination.
2. What skills are needed for logistics jobs?
Logisticians need to maintain accurate records and manage multiple tasks in a fast-paced setting. They must also possess strong problem-solving skills to address unexpected challenges, such as delivery delays, and make necessary adjustments to resolve issues effectively.
3. What are the 7 C’s of logistics?
The 7-C’s of Logistics: Connect, Create, Customize, Coordinate, Consolidate, Collaborate, and Contribute. It offers an essential framework for effective supply chain management in today’s business environment.
4. What is C and F in logistics?
Cost and Freight (C&F) is a trade term where the seller covers the cost of goods and freight to the specified destination. The buyer, however, is responsible for unloading charges, import duties, local taxes, and insurance.

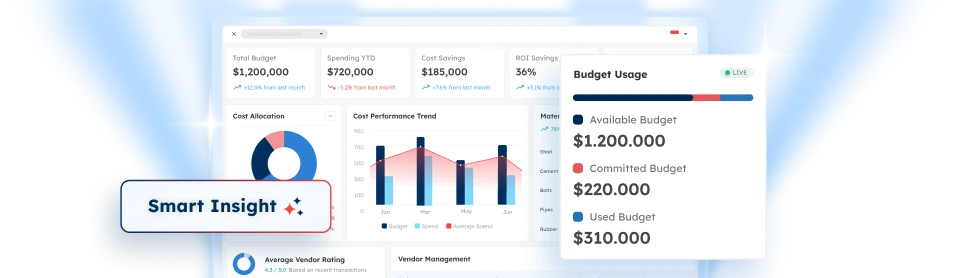


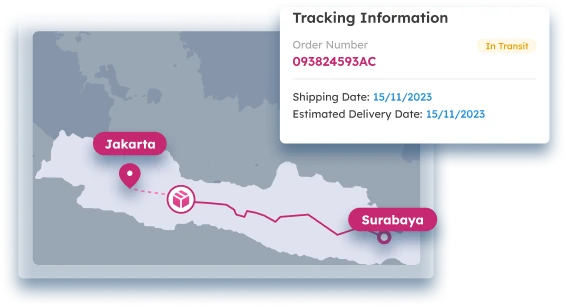







 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















