Any business with a high volume of goods must optimize every process and product. However, many companies still use manual methods to manage them. However, using a WMS for business can simplify and speed up warehouse operations.
Without implementing a WMS, you’re likely to experience numerous errors, such as incorrect inventory recording, difficulty managing goods across multiple warehouses, shipping errors, and even difficulty monitoring stock status and inventory movement.
According to adsm.com, using a warehouse management system is crucial for businesses, especially in Singapore, a business hub focused on optimizing the region’s high volume of goods. This system is the best solution for minimizing downtime and maximizing throughput.
In addition to its essential uses, companies must also use a WMS that truly suits the workflow in the warehouse, the volume of goods managed, and the scale of the business they operate. This is important because selecting the right WMS can help optimize operational efficiency.
This article will fully discuss what a warehouse management system guide is, its features and how it works, its benefits, and 10 examples of the best WMS software you can use to optimize your warehouse business processes. Learn more here.
- A warehouse management system (WMS) is a software solution that oversees and automates the daily functions of a warehouse or distribution center
- The benefits of using WMS are improved accuracy, increased efficiency, cost reduction, enhanced visibility, scalability, and real-time inventory monitoring
- Types of WMS are standalone WMS, integrated WMS, and cloud-based WMS.
- 10 examples of the top WMS software, including: ScaleOcean, Oracle, Infor, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Zoho, Fishbowl, and many others
- ScaleOcean is the best recommended WMS software that can be integrated with various other business systems and provides customization according to business needs.

What is a Warehouse Management System?
A warehouse management system (WMS) is a software solution that oversees and automates the daily functions of a warehouse or distribution center, including inventory receipt and order fulfillment for shipment to customers.
Implementing WMS can streamline processes such as receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping, offering real-time insights into inventory and labor. This helps minimize errors, save time, and cut costs.
WMS software can either function as a standalone solution or as part of a broader Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, and it can be deployed on-premises or through the cloud.
WMS also provides companies with real-time visibility into stock levels, improves inventory management, and increases overall productivity. As a result, businesses can reduce errors, save money, and ensure that goods are delivered on time to customers, all of which contribute to improved supply chain performance.
Benefits of Using a WMS Warehouse Management System
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) offers numerous benefits that enhance warehouse operations, from improving accuracy to reducing costs. By automating and optimizing key processes, WMS enables businesses to run more efficiently, maintain higher customer satisfaction, and scale effectively with demand.
Below are some of the significant benefits of using a WMS, including:
1. Improved Accuracy
Implementing warehouse management software can minimize human errors in order fulfillment and inventory management by automating processes and providing real-time data.
This leads to more accurate inventory counts and order picking, ensuring customers receive the correct products on time. As a result, businesses experience fewer returns and exchanges, which improves overall customer satisfaction and reduces costly mistakes.
2. Increased Efficiency
A warehouse management system (WMS) can automate repetitive tasks such as picking, packing, and shipping, reducing human error and increasing operational speed. This results in smoother workflows, faster order fulfillment, and a more efficient warehouse environment overall.
3. Cost Reduction
A WMS helps companies to reduce operational costs by increasing process efficiency warehouse management guide and reducing costly errors such as mis-picks and incorrect shipments.
It also helps businesses avoid overstocking by automating reordering and maintaining optimal inventory levels. By cutting down on labor hours and wasted space, a WMS leads to significant cost savings in warehousing and logistics.
4. Enhanced Visibility
A WMS offers real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and the location of products within the warehouse. It also tracks shipments in transit, providing complete transparency across the supply chain.
This improved visibility allows for faster decision-making, better demand forecasting, and greater responsiveness to changes in the supply chain.
5. Scalability
A WMS can easily scale with a growing business, accommodating increased inventory, more complex processes, and a higher volume of orders. Whether a company is expanding its warehouse capacity or adding new product lines, the system adapts to meet changing needs.
The scalability of WMS ensures that businesses can continue to operate efficiently as they grow, without outgrowing their warehouse management system.
6. Real-time Inventory Monitoring
A warehouse management system (WMS) provides real-time visibility into stock levels, allowing businesses to accurately track inventory movements. This lowers the possibility of errors, improves demand forecasting, and ensures optimal stock availability to meet customer demands.
7. Optimized Workforce Management
A WMS uses data to assign tasks based on employee availability, skill sets, and workload, ensuring efficient labor utilization. This reduces idle time, enhances productivity, and minimizes delays caused by poor task allocation.
8. Strengthened Customer and Supplier Relations
By ensuring accurate and timely order fulfillment, a WMS boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty. Improved inventory management and communication also enhance supplier relationships, ensuring smoother collaboration and reliable supply chains.
