In today’s competitive market, businesses in Singapore are actively looking for ways to streamline operations and improve efficiency. As many as 78% of SMEs prioritize operational efficiency, with 63% using cloud technology to accelerate their digital transformation. To optimize every business process, the solution can be assisted by the phase of ERP implementation.
The Singapore government can use an ERP system to support this effort through the SME Go Digital program, which provides tools to help businesses start their digital journey. Implementing an ERP system can increase productivity by up to 20%, allowing businesses to better integrate their processes and improve overall efficiency.
According to Research Nester, the ERP implementation market in Singapore was valued at over USD 938.61 million in 2024 and is expected to approach USD 4.32 billion by 2037, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 12.7% during this time.
This development indicates the increasing use of ERP systems as firms seek to improve operational efficiency and remain competitive in the digital age. Here is an explanation of how ERP is implemented with its 9 stages.
- ERP implementation is the process of integrating an ERP system to streamline core business operations, improving efficiency and productivity across various departments.
- Key phases of ERP implementation include discovery, design configuration, business case development, user training, and deployment for smooth adoption.
- Best practices for ERP implementation include setting clear goals, involving stakeholders, choosing the right vendor, focusing on data cleansing, and providing intensive training.
- ScaleOcean ERP is the best solution for businesses in Singapore, offering scalable features, local support, compliance with regulations, and competitive pricing with government subsidies.

What is ERP Implementation?
ERP implementation refers to the overall process of implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system in an organization. This implementation process is essential to integrate, simplify, and automate core business processes across departments ranging from finance to supply chain and more, with the inclusion of artificial intelligence in ERP for enhanced efficiency.
The benefit of ERP implementation is enables businesses to optimize their core operations, boost productivity, and enhance overall efficiency. ERP components are also systems that generally encompass finance, human resources, logistics, manufacturing, supply chain management, and customer relationship management as core components.
On a worldwide basis, 45% of businesses struggle owing to fragmented systems. Locally, many businesses in Singapore continue to rely on outdated systems that are not integrated, generating inefficiencies. Selecting the appropriate ERP system relies on factors such as scalability, features tailored to specific industries, and the ability to integrate with other systems. These important key considerations include:
- Customization & Standard Features: Excessive customizations may impede the implementation of enterprise resource planning and raise expenses.
- Cloud & On-premise ERP: Cloud-based solutions present adaptability, whereas on-premise ERP offers enhanced control.
- Integration System: The ERP system must be compatible with current tools, like CRM, HR, or financial software.
6 Key Phases of ERP Implementation
Implementing an ERP system is a structured process that involves several critical stages. Six key phases of the ERP implementation process include discovery and planning, design and configuration, business case development, testing and user training, deployment, and support and maintenance. Below are the key phases of ERP implementation:
1. Discovery and Planning
The planning step supports a successful ERP deployment by matching the system with enterprise management objectives such as accounting, inventories, and CRM. It establishes defined objectives, identifies resources, and uses initiatives such as SMEs Go Digital to cut expenses and increase productivity. The next stages to consider are:
- Set clear objectives and scope: Establish specific goals for the ERP system, like boosting efficiency, cutting costs, or improving reporting. Make sure the project scope is well-defined to stay focused and aligned with your overall business goals.
- Assemble a project team: Form a team with a project manager, key functional experts, and an executive sponsor. This ensures everyone is on board, resources are allocated correctly, and the implementation stays on track.
- Select a vendor: Take time to research and choose an ERP vendor that fits your company’s needs, budget, and plans. The right partner will help you customize the system to support growth and improve operations.
- Conduct a needs assessment: Review your current systems and processes to find areas that need improvement. Conduct a gap analysis to highlight what’s missing and ensure the ERP system meets your company’s unique requirements.
2. Design and Configurations
This phase is all about tailoring the custom-built ERP system to your specific business needs and improving operations. It entails redesigning procedures, configuring software, and determining how it will interact with other systems. Here are the actions to take:
- Redesign business processes: Use insights from the previous analysis to create smoother workflows. The aim is to align your processes with ERP’s best practices, while keeping customizations to a minimum and maximizing efficiency.
