When managing inventory according to market demand, companies must pay attention to several factors to ensure that inventory is neither insufficient nor excessive. If either of these factors occurs, the business will experience significant losses.
This is especially true for businesses in the manufacturing and distribution sectors, where maintaining appropriate inventory levels is crucial for smooth operations. One way to do this is by managing safety stock efficiently.
In a fast-paced market like Singapore, where demand and supply chains can shift quickly, it ensures that businesses can continue to meet client demands despite disruptions.
Safety stock is a solution businesses can use to avoid stockouts when demand spikes. However, you must also manage it effectively to avoid overstocking and maintain a balance between storage costs and the risk of stockouts.
This article will discuss safety stock in detail, including its definition, importance, how to manage it, why businesses should maintain it, and how to calculate it and use examples to simplify management. Learn more here!
- Safety stock is an additional inventory buffer maintained by a company to guard against unexpected spikes in customer demand or supply delays.
- To accurately calculate safety stock, you can use the following formula: Safety Stock = (Maximum Daily Usage x Maximum Lead Time) – (Average Daily Usage x Average Lead Time)
- The reason businesses need safety stock is to prevent stockouts, buffer against supply chain disruptions, maintain customer satisfaction, smooth production planning, and many other
- ScaleOcean’s Inventory System offers the ideal solution for businesses looking to enhance their safety stock management, with integration and automation solutions.

What Is Safety Stock?
Safety stock is an additional inventory buffer maintained by a company to guard against unexpected spikes in customer demand or supply delays. It acts as a safeguard to avoid stockouts and ensure smooth business operations by addressing risks from supply chain fluctuations.
As examples, supplier delays, production issues, or inaccurate forecasts, finding the optimal level is key, as excessive stock raises costs, while insufficient stock can lead to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
Why Is Safety Stock Important?
Safety stock is essential for maintaining a steady flow of operations in businesses that rely on consistent supply and demand. It acts as a cushion to absorb unexpected disruptions, such as supplier delays or sudden surges in customer orders.
By having it in place, companies can avoid stockouts, which can lead to lost sales, damaged customer relationships, and missed business opportunities. Moreover, it helps businesses manage the uncertainties in forecasting demand and supply chain operations.
With the right strategy, businesses can balance operational efficiency, cost control, and customer satisfaction, ensuring long-term success.
What Is a Good Safety Stock Level?
A good safety stock level strikes a balance between preventing stockouts and avoiding excess inventory costs. It depends on factors such as demand variability, lead time, and the reliability of suppliers.
To determine the right amount, businesses must analyze historical sales data, forecast demand trends, and assess the potential risks of supply chain disruptions. A well-calculated safety stock ensures that companies can meet customer demand without overstocking, which ties up capital and incurs storage costs.
The goal is to keep inventory levels optimized, enough to cover unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply, but not so much that it negatively impacts profitability.
How Can Safety Stock Improve Inventory Management?
Safety stock plays a crucial role in improving inventory management by ensuring that businesses can continue operations smoothly, even in the face of demand fluctuations or supply chain disruptions.
By maintaining a buffer of extra inventory, companies can avoid stockouts that could lead to missed sales and dissatisfied customers. It helps strike a balance between having enough inventory to meet demand and minimizing overstock, which can tie up capital and increase storage costs.
With the right amount of safety stock, businesses can improve their order fulfillment rates, maintain higher customer satisfaction, and enhance overall operational efficiency, ultimately leading to better inventory flow and reduced risks in the supply chain.
How to Calculate Safety Stock
Calculating safety stock involves analyzing various factors such as demand variability, lead time, and supply chain reliability to determine the optimal buffer inventory.
The process requires businesses to assess historical sales data, forecasted demand, and potential disruptions in the supply chain to calculate a safety stock level that minimizes the risk of stockouts while avoiding excess inventory.
