Purchase journal tracking credit purchases accurately is critical for organizations, particularly in Singapore. The purchase journal promotes financial transparency, manages cash flow, and ensures regulatory compliance. Businesses that efficiently handle credit transactions through the purchase journal can make better financial decisions and contribute to long-term profitability.
This article discusses the significance of the purchase journal, its format, and how it relates to accounting practices. It will also cover the various types of purchase journals, how to record entries, and their limits. Business owners in Singapore will discover concrete information to improve their financial management.
- A purchase journal is a specialized accounting tool used by businesses to track credit purchases, helping manage outstanding debts and providing a clear understanding of financial commitments.
- The purchase journal format captures crucial details, including transaction date, supplier name, invoice number, and amounts owed, ensuring accurate tracking of liabilities and simplifying financial record-keeping.
- Recording journal entries for purchase credits ensures that asset increases and liabilities are properly accounted for, maintaining accurate financial records necessary for tracking profitability ratios.
- ScaleOcean accounting software automates the purchase journal recording process, integrating purchasing and accounting functions to reduce errors, save time, and improve cash flow and supplier relationship management.

What is a Purchases Journal?
A purchase notebook is a specialized accounting instrument that firms use to track credit purchases of products and services. This notebook keeps account of all credit purchases, allowing businesses to better manage their outstanding debts. Similarly, a purchase requisition helps businesses initiate and track procurement requests, ensuring they manage their financial commitments effectively. Businesses that keep accurate records of these transactions can efficiently monitor their liabilities and retain a clear understanding of their financial commitments.
The purchase notebook is critical to ensure accurate financial reporting throughout the accounting cycle. Companies can categorize and organize credit purchases, which are then posted to the general ledger. This method is critical for maintaining openness in financial records and ensuring that the company follows accounting standards.
Characteristics of a Purchases Journal
The purchase journal specifically captures credit purchases. Unlike other accounting journals, it does not include monetary transactions, which businesses usually document in the cash receipts journal. This allows businesses to focus solely on credit-based purchases, ensuring they track liabilities appropriately.
In addition, the purchase notebook arranges entries by supplier or creditor, making it easier to track outstanding bills. It also plays an important function in keeping accurate records for auditing purposes, ensuring that enterprises adhere to Singapore financial accounting standards and local regulatory obligations.
Also, using the best purchase order software helps automate the process, making it easier to generate, track, and manage purchase orders. It ensures that businesses maintain accurate records of credit purchases, reduces human errors, and streamlines the entire procurement workflow.
Accounting for a Purchases Journal
In accounting, businesses use the purchase journal to carefully record all credit purchases. They typically maintain the journal daily, and they record the entries in the general ledger. The purchase journal entry often entails debiting an asset account, such as inventory, and crediting accounts payable, which represent the amount owing to the supplier.
The best accounting software in Singapore can automate these entries, making the process more efficient. Such software usually connects easily with your financial system, ensuring that all transactions are properly recorded in your reports.
Purchases Journal Format
The purchase notebook follows a consistent structure that captures crucial facts about each credit purchase. Typically, this comprises columns for the transaction date, supplier name, invoice number, and a brief description of the purchased goods. Furthermore, the amount owed is carefully documented to track outstanding liabilities. In the purchasing process in business, the amount owed is carefully documented to track outstanding liabilities.
A well-organized purchase diary template also includes columns for debited accounts, which frequently refer to inventories or another appropriate asset account. Another important column is accounts payable, which helps track the money owed to suppliers. Using such a template makes the process easier, especially as the company grows and handles more transactions.
According to Singapore Legal Advice, For small entities in Singapore, such as those defined by the SFRS (meeting at least two of three criteria: annual revenue under S$10 million, assets under S$10 million, or no more than 50 employees), maintaining accurate purchase journals becomes even more crucial for regulatory compliance and financial clarity.