- Configure the software: Set up the system and tailor specific modules, like finance, HR, and inventory, to match your business needs and support the new workflows.
- Plan integrations: Decide how the ERP will work with other existing tools, like CRM software, so that all systems connect smoothly and data flows without disruptions across the business.
3. Business Case Development
During this phase, businesses develop a strong business case to justify their investment in an intelligent ERP system. The case assesses costs, advantages, and risks, including ERP system advantages and drawbacks, while showing how it addresses issues, increases efficiency, and provides ROI. The next steps are:
- Develop customizations: Build custom features, reports, or integrations to fill any gaps identified during the design phase. These adjustments will make sure the ERP system works perfectly for your business and fits seamlessly into existing operations.
- Prepare and migrate data: Extract, clean, and format data from old systems before transferring it to the new ERP. A test run is often done to ensure everything is transferred correctly and that there are no issues before the final data migration.
- Develop training materials: Create clear and easy-to-understand training resources like guides, videos, and tutorials. This will help employees quickly get up to speed with the new ERP system, making the transition smoother and ensuring they use the system effectively.
4. Testing and User Training
Testing and training are critical to ensuring that the ERP system functions properly and that users can navigate it easily. This phase entails thorough system testing to identify problems, followed by extensive user training to guarantee staff can use the system efficiently and avoid errors. The next steps are:
- Perform system testing: Run comprehensive tests to verify that the entire ERP system, with all its modules and integrations, operates smoothly. This includes unit testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT), ensuring ERP data security and fixing any potential issues before launch.
- Train employees: Offer targeted training for different roles, ensuring that all employees know how to use the new ERP system efficiently. Proper training helps users feel confident in navigating the system and ensures they’re ready to perform their tasks once it’s live.
5. Deployment
The deployment phase signifies the ERP system’s official launch. It entails final testing, data validation, and confirming that everything functions as expected. A phased or pilot deployment can be used to reduce risks and ensure a smooth transition, resulting in increased efficiency and improved workflows. The next steps are:
- Final preparations: Wrap up any last data migrations, finalize configurations, and double-check that everything is ready for launch. This step ensures the ERP system is properly set up with all data in place and the system is ready to go live.
- Launch the ERP: Deploy the ERP system based on the chosen strategy, whether rolling out everything at once or in stages. To ensure a smooth transition, consider offering an ERP system demo before full implementation, minimizing disruption and ensuring a controlled launch.
- Provide immediate support: The project team and vendor will be available to help users with any questions or issues. This support ensures a smooth transition as users adjust to the new system and that any issues are resolved quickly.
6. Support and Maintenance
After the ERP system is online, continual support and maintenance are required for peak performance. This involves monitoring, fixing issues, and deploying updates to reduce downtime, increase security, and enhance functionality. Regular upgrades ensure that the system reacts to changing ERP trends. The following steps are:
- Ongoing support: Set up a reliable support team to assist users with both technical and operational challenges. This helps ensure that any issues are quickly addressed, allowing users to adapt and keep operations running smoothly with the new ERP system.
- Evaluate performance: Monitor the system’s performance by comparing it to the original objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs). This ensures the system delivers a successful return on investment (ROI) and meets the company’s goals effectively.
- Continuous enhancement: Keep improving the ERP system by refining workflows and adding updates as necessary. Maintaining the ERP system with regular enhancements ensures it stays current with the company’s evolving needs and supports ongoing business growth.
Challenges in ERP Implementation & Their Solutions
Implementing an ERP system can be a transformative step for any business, but it is not without its challenges. From financial constraints to employee resistance, companies in Singapore with complex businesses often face several hurdles during the phase of ERP implementation. Here’s the explanation:
1. High Costs
One of the major hurdles to ERP installation is the high cost of the process, which includes software, customization, and training costs. To mitigate this, firms should look into government subsidies and incentives, such as SMEs Go Digital in Singapore, offering effective grant management solutions for small and medium-sized businesses.