Understanding the right formula and factors to consider is crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient inventory management system. There are several safety stock formulas that you can use according to your business needs, including:
1. Basic Safety Stock Formula (Max/Average Method)
The basic safety stock formula is a straightforward way to calculate the buffer inventory needed to protect against variability in demand and supply. It is typically calculated as:
Safety Stock = (Maximum Daily Usage x Maximum Lead Time) – (Average Daily Usage x Average Lead Time)
This formula ensures that a business has enough inventory to cover the maximum demand during the lead time period, helping prevent stockouts. This formula is best used for a simple estimate, but less accurate when variability is high.
2. Lead Time Calculation
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes for an order to be placed and for the products to be delivered. To calculate it based on lead time, businesses consider how quickly inventory is consumed during this period. This is the formula you can use for calculating it based on lead time:
Z x Average sales x σLT
A common approach is to multiply the average daily usage rate by the lead time in days to determine how much stock is needed during the lead time.
3. Safety Stock with EOQ (Economic Order Quantity)
EOQ is a method for determining the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs. The calculation with EOQ ensures that businesses maintain a buffer stock while ordering the optimal quantity.
√DS/H
The safety stock is added to the EOQ formula to account for uncertainties in demand and lead time.
4. Inventory Position Safety Stock
Inventory position takes into account both the actual inventory and any pending orders (on-order stock).
This method is used to calculate it based on the total inventory position, which ensures businesses consider both their current stock levels and incoming orders when determining how much extra inventory is needed to prevent shortages. The formula is:
Inventory Position = Inventory on Hand – Backorders + Inventory Currently on Order
5. Safety Stock with Reorder Point
The reorder point is the inventory level at which a new order is placed to replenish stock. The formula in this case ensures that an order is placed before running out of stock, accounting for lead time and demand variability.
Reorder Point = (Average Demand per Period x Average Lead Time) + Available Safety Stock
This ensures businesses reorder in time to avoid stockouts during replenishment.
6. Greasley’s Formula (Statistical Formula)
Greasley’s formula calculates safety stock by factoring in both lead time demand and its standard deviation. It’s particularly useful for businesses dealing with uncertain demand. The formula is:
Z × σLT × Davg
Z-score represents the service level factor, for example, 1.65 for a 95% service level. σLT represents the standard deviation of lead time. D avg represents the average daily demand.
7. The Heizer Render Formula
Heizer and Render’s formula is a more detailed calculation used in inventory management to incorporate demand variability and lead time. It provides a more accurate calculation for safety stock when using complex supply chain models. Here is the formula:
(Z-score) x (σLT)
8. The Fixed Formula
The fixed formula involves setting a fixed safety stock level that does not change based on demand or supply fluctuations. The formula is simple:
Safety Stock = Average Daily Sales x Number of Stock Days
This formula is often used when businesses prefer a conservative approach to inventory management, maintaining the same buffer level regardless of demand or lead time changes.
9. Complementary Formulas
Complementary formulas combine various inventory metrics, such as demand rate, lead time, and order quantity, to determine an optimal level of safety stock.
These formulas often adjust based on specific industry needs, including factors like supplier reliability, seasonal fluctuations, and market trends. They aim to ensure that safety stock levels are precisely matched to business requirements without overstocking or risking stockouts.
Take, for example, safety stock management in the manufacturing sector. According to ICTTM, Singapore’s manufacturing sector, which contributed 18.6% of GDP in 2023, will continue to prioritize digital transformation and risk management to enable long-term growth.
One factor is having sufficient inventory to meet surging demand. This is why it is crucial in manufacturing companies to ensure smooth production and distribution.
In this context, digital technology is key to supporting safety stock management. With ERP solutions, companies can obtain accurate and up-to-date data on inventory levels, lead times, and market demand. This enables faster, data-driven decision-making, which is crucial for maintaining operational continuity and meeting customer expectations.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Calculate Safety Stock
Calculating safety stock is critical for organizations to maintain proper inventory levels, avoid stockouts, and reduce surplus stock. For businesses in fast-paced markets like Singapore, accurate calculations are critical to maintaining smooth operations and avoiding delays in client demand or production schedules.