Key Features and What Does a WMS System Do?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software solution that enhances efficiency, accuracy, and real-time decision-making, ensuring a seamless flow of goods in a warehouse. Here’s how a WMS works in key areas of warehouse management.
1. Inventory Management
With a WMS, inventory levels are tracked in real time, providing accurate and up-to-date information. It helps manage stock across multiple locations, optimizes reorder points, and minimizes stockouts, leading to better control over inventory and improved forecasting.
For businesses utilizing a bonded warehouse, the system can also track goods that are stored under customs supervision, ensuring compliance with regulations while maintaining accurate inventory management.
2. Receiving and Put-away
A WMS manages the receiving process by tracking incoming shipments, verifying items, and assigning optimal storage locations. It automates the put-away process, ensuring products are stored efficiently and ready for future retrieval, reducing manual handling and errors.
An efficient warehouse layout plays a key role in optimizing the receiving and put-away process. By designing the layout to align with product types and flow, a WMS can automatically direct items to the best storage locations, further enhancing space utilization and retrieval efficiency.
3. Picking, Packing, and Fulfillment
The WMS software streamlines the order picking process by directing warehouse workers to the correct products efficiently. It integrates with packing systems to ensure accurate order fulfillment, reducing errors and ensuring that items are correctly packed and ready for shipment.
4. Shipping
A WMS automates the shipping process by generating shipping labels, tracking shipments, and managing transportation routes. It ensures that orders are shipped on time and accurately, improving customer satisfaction and reducing costly shipping mistakes.
5. Labor Management
A work management system (WMS) helps to optimize labor by providing real-time data on workforce productivity. It enables managers to effectively assign tasks, track performance, and ensure workers are focused on high-priority tasks, thereby increasing overall warehouse productivity.
6. Warehouse Data Metrics and Analytics
A WMS provides detailed metrics and analytics about warehouse performance. It monitors key performance indicators (KPIs) such as inventory turnover, order accuracy, and throughput, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions to constantly improve warehouse operations.
7. Yard and Dock Management
A WMS integrates yard and dock management to ensure smooth operations. It tracks the movement of goods in and out of the warehouse, schedules dock times, and coordinates the placement of trucks, reducing wait times and optimizing warehouse throughput.
Types of Warehouse Management Systems
A warehouse management system (WMS) is a software solution designed to optimize warehouse operations. There are various types of WMS, each catering to specific business requirements.
These range from standalone systems to integrated and cloud-based solutions, ensuring flexibility and efficiency based on company needs. Here are the types of warehouse management software that you can use in your warehouse operation, including:
1. Standalone WMS
A standalone WMS is a dedicated system focused solely on warehouse operations, such as inventory tracking and order fulfillment, making it ideal for businesses that require advanced warehouse functionality without the need for integration with other enterprise systems.
2. Integrated WMS
An integrated WMS is part of a larger supply chain or ERP system, offering seamless data flow between warehouse operations and other business processes, which is perfect for businesses seeking comprehensive visibility and coordination across all departments.
3. Cloud-based WMS
A cloud-based WMS operates on remote servers, providing real-time access to data from anywhere, making it scalable, cost-effective, and ideal for businesses that prioritize flexibility, easy updates, and reduced IT infrastructure costs.
Smart Warehousing Technology
Smart warehousing technology leverages advanced tools and systems to optimize warehouse operations, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. It integrates automation, real-time data, and intelligent systems to create a seamless and future-ready logistics environment.
1. Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation uses technologies like conveyor belts, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and robotic systems to streamline tasks such as sorting, picking, and packing.
A warehouse barcode scanning system further enhances these processes by improving accuracy and speed. This reduces manual labor, minimizes errors, speeds up operations, and lowers operational costs by increasing overall productivity and accuracy.
2. Voice-Picking Technology
Voice-picking technology allows workers to receive picking instructions via voice commands through headsets. This system improves accuracy, enhances productivity, and reduces training time by enabling hands-free, intuitive task execution while allowing employees to focus on their tasks without interruption.
3. Mobile Devices
Warehouse management software in mobile devices, such as handheld scanners and tablets, enables real-time inventory tracking and order management through mobile ERP software.
They provide workers with instant access to critical data, improving operational efficiency by ensuring quick decision-making, reducing delays, and ensuring seamless communication and task coordination across the warehouse.
4. AI and Internet of Things (IoT) in Warehouse Management
AI and IoT in a warehouse management system enable predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and smart decision-making by using sensors and connected devices.