Furthermore, choosing a provider with competitive pricing and scalable solutions can help you save money without sacrificing quality. Organizations can efficiently manage their budgets while meeting their ERP objectives by leveraging available resources and making informed decisions.
2. Employee Resistance
Employee resistance is a common issue during ERP deployment. This resistance is usually caused by fear of change or a lack of understanding of the new system. To address this, companies should provide comprehensive training programs. These programs will equip staff with the skills to use the ERP system effectively.
Clear communication regarding the system’s benefits, such as increased productivity and streamlined processes, can also serve to assuage worries and develop a positive attitude toward change. Organizations can foster adoption and increase trust by incorporating employees early in the process and giving continuing assistance.
3. Integration with Legacy Systems
Integrating a new ERP system with existing legacy systems can be complex and difficult, often resulting in compatibility concerns. Businesses might utilize middleware to achieve a smooth integration, a software layer that serves as a link between the new ERP system and legacy systems.
To minimize interruptions, a hybrid strategy can be used, in which some legacy systems are kept while others are updated. Consulting with IT specialists and choosing the top ERP software for business can help address integration challenges, ensuring data integrity and operational continuity.
4. Risk of Downtime
The risk of downtime during ERP deployment is significant, as it can disrupt business operations and result in financial losses. To reduce this danger, extensive testing is required before the system goes online. This includes running several tests to identify and fix any technical issues or flaws.
Furthermore, adopting the system in stages rather than all at once can assist in mitigating the effects of potential downtime. With ScaleOcean Software, a dedicated support team remains on standby throughout the initial go-live phase to resolve any difficulties quickly, ensuring business continuity and minimizing disruptions.

Best Practices for Successful ERP Implementation in Singapore Companies
Follow these recommended practices to ensure that your ERP system maximizes its benefits. By following tried-and-true tactics, you may reduce risks, increase efficiency, and achieve your company’s objectives. To ensure your ERP system delivers maximum benefits, you can follow these best practices:
1. Set Clear Goals
Setting specific, quantifiable goals is the cornerstone of a successful ERP installation. These goals should be consistent with your business objectives and serve as a standard for evaluating the system’s success.
For example, setting a goal of 95% inventory accuracy not only establishes a clear target but also aids in the prioritization of features and functionalities during the implementation phase. Well-defined goals ensure that the ERP system is adapted to your specific requirements and produces measurable outcomes.
2. Involve Stakeholders from the Start
Involving stakeholders early is essential for gaining buy-in and ensuring the ERP system meets all department needs. Forming a project team with representatives from IT, finance, operations, and other key areas promotes collaboration. This ensures multiple perspectives are considered during the implementation process.
This method helps to identify possible issues early on and ensures that the system is structured to enable cross-functional processes. Engaging stakeholders throughout the process promotes trust and smoother adoption.
3. Choose the Right Vendor
Selecting the correct ERP vendor is a key decision that will have a big impact on the success of your implementation. Look for a vendor who not only provides reliable solutions but also understands your sector and the local business environment. Based on Medium, a critical criterion for selecting the right ERP vendor is ensuring that they have expertise in your industry, as industry-specific ERP solutions often come with pre-configured modules tailored to the sector’s needs.
For example, ScaleOcean ERP offers bespoke solutions as well as local assistance, making it an excellent alternative for Singapore firms. A provider with a solid track record and excellent customer service ensures that you have the resources and skills required for a smooth installation.
4. Focus on Data Cleansing
Accurate data is critical to the success of any ERP system. Nevertheless, 40% of ERP initiatives fail owing to erroneous or insufficient data. Before implementation, spend effort purifying your data to remove duplicates, repair errors, and verify consistency.
Having clean data not only improves system performance but also helps with better decision-making and smoother operations. A thorough data cleaning process ensures that the cloud-based ERP system runs efficiently, providing reliable information for better business outcomes.
5. Provide Intensive Training
Training is an important part of a successful phase of ERP implementation since it ensures that staff feel comfortable utilizing the new system. Leveraging programs such as SkillsFuture in Singapore can help improve staff skills and shorten the learning curve.