Here’s a step-by-step guide for firms to accurately determine safety stock.
1. Gathering Necessary Data
To begin, organizations must gather information on past demand trends, lead times, and variability in both. This information is critical for doing correct safety stock estimates.
Businesses, for example, could evaluate previous sales data to identify demand changes, track supplier lead times, and account for any historical disruptions. Accurate data allows organizations to properly change stock levels, preventing both overstocking and stockouts.
2. Applying Chosen Formula
After acquiring the relevant data, organizations use the recommended safety stock algorithm. Standard deviation is a widely used strategy for accounting for differences in demand and lead time.
It is often calculated using a formula that takes into account demand unpredictability and the time required to refill stock, similar to how businesses calculate standard cost to manage production expenses accurately.
This method assists organizations in areas such as retail or manufacturing, where demand is unpredictable, and supply chain disruptions are prevalent, in determining the optimal buffer stock necessary.
3. Utilizing Tools and Software for Accuracy
Businesses can increase accuracy and efficiency by implementing inventory management tools or software, such as safety stock formula Excel templates or specialized platforms. These technologies automate calculations, accelerating the process and reducing human error.
In today’s business environment, where fast adjustments are vital, software enables businesses to monitor stock levels in real time, automatically triggering reorder points and ensuring that it remains in sync with changing demand and supply situations.
Safety Stock Example Calculation
To facilitate deeper understanding, consider the following example of a safety stock calculation based on standard deviation. First, understand this data:
- Average weekly demand (D): 100 units
- Standard deviation of demand (σ): 20 units
- Lead time (L): 2 weeks
- Service level (Z): 1.65 (for 95% service level)
Step 1: Calculate Standard Deviation of Lead Time Demand
Standard Deviation of Lead Time Demand=σ × √L= 20 × √2 = 28.28 units
Step 2: Calculate Safety Stock
= Z x Standard Deviation of Lead Time Demand
= 1.65 x 28.28 = 47 units
Step 3: Calculate Reorder Point
Reorder Point = (D x L) + Safety Stock = (100 x 2) = 247 units
With this calculation, here are the results:
Final Results:
- Safety Stock: 47 units
- Reorder Point: 247 units
When inventory reaches 247 units, it’s time to reorder.
Why Do Businesses Need Safety Stock? 12 Reasons to Keep It
Safety stock is crucial for businesses to maintain a smooth and efficient operation, especially when dealing with fluctuating demand and potential supply chain disruptions.
By keeping a buffer of inventory, companies can ensure they can meet customer demands without facing stockouts, ultimately protecting their bottom line and customer satisfaction. Here are the reasons businesses need it and should keep it, including:
1. Prevent Stockouts
Safety stock acts as a cushion against unexpected spikes in demand or delays in supply, ensuring that businesses do not run out of products, which can lead to missed sales opportunities and damaged customer relationships.
2. Buffer Against Supply Chain Disruptions
External factors like shipping delays, supplier issues, or natural disasters can affect the timely delivery of goods. It ensures that businesses are prepared for such disruptions and can continue operations without major interruptions.
3. Maintain Customer Satisfaction
By having enough inventory available, businesses can fulfill customer orders promptly, leading to higher satisfaction levels, repeat business, and stronger customer loyalty.
4. Smooth Seasonal Demand Fluctuations
Some businesses face seasonal spikes in demand. It helps businesses manage these peaks by ensuring there’s enough product on hand to meet temporary increases in demand without overstocking or understocking.
5. Improve Production Planning
Safety stock allows manufacturers to keep production running smoothly, even when there are delays in raw material shipments or unexpected issues in the production process, reducing the risk of halting production due to stockouts.