These technologies track inventory, equipment, and environmental conditions, optimizing workflows, reducing downtime, and providing valuable insights that drive better management and operational improvements.
5. Warehouse Robots
Using warehouse robots, like autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and robotic arms, automate repetitive tasks such as picking, packing, and transporting goods.
They help enhance speed, accuracy, and scalability by performing tasks faster and more consistently than human workers, improving overall warehouse efficiency and throughput.
6. Augmented and Virtual Reality Apps
WMS can also use technology AR and VR apps to assist in training, inventory management, and order picking by overlaying digital information onto the physical environment.
These technologies provide workers with interactive, real-time guidance, improving accuracy in task execution, reducing errors, and enhancing training by simulating real-world scenarios.
10 Top Warehouse Management Systems
As smart warehousing continues to revolutionize logistics, adopting the right Warehouse Management System (WMS) becomes crucial for optimizing operations.
In this section, we will explore the top 10 WMS solutions available in Singapore, offering businesses the tools to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and stay ahead in a competitive market.
1. ScaleOcean
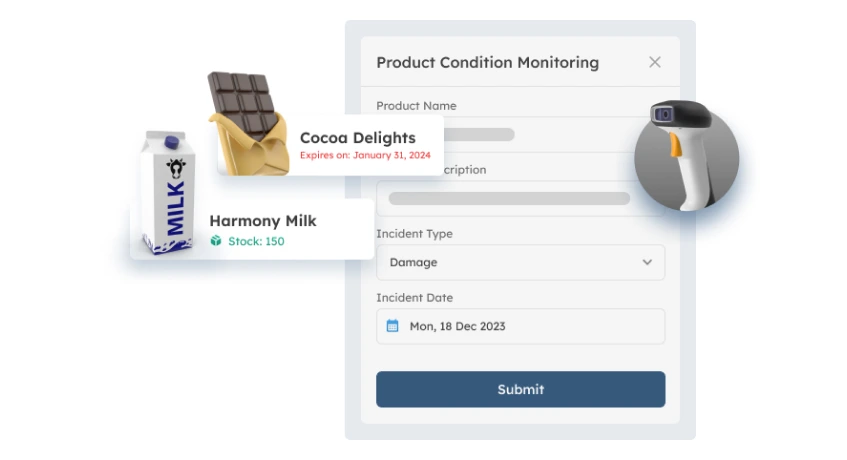
ScaleOcean Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a comprehensive and advanced solution specifically designed to improve the efficiency of warehouse operations.
Implementing ScaleOcean’s WMS offers real-time tracking and management of inventory, allowing businesses to monitor stock levels, reduce errors, and ensure timely order fulfillment.
The software automates key warehouse processes, including inbound and outbound goods handling, stock processing, and scheduling, which significantly enhances operational accuracy and reduces manual labor.
Features like barcode management, automated stock transfers, and real-time visibility simplify complex tasks, improving overall workflow and providing businesses with valuable insights for better decision-making, ensuring smooth, streamlined warehouse operations.
With our free demo, you can explore how ScaleOcean WMS optimizes warehouse operations, streamlines workflows, and enhances overall productivity, helping your business stay ahead.
Key Features:
- Unlimited users at no additional cost
- Offers flat pricing and is suitable for mid-sized to enterprise companies
- A multi-warehouse solution that can manage multiple warehouse locations with seamless integration on a single platform, so companies can track stock transfers and optimize warehouse space utilization efficiently.
- It can be integrated with other business systems, such as logistics, accounting, distribution, CRM, and sales, all managed within a single platform.
- Providing in-depth customization of modules and features tailored to the specific workflow and business needs of your warehouse.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
2. Oracle
Oracle Fusion Cloud Warehouse Management is a robust, cloud-based solution that enhances the management of warehouse operations. It offers real-time insights into inventory, optimizes warehouse workflows, and automates key processes, such as order picking, shipping, and stock movement.
By leveraging Oracle’s cloud infrastructure, this solution integrates seamlessly with other enterprise applications to streamline logistics, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Key Features:
- Inventory Management
- Order Picking and Packing
- Shipping and Delivery
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
3. Infor
Infor warehouse management software is an end-to-end solution designed to streamline and automate warehouse operations. It helps businesses manage inventory, optimize storage, and improve order fulfillment through intelligent routing, real-time tracking, and automation of key processes.
With a focus on minimizing errors and reducing manual labor, Infor WMS integrates seamlessly with other Infor ERP modules and third-party systems, providing businesses with better visibility, enhanced efficiency, and reduced operational costs.