Comprehensive training sessions, combined with ongoing support, enable personnel to use the system to its maximum capacity. Prioritizing training allows you to reduce resistance, increase productivity, and ensure a smooth transition to the new ERP system.
Why ScaleOcean ERP is Ideal for Businesses in Singapore
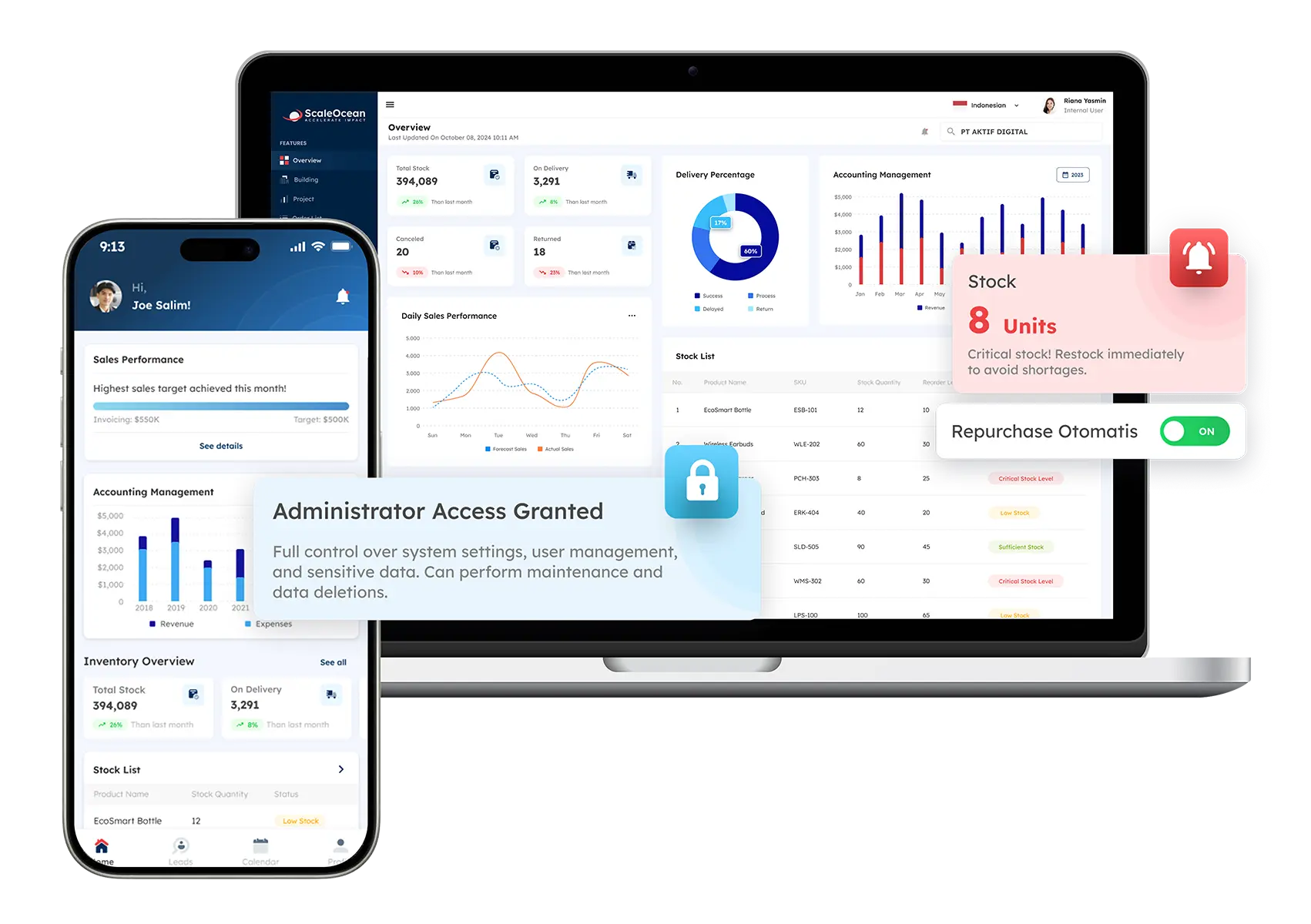
This hands-on experience demonstrates how ScaleOcean can help you streamline your processes, increase efficiency, and maintain compliance with local legislation. Here’s what makes ScaleOcean stand out for firms trying to streamline their operations:
1. Key Features
When selecting an ERP system, it is critical to examine the features that will most effectively support your business operations. ScaleOcean ERP provides a variety of functions tailored exclusively to the demands of Singapore-based organizations. Here are some of the notable features that differentiate ScaleOcean:
- Compliance with GST, PDPA, and IRAS regulations: ScaleOcean ensures that your ERP system is fully compliant with Singapore’s tax and data protection regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Multi-language support (English, Mandarin, Malay): The system’s multi-language capabilities make it accessible to diverse teams and facilitate smooth communication across various departments.