Four Types & Examples of Purchases Journals
In the world of accounting, there are several types of purchases journals used to record different types of transactions, especially related to purchases made on credit. These journals help businesses track their financial obligations and manage their liabilities. Understanding the various types of purchase journals is essential for accurate financial reporting and maintaining organized records. The following are the four most common types of purchase journals used by businesses:
1. Purchase Journal
The most popular type is the purchase journal, which is used to track all credit purchases made by a business. It is the principal tool for managing outstanding debts and obligations.
This journal assists firms in carefully capturing all credit purchases and ensuring that financial records reflect precise amounts owing to suppliers. Implementing procurement risk management practices at this stage is essential to effectively monitor risks related to supplier payments and cash flow.
Understanding the procurement vs. purchasing distinction can also help businesses streamline their processes and ensure efficient management of both procurement activities and financial obligations. It is critical for monitoring the company’s payables and managing cash flow effectively.
2. Trade Journal
A trade journal records purchases from specific suppliers or trade partners, often used by businesses with long-term relationships with certain vendors. This journal helps businesses track purchases made on credit from a limited set of suppliers. It is beneficial for businesses that regularly deal with a small group of partners, providing a clear and focused record of transactions. This can help simplify vendor relationship management and improve purchasing strategies by utilizing different methods of purchasing.
3. Posting in Ledger
Businesses enter transactions in the buy diary and then post them to the ledger. This ensures that they include the purchase entries in the company’s overall financial records. For example, companies may use a blanket order to place long-term purchase agreements, which are then recorded and posted to the ledger.
By doing so, businesses can link these transactions to other financial data, enabling better tracking, reporting, and analysis. This method is essential for keeping a complete record of the company’s financial health and success.
4. Cash Receipts Journal
After businesses record transactions in the purchase journal, they post them to the ledger. This ensures that the purchase entries integrate into the company’s broader financial records. By posting to the ledger, businesses can link these transactions with other financial data, allowing for better tracking, reporting, and analysis. This process is crucial for maintaining a comprehensive record of the company’s financial health and performance.
What is a Purchase Credit Journal Entry?
A business records a purchase credit journal entry when it buys goods or services on credit, meaning it will make the payment at a later date. This entry involves debiting an asset account, such as inventory or supplies, to reflect the increase in assets. On the other side, the business credits accounts payable to show the amount it owes to the supplier.
It’s important to understand that businesses purchase credit journal entries only when they don’t make an immediate cash exchange. If they make the payment in cash at the time of the purchase, they record a different entry called a cash purchase journal entry. This distinction helps businesses maintain accurate records of their credit transactions and cash flows.
How to Record a Journal Entry of Purchase Credit?
Recording a purchase credit journal entry helps businesses track credit purchases and manage liabilities. It ensures that assets increase and liabilities are properly accounted for, keeping financial records accurate. This accuracy is essential for financial metrics, including profitability ratios, which rely on precise asset and liability tracking. The steps for appropriately recording a purchase credit journal entry are as follows:
1. Debit the Asset Account
First, debit the relevant asset account, such as inventories or office supplies. This represents the rise in assets that the company has purchased. Debiting the asset account ensures that the purchase is accurately recorded and reflects the addition of goods or services to the company’s resources.
2. Credit Accounts Payable
Next, credit the accounts payable with the amount owed to the supplier. This demonstrates the responsibility incurred by the firm, ensuring that it is recognized as an outstanding debt that must be paid in future. Crediting accounts payable allows organizations to accurately track their financial obligations.
3. Ensure Accuracy in Financial Records
Finally, confirm that you have properly entered the journal item in your financial system. This phase is critical for maintaining accurate and up-to-date financial reporting by ensuring that you capture all transactions correctly. Accurate record-keeping helps firms manage their money and provides a solid foundation for decision-making.
Example of Purchase Credit Journal Entry
The purchase credit journal entry plays a vital role in a company’s accounting process. It records transactions where the company purchases goods or services on credit. This entry ensures that the business’s financial records accurately reflect both the increase in assets, such as inventory, and the corresponding liability, shown as accounts payable. Proper recording of such transactions is essential for maintaining transparency and ensuring compliance with accounting standards.