Key Features:
- Inventory Management
- Business intelligence
- Labor management
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
4. SAP
SAP Warehouse Management is a powerful, integrated solution made to streamline and optimize warehouse operations within an organization. This software allows businesses to manage the entire warehouse lifecycle, from inventory management to order fulfillment.
It enables real-time tracking of stock, automates processes like picking, packing, and shipping, and provides deep visibility into warehouse performance. SAP WMS integrates seamlessly with other SAP ERP modules to ensure smooth coordination across departments, improving efficiency and enhancing overall supply chain operations.
Key Features:
- Goods Receipt and Issue
- Picking and Packing Optimization
- Integration with other SAP Modules
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
5. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a recommended warehouse management software that can optimize warehouse operations across the supply chain. This software allows businesses to streamline inventory management, automate warehousing processes, and improve order fulfillment.
It offers robust features like real-time inventory tracking, automated picking and packing, and seamless integration with other Dynamics 365 modules.
Key Features:
- Workflow support
- Inventory movement
- Inventory management
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
6. Zoho
Zoho Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a comprehensive solution tailored to simplify warehouse operations for businesses of all sizes. It provides real-time inventory management, order fulfillment, and streamlined logistics.
The software offers key features like barcode scanning, stock tracking, and seamless integration with Zoho’s suite of applications, ensuring smooth coordination between different departments.
Key Features:
- Multi-warehouse management
- Barcode scanning integration
- Reporting and analytics
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
7. Fishbowl
Fishbowl is a Warehouse Management System (WMS) that is a robust and scalable inventory management solution designed to optimize warehouse operations for businesses of various sizes. It automates inventory control methods, order fulfillment, and stock tracking, offering real-time visibility across the warehouse.
Fishbowl WMS integrates seamlessly with various accounting software and ERP systems, allowing businesses to manage their warehouse processes more efficiently. The system supports barcode scanning, automated stock transfers, and real-time reporting.
Key Features:
- Receiving and Put-Away
- Shipping and Fulfillment
- Purchase Order Management
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
8. Körber
Körber WMS is a scalable solution designed to optimize and automate warehouse management operations. This software helps businesses gain full visibility and control over their warehouse processes, from inventory tracking to order fulfillment.
Körber WMS integrates seamlessly with various supply chain and ERP systems, providing real-time data and analytics. The platform supports intelligent routing, automated picking, and efficient stock management.
Key Features:
- Advanced Reporting and Analytics
- Integration Capabilities
- Warehouse Optimization
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
9. Manhattan Active
Manhattan Active Warehouse Management is a cutting-edge, cloud-native solution tailored to revolutionize warehouse operations. It offers full visibility and control over inventory, order fulfillment, and warehouse processes through real-time data.
This software leverages advanced technologies like machine learning, automation, and artificial intelligence to optimize warehouse workflows, including picking, packing, and shipping.
Key Features:
- Slotting Optimization
- Order Streaming
- Cloud-Native Platform
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
10. Elite
Elite Warehouse Management is a robust and flexible software solution that optimizes warehouse operations. It provides real-time inventory tracking, order management, and warehouse management guide automation to ensure operational efficiency.
The software streamlines tasks such as order picking, stock management, and shipping, providing businesses with greater control and accuracy in their warehouse functions. Elite WMS uses barcode scanning, intelligent reporting, and ERP integration to reduce errors, boost productivity, and improve customer satisfaction.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Inventory Tracking
- Advanced Picking and Packing Optimization
- Advanced Reporting and Analytics
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|

WMS vs. WCS: Difference Between The Both Systems
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Warehouse Control Systems (WCS) are both crucial components of warehouse automation, but they serve different purposes and functionalities.
Understanding the differences between these systems can help businesses choose the right technology for their operations. Here are the differences between WMS and WCS:
1. WMS (Warehouse Management System)
A WMS is a software application designed to manage and optimize warehouse operations. It focuses on high-level functions like inventory tracking, order fulfillment, receiving, put-away, picking, and shipping.
Warehouse management system software is typically used to manage inventory levels in real-time, ensuring that the right products are in the right place at the right time.
It also integrates with other systems like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS) to streamline processes. WMS is more about managing resources and workflow within the warehouse.
2. WCS (Warehouse Control System)
A WCS, on the other hand, is a system that manages the real-time control of automated equipment within a warehouse. It connects with machinery like conveyors, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), robotic systems, and sortation systems.
The primary function of a WCS is to direct and control the movement of goods through the warehouse, ensuring that items are transported, sorted, and stored according to instructions from the WMS. A WCS optimizes the use of the warehouse’s automation infrastructure.