6. Minimize the Risk of Stockouts in Critical Products
For high-demand, critical items, safety stock is essential to avoid the negative impact of running out of stock, particularly when these items are crucial to daily operations or customer satisfaction.
7. Avoid Lost Sales
When demand outstrips supply, businesses may lose sales opportunities. Safety stock helps businesses avoid such scenarios, ensuring they can meet demand without relying solely on real-time supply and demand fluctuations.
8. Enhance Operational Efficiency
By keeping the right level of safety stock, businesses can optimize inventory levels, reduce reorder frequency, and avoid unnecessary rush orders, making their operations more streamlined and cost-effective.
9. Supports Just-In-Time (JIT) Operations
Safety stock can complement JIT inventory practices, which minimize stock levels by providing a backup when JIT operations face delays or inaccuracies, ensuring smooth operations while reducing waste and excess inventory.
10. Buffer Against Forecasting Errors
Demand forecasting is not always accurate. It helps to buffer against forecasting errors by ensuring that unexpected changes in demand do not lead to stockouts, providing a safety net for inaccuracies in predicting sales.
11. Strengthen Supplier Relationships
Having safety stock can improve supplier relationships by ensuring that businesses are less reliant on the precise timing of deliveries. This can reduce stress on suppliers and lead to more reliable, long-term partnerships.
12. Ensure Business Continuity
In highly competitive industries, any disruption in supply or demand can lead to significant consequences. It ensures that businesses can continue to operate and fulfill orders, even when external factors or internal inefficiencies arise.
Factors Necessitating Safety Stock
Several causes contribute to the requirement for safety stock, which helps firms manage risks and maintain consistent operations. Understanding these elements is critical in dynamic marketplaces, especially for enterprises in retail, manufacturing, and distribution, to ensure that operations run smoothly.
Here are the factors necessitating safety stock, including:
1. Demand Variability
Seasonality, promotional events, and market trend shifts can all cause demand swings. When demand is uncertain, firms require a buffer stock to avoid stockouts and ensure they can continue to fill orders.
Companies that retain safety stock can endure demand peaks or troughs without jeopardizing their capacity to meet customer expectations. Efficient management of Stock-Keeping Unit (SKU) data helps businesses better predict and handle such demand fluctuations.
2. Supply Chain Uncertainties
Supply chain interruptions, such as transportation delays or production issues with suppliers, can cause crucial shortages.
It protects against these uncertainties by ensuring that businesses have enough stock on hand to continue operations. This buffer reduces the likelihood of stockouts and avoids delays to customer service and manufacturing schedules.
3. Lead Time Fluctuations
Lead time is the time between placing an order with a supplier and receiving it. Any variations in lead time, such as extended or uneven delivery schedules, might have an influence on inventory levels.
Safety stock is required in these circumstances to fill the gap during delays, ensuring that firms do not endure stockouts while waiting for new shipments.
Challenges & Risks of Safety Stock
Managing safety stock is crucial for maintaining smooth operations in manufacturing and supply chains. However, several challenges and risks come with its management. Companies must address these issues to ensure that safety stock levels are optimized, reducing the risk of stockouts or excessive inventory.
Understanding these common challenges can help businesses implement better strategies for more efficient and cost-effective inventory management.
1. Inaccurate Demand Forecasting
One of the primary challenges in managing safety stock is inaccurate demand forecasting. If demand is underestimated or overestimated, businesses may either face stockouts or overstocking. Accurate demand forecasting is essential to determine the right amount of safety stock, reducing the risk of unnecessary inventory or missed sales opportunities.
2. Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions, such as transportation delays, labor shortages, or supplier issues, can impact the availability of materials. These disruptions lead to difficulties in maintaining optimal safety stock levels. Businesses must factor in these uncertainties when determining how to ensure continuous operations despite external challenges.
3. Overstocking and Excess Inventory
Overstocking is a significant risk that occurs when safety stock levels are set too high. This not only ties up capital in excess inventory but also incurs storage costs. Additionally, businesses must be mindful of obsolete inventory, which can result from overstocking items that are no longer in demand or have lost their value.