Limitations of Purchase Credit Journal Entry
While the buy credit diary entry is an important tool for tracking credit transactions, it does have some drawbacks. One major disadvantage is that it does not include currency transactions, which must be recorded separately in other journals. This means that organizations must manage credit and cash purchases in separate systems, increasing the complexity of financial tracking.
According to ACRA, as accounting standards evolve to address emerging complexities, businesses must adapt their systems to manage transactions efficiently. For instance, the Exposure Draft ED/2023/5 issued on 30 November 2023 highlights the need for continuous updates to accounting practices for enhanced clarity and regulatory compliance.
Furthermore, employing this journal demands organizations to keep an accurate financial system and regularly update their outstanding payables. This might be time-consuming and difficult for larger firms with a high volume of transactions. Effective handling of these entries is critical to avoiding financial reporting problems and making timely payments to suppliers.
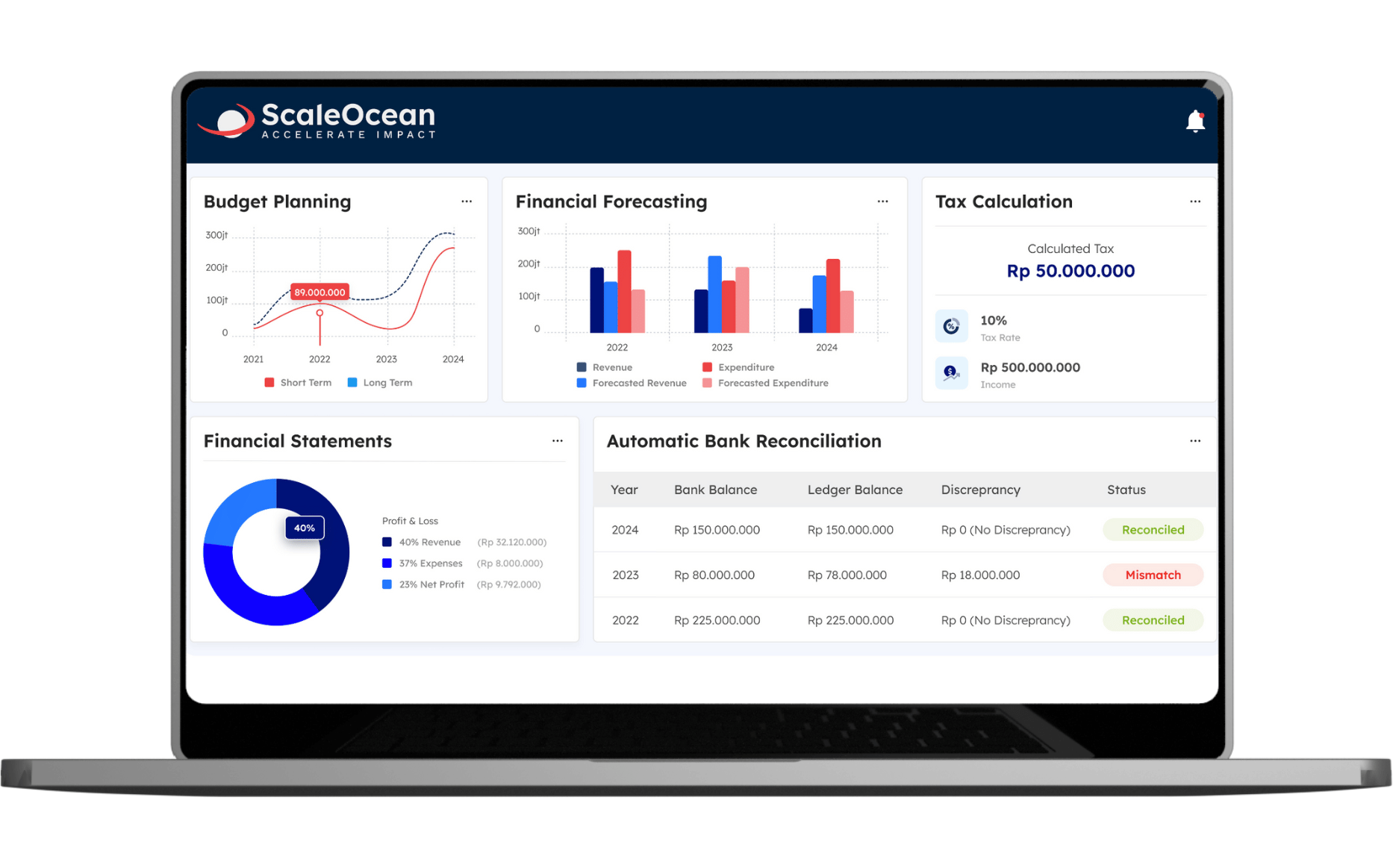
Automate Purchase Journal Recording with ScaleOcean Accounting Software
Integrating purchasing and accounting systems is critical for increasing corporate efficiency and financial accuracy. ScaleOcean’s purchasing software automates purchase tracking and journal keeping, resulting in fewer errors and saved time. This provides accurate financial reporting, allowing firms to better manage cash flow, inventory, and supplier relationships.
ScaleOcean also provides a free demo for organizations to try out the benefits firsthand, with the added benefit of using the CTC grant for eligible enterprises. This allows you to explore the software’s features and see how it can help you streamline your accounting procedures. The following is a list of main characteristics of ScaleOcean software:
- Automated Financial Processes, Automates purchase journal recording and financial tracking for accurate, efficient data entry.
- Integrated Modules, Seamlessly integrates purchasing, sales, inventory, and accounting for streamlined operations.
- Real-Time Reporting, Provides real-time financial reports and analysis for quick decision-making.
- Unlimited Users, Offers unlimited user access with no extra fees, ideal for growing businesses.
- Flat Pricing, Transparent, flat pricing with no hidden fees, perfect for medium to large enterprises.
Conclusion