3. Key Differences
While a WMS focuses on managing inventory and warehouse operations, a WCS is primarily concerned with controlling the flow of materials through automated systems.
A WMS provides the high-level strategy for inventory management, whereas a WCS offers the real-time operational control needed to execute those strategies. Together, they form a warehouse management execution system that ensures seamless operations and strategic alignment.
In many use cases in different industries, such as the manufacturing and distribution industry, WMS and WCS work together, with the WMS providing data and instructions to the WCS, which then controls the automation equipment to move goods efficiently within the warehouse management guide.
How to Choose the Right Warehouse Management System Software
Choosing the right Warehouse Management System (WMS) software is essential for optimizing warehouse operations. The right WMS should align with your business needs, enhance efficiency, and support growth.
Below are the key steps to help you make an informed decision when selecting the best WMS for your business.
1. Define Your Business’s Needs and Objectives
Before choosing a WMS, it’s important to clearly define your business’s specific needs and objectives. Consider factors like inventory size, types of products, and the complexity of your warehouse operations.
For example, a high-volume e-commerce warehouse might require a more advanced system with real-time inventory tracking and integration with e-commerce platforms. Identifying these needs will ensure that the software you select can effectively address your operational challenges.
2. Research and Evaluate Deployment Models
WMS software can be deployed either on-premise or as a cloud-based solution, each with its advantages. On-premise systems offer more control over the software and data, but require significant infrastructure and maintenance.
Cloud-based systems offer flexibility, scalability, and lower upfront costs but depend on internet access. Evaluate which deployment model best fits your business size, budget, and future growth plans, and consider factors like security, data storage, and system maintenance.
3. Compare Features and Capabilities of Vendor WMS
Different WMS vendors offer varying features, so it’s crucial to compare the functionalities that each system provides. Look for essential features such as inventory management, order picking, shipping integration, and real-time analytics.
Consider advanced features like labor management, integration with ERP systems, and automated reordering. Choose a WMS that meets your immediate needs and also provides the flexibility to support future business growth and evolving requirements.
4. Assess Vendors and Test the Software
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, assess the vendors’ reputation, support services, and customer reviews. It’s crucial to ensure that the vendor offers strong customer support, regular software updates, and a responsive troubleshooting process.
Test the software through demos or pilot programs to ensure it aligns with your operational needs. This hands-on experience can help you understand the user interface, workflow integration, and system efficiency before making a final decision.
5. Consider Cost and ROI
When evaluating WMS software, consider both the initial cost and the long-term return on investment (ROI). While some systems may require a significant upfront investment, they may offer greater functionality and long-term savings through improved efficiency, reduced labor costs, and fewer errors.
Calculate the expected ROI by factoring in cost savings, productivity gains, and error reduction. Ensure that the WMS fits within your budget and provides measurable benefits that justify its cost over time.
Conclusion
Warehouse Management System (WMS) is an essential solution and technology for optimizing warehouse operations, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring accurate order fulfillment.
By automating key processes such as inventory tracking, order picking, and shipping, a WMS helps businesses streamline their operations and improve customer satisfaction.
As we’ve explored the top 10 WMS recommendations, it’s clear that choosing the right system is crucial for long-term success. Among these, ScaleOcean’s WMS stands out as an ideal solution for your efficient warehouse.
ScaleOcean offers robust features, seamless integration, and scalability to meet the unique needs of your business. With ScaleOcean’s WMS, you can transform your warehouse operations, reduce errors, and drive efficiency. Take a free demo with ScaleOcean to get the best solution that suits your business.
FAQ:
1. Is WMS difficult to learn?
Implementing a WMS is more challenging than it sounds. It requires significant effort and may lead to costly downtime and a steep learning curve if not executed properly.
2. What is the difference between SCM and WMS?
A WMS guarantees smooth warehouse operations, while SCM offers a comprehensive perspective of the entire supply chain, from procurement to final delivery. Integrating both systems can enhance efficiency, support better decision-making, and create a more agile and robust supply chain.
3. What is ERP vs WMS?
For instance, while a WMS is tailored to manage warehouse logistics, an ERP solution collects data from all departments, including warehouse management, into a centralized database. This integration consolidates company-wide processes into one system, removing data silos and improving connectivity between departments.
4. What are the 5 S of warehouse management?
The 5S checklist for warehousing management offers a systematic method for organizing and maintaining a warehouse to boost productivity, safety, and efficiency. It consists of five essential steps: Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain.













 PTE LTD..png)
.png)

.png)








.png)
.png)
