Striking a balance between ensuring product availability and preventing excess stock is crucial to avoid higher holding costs and potential obsolescence.
4. Inconsistent Replenishment Cycles
Inconsistent replenishment cycles can cause problems when managing safety stock. If replenishment isn’t timely or reliable, businesses may run out of stock or accumulate excess inventory.
It’s important to establish predictable and efficient supply chain processes to maintain consistent replenishment, ensuring safety stock is replenished at the right time.
5. Lack of Real-time Data and Visibility
A lack of real-time data and visibility across the supply chain makes it challenging to manage safety stock accurately. Without up-to-date information on stock levels, demand patterns, and lead times, businesses cannot make informed decisions about safety stock levels.
Implementing an integrated system like ERP ensures real-time tracking and data accuracy, improving inventory control.
When to Implement Safety Stock
When introducing safety stock, organizations must identify high-risk scenarios when it is most required, especially in dynamic industries such as retail, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
Different inventory processes and types with varying demand patterns or items that rely on suppliers with unpredictable delivery schedules are particularly sensitive to disruptions. In these circumstances, keeping it allows organizations to continue satisfying consumer requests while avoiding revenue losses or production delays.
Furthermore, continuously analyzing demand and supply variations enables organizations to proactively modify safety stock levels. Companies, particularly those in industries with volatile market conditions, may ensure they have enough inventory to handle risks by evaluating past data and projecting probable supply chain interruptions.
By incorporating effective inventory control practices, this technique reduces the likelihood of stockouts, assuring smooth operations and increased customer satisfaction.
Safety Stock Usage Tips and Strategies
Effectively managing safety stock is key to balancing supply and demand while minimizing costs. By implementing the right strategies, businesses can ensure they maintain adequate inventory levels without overstocking.
Below are several practical tips and strategies to optimize the use of safety stock and improve overall inventory management efficiency.
1. Use Historical Data for Accurate Forecasting:
Rely on historical sales data to predict demand trends and set appropriate safety stock levels. By analyzing past sales patterns, businesses can anticipate future demand fluctuations and adjust it accordingly, minimizing the risk of stockouts and excess inventory.
2. Consider Lead Time Variability
Account for lead time variability when calculating safety stock. If lead times are inconsistent, it’s crucial to increase safety stock levels to buffer against potential delays. Incorporating variability into your calculations ensures that disruptions in the supply chain don’t result in stockouts.
4. Implement Reorder Point (ROP) Systems
Use a reorder point (ROP) system to trigger automatic replenishment orders when inventory reaches a predetermined level. By linking safety stock levels to ROP, businesses can reduce the chances of running out of stock and improve inventory turnover, ensuring timely restocking based on real-time demand.
5. Adopt Demand-Driven Inventory Models
Consider adopting a demand-driven inventory management model, where safety stock levels are adjusted based on real-time demand signals rather than static forecasts. This approach ensures it is dynamically adjusted to match actual demand, preventing overstocking or understocking situations.
6. Leverage Technology for Real-Time Monitoring
Use integrated technology, such as ERP and inventory management systems, to monitor stock levels in real time. This allows businesses to track safety stock levels, adjust replenishment schedules, and react quickly to fluctuations in demand or supply chain issues, optimizing inventory management across all channels.
You can optimize your safety stock management strategy with Scaleocean inventory software, ensuring real-time tracking, automated replenishment alerts, and seamless integration with other business systems. This enables more accurate forecasting, reduces stockouts, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Take a free demo to get this solution!

Safety Stock Examples in Industry
In businesses such as retail and manufacturing, safety stock is critical for controlling demand swings and supply chain disruptions. Both sectors rely on safety stock to ensure efficient operations and customer satisfaction.