Automating the purchase journal recording process is an important step towards optimizing business processes and increasing financial accuracy. Businesses that integrate purchasing and accounting systems can eliminate errors, save time, and gain greater control over their cash flow and supplier relationships. This integration results in more effective financial reporting and smoother business operations.
To supplement these advantages, ScaleOcean provides a comprehensive set of tools designed to optimize accounting operations. ScaleOcean’s Purchasing Software is meant to simplify your company’s financial operations by providing features like automated purchase tracking, real-time financial reporting, and seamless connection. ScaleOcean is the right answer for businesses looking for precision and efficiency in their operations, whether managing purchases or handling complex accounting responsibilities.
FAQ:
1. What is the purchase journal?
A purchase journal is an accounting tool used to record all purchases made on credit by a business. It tracks transactions where payment is deferred, allowing the business to manage outstanding debts effectively. This journal helps in monitoring liabilities and ensures proper tracking of purchases made from suppliers.
2. What is the difference between sales journal and purchase journal?
The sales journal is used to document credit sales, while the purchase journal records credit purchases. The sales journal captures transactions where goods or services are sold on credit, whereas the purchase journal focuses on acquisitions made on credit. Both journals are essential for managing a company’s financial records, but they serve different purposes.
3. What will be the journal entry for purchase?
When a purchase is made on credit, the journal entry typically involves:
1. Debiting the relevant asset account (e.g., inventory or supplies) to reflect the increase in assets.
2. Crediting the accounts payable, which indicates the amount owed to the supplier.
This process ensures the proper recording of credit purchases in financial statements.
4. What kind of transactions are recorded in a purchases journal?
A purchases journal records transactions where goods or services are bought on credit. These are purchases where payment will be made in the future, and they are documented to track outstanding liabilities. Cash transactions or purchases where immediate payment is made are not included in this journal.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