- Scalable solutions for SMEs to large enterprises: Whether you run a small business or a large enterprise, ScaleOcean’s ERP system grows with your needs, providing flexible solutions that scale as your business expands.
2. Local Advantages
In addition to its comprehensive features, ScaleOcean ERP provides special benefits customized to the Singapore market. These local benefits ensure that firms can smoothly incorporate the ERP system into their operations, increasing efficiency and growth potential. Here are the local advantages of using ScaleOcean:
- Support team based in Singapore: Having a local support team ensures that businesses can quickly address any issues and receive personalized, timely assistance.
- Competitive pricing with government subsidies: ScaleOcean offers cost-effective pricing, making it a viable choice for businesses looking to optimize operations while benefiting from government subsidies.
3. Testimonial: “With ScaleOcean, we successfully implemented ERP in three months, improving efficiency by 25%”
Companies that have implemented ScaleOcean ERP have seen impressive results, with one example achieving a 25% increase in efficiency within just three months. This rapid success is driven by ScaleOcean’s user-friendly design, which streamlines implementation, reduces disruption, and enables businesses to quickly benefit from improved automation, data visibility, and collaboration.
Also Read: How Much Does ERP Cost? 2025 ERP Price
Conclusion
ERP deployment is a critical step for Singapore organizations aiming to increase productivity, streamline operations, and remain competitive. Companies that implement an integrated ERP system can overcome problems such as system fragmentation and manual processes, resulting in increased productivity and profitability. Begin your ERP adoption journey today by consulting with ScaleOcean.
Businesses with fully integrated ERP systems see a 200% return on investment (ROI) in three years. To explore how ScaleOcean can help your organization, schedule a free demo and learn firsthand how our ERP system can accelerate your change. Companies in Singapore can significantly enhance their efficiency, production, and profitability by following a planned ERP installation plan. Contact ScaleOcean to begin your transformation.
FAQ:
1. What are the 5 components of ERP?
ERP systems vary based on organizational needs but typically include five core components: finance (accounting, budgeting), human resources (payroll, recruitment), supply chain management (inventory, logistics), manufacturing or production, and customer relationship management (sales, marketing). These integrate to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
2. What is ERP and how does it work?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software system that integrates and streamlines core business processes, such as finance, HR, manufacturing, supply chain, sales, and procurement, into a unified platform. It centralizes data, offering a single source of truth, automating workflows, and providing real-time insights to enhance efficiency and decision-making across the organization.
3. What is the main purpose of ERP?
The primary purpose of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is to enhance organizational efficiency by optimizing the management and utilization of company resources. It integrates core business processes, like finance, HR, supply chain, and operations, into a unified system, centralizing data, improving workflows, and enabling better decision-making for increased productivity and competitiveness.
4. What are the 5 pillars of ERP?
The 5 pillars of ERP are Finance, Human Resources (HR), Supply Chain Management (SCM), Manufacturing or Operations, and Customer Relationship Management (CRM). These core components and characteristic ERP integrate key business processes, supported by successful implementation strategies like proper planning, strong project management, stakeholder communication, data migration, and continuous testing for seamless adoption and efficiency.











 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