Fashion shops, for example, frequently boost safety stock during peak seasons such as the holidays to minimize stockouts, whereas automotive manufacturers keep raw material safety stock on hand to prevent production halts due to supplier delays.
Businesses can gain useful insights into optimizing safety stock strategies by reviewing case studies from diverse industries. Maintaining efficiency requires regular assessment and adjustment of stock levels in response to changes in demand, lead time, and supply conditions.
Integrating inventory management systems and automating stock adjustments can assist organizations in aligning safety stock with real-time conditions, lowering the chance of stockouts and enhancing overall supply chain stability.
What is the Difference Between Safety Stock and Cycle Stock?
Safety stock and cycle stock are both integral parts of inventory management, but they serve different purposes. Cycle stock refers to the regular inventory used to meet customer demand during normal operations.
It’s replenished through regular ordering cycles and typically reflects the average demand within a given period. In contrast, it is extra inventory kept on hand to account for uncertainties, such as unexpected demand spikes or supply chain disruptions.
The key difference is that cycle stock is based on forecasted demand, while safety stock acts as a buffer against unexpected fluctuations. While cycle stock is regularly used and replenished, safety stock is only used when demand exceeds expectations or when there are delays in supply.
Too Much Safety Stock vs. Too Little
Maintaining the right balance of safety stock is crucial for efficient inventory management. Too much safety stock can lead to overstocking, tying up valuable capital in excess inventory, and increasing storage costs.
It can also lead to product obsolescence or waste, especially in industries with fast-moving products. On the other hand, too little safety stock increases the risk of stockouts, which can result in missed sales opportunities, disrupted production schedules, and dissatisfied customers.
Striking the right balance ensures product availability without incurring unnecessary costs, and it requires careful monitoring of demand patterns, lead times, and supply chain variability to optimize safety stock levels.
Safety Stock Technology and Tools
In today’s fast-paced business environment, leveraging technology and tools for safety stock management is essential for improving accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making. Various software and technologies enable businesses to track, calculate, and adjust safety stock levels in real-time, minimizing risks and optimizing inventory.
Below are some key technologies and tools to enhance safety stock management.
1. ERP Systems for Real-Time Data Tracking
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems provide businesses with real-time data on inventory levels, demand, and lead times. By integrating safety stock management within an ERP system, businesses can monitor stock levels across multiple locations, automate replenishment orders, and gain insights into optimal safety stock thresholds.
2. Inventory Management Software (IMS)
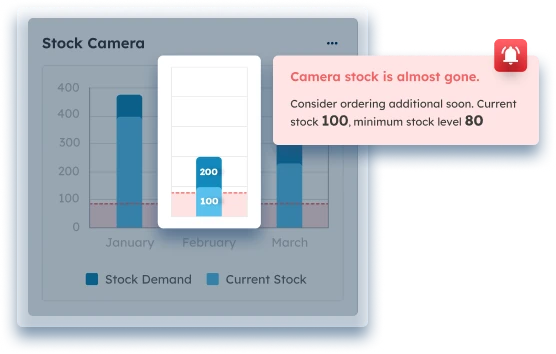
Inventory Management Software (IMS) is designed to help businesses track and control stock levels, including safety stock. These systems often come with advanced features like automated alerts for low stock, real-time tracking, and predictive analytics to ensure it is maintained at optimal levels based on current demand and lead time data.
3. Cloud-Based Solutions for Scalability
Cloud-based inventory management platforms offer scalability and flexibility in managing safety stock. With cloud technology, businesses can easily adjust stock levels based on real-time demand, integrate with multiple supply chain partners, and access critical data from anywhere, improving decision-making and operational efficiency.
4. Automated Replenishment Systems
Automated replenishment systems ensure that safety stock levels are maintained by automatically placing orders when inventory reaches predefined reorder points. These systems can be integrated with demand forecasting and inventory management tools, ensuring accurate and timely replenishment of safety stock without manual intervention.
ScaleOcean provides an effective ERP system for inventory management with a technology-based approach to optimize safety stock management. Through the inventory software module, companies can perform real-time and automated stock control.
ScaleOcean’s inventory system is also integrated with other modules, such as procurement and accounting, enabling automatic stock updates with every purchase or sale transaction, minimizing the risk of data discrepancies between departments and improving operational efficiency.
Monitoring Safety Stock Real-Time with ScaleOcean’s Inventory System
Effective inventory management is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their operations and reduce costs. ScaleOcean’s best inventory system provides real-time monitoring of safety stock, ensuring that businesses can maintain optimal stock levels without overstocking or running into shortages.
ScaleOcean inventory software offers an all-in-one ERP solution designed to streamline inventory management with over 200 specialized modules that address every aspect of the process.
Whether your business operates from a single location or multiple branches, ScaleOcean ensures seamless integration across all sites, connecting them to a unified platform for real-time inventory visibility and control.
Furthermore, the system’s customizable integration capabilities allow for smooth synchronization with other platforms your business may already use, enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring that your inventory systems work together effortlessly.
ScaleOcean provides a free demo to help organizations optimize their safety stock and inventory management strategies. Businesses may also be eligible for the CTC (Cost to Company) grants, which can help them with their digital transformation.
Therefore, here are the features that can help businesses manage safety stock comprehensively
- Real-Time Inventory Monitoring: Provides full visibility of inventory across all company locations and branches, allowing businesses to directly monitor the amount of safety stock available.
- Automatic Replanning Alerts: An automated inventory replenishment alert feature, letting you know when to order new items to meet predetermined safety stock levels.
- AI Inventory Forecasting: Using advanced forecasting algorithms to access historical data and sales trends to predict future stock needs and accurately plan safety stock.
- Stock Visibility Across Channels: If your business has multiple distribution channels or multiple sales channels, Scaleocean can provide integrated stock visibility across all channels and ensure optimal safety stock levels remain across all platforms, both online and offline.
- Dynamic Safety Stock Calculation: Automatically calculates safety stock dynamically based on demand variability and your business’s lead times.
With its best-in-class solutions, ScaleOcean helps companies manage safety stock more efficiently, reduce overstocking and stockout costs, and improve supply chain reliability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effectively managing safety stock is crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient supply chain. By optimizing inventory levels, businesses can prevent costly stockouts and minimize overstocking, which ties up valuable resources.
With the right tools and strategies in place, companies can strike the perfect balance between supply and demand. ScaleOcean’s Inventory System offers the ideal solution for businesses looking to enhance their safety stock management.
With real-time inventory monitoring, dynamic safety stock calculations, and seamless integration across multiple branches and platforms, ScaleOcean empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions and ensure that safety stock is always at optimal levels.
Its customizable features, combined with advanced forecasting and replenishment alerts, provide a comprehensive, all-in-one solution for businesses of all sizes. Take a request demo to get this solution!
FAQ:
1. What is the 50% rule of safety stock?
The 50% safety stock rule recommends keeping a safety stock level that is 50% of the average demand during lead time (half of the stock typically used during the reorder period). To calculate this, multiply your average weekly sales by the lead time in weeks, then divide the result by two.
2. What is the McKinsey method of safety stock?
The McKinsey method integrates several factors, including historical demand, inventory costs, and the desired service level, to develop a well-rounded safety stock strategy.
3. What is the Z score in safety stock?
Z-scores indicate the number of standard deviations needed to meet a specific service level. They correspond to various service level percentages, such as 1.28 for a 90% service level, 1.65 for 95%, 1.96 for 97.5%, and 2.33 for 99%.
4. What are alternatives to holding safety stock?
Buffer stock is the quantity needed to protect against demand fluctuations or spikes caused by customers. It functions similarly to safety stock and is sometimes referred to as “buffer safety inventory.”










 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















